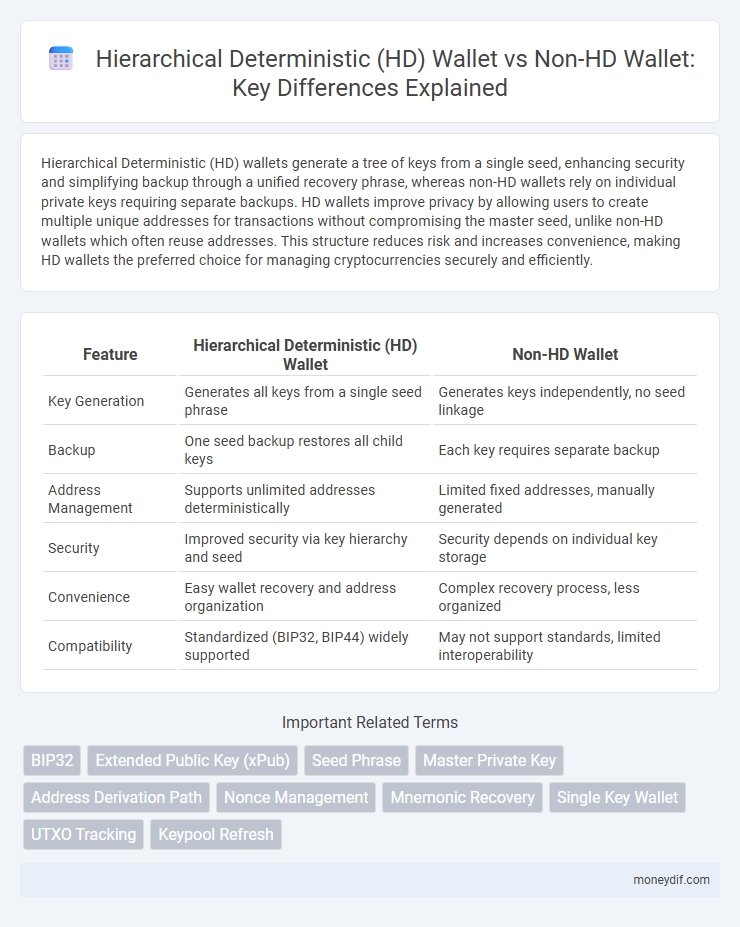
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets generate a tree of keys from a single seed, enhancing security and simplifying backup through a unified recovery phrase, whereas non-HD wallets rely on individual private keys requiring separate backups. HD wallets improve privacy by allowing users to create multiple unique addresses for transactions without compromising the master seed, unlike non-HD wallets which often reuse addresses. This structure reduces risk and increases convenience, making HD wallets the preferred choice for managing cryptocurrencies securely and efficiently.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallet | Non-HD Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Key Generation | Generates all keys from a single seed phrase | Generates keys independently, no seed linkage |
| Backup | One seed backup restores all child keys | Each key requires separate backup |
| Address Management | Supports unlimited addresses deterministically | Limited fixed addresses, manually generated |
| Security | Improved security via key hierarchy and seed | Security depends on individual key storage |
| Convenience | Easy wallet recovery and address organization | Complex recovery process, less organized |
| Compatibility | Standardized (BIP32, BIP44) widely supported | May not support standards, limited interoperability |
Introduction to Wallet Types: HD vs Non-HD
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets generate a tree-like structure of keys from a single seed, enhancing security and ease of backup by allowing users to restore all keys using one mnemonic phrase. Non-HD wallets store multiple independent private keys separately, requiring individual backups for each key, which increases the risk of loss and complicates key management. HD wallets are preferred for their deterministic key derivation, improved privacy through frequent address changes, and simplified recovery process compared to non-HD wallets.
What is a Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallet?
A Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallet generates a tree of keys from a single master seed, enabling users to create numerous unique addresses without compromising the seed's security. This structure simplifies backup and recovery since only the master seed needs to be stored securely, unlike non-HD wallets where each key requires individual backup. HD wallets enhance privacy by allowing users to manage many addresses while maintaining a unified control and seamless management of funds.
Understanding Non-HD Wallets
Non-HD wallets generate and store a fixed set of private keys without deriving them from a master seed, limiting flexibility and backup options. Each private key in a Non-HD wallet must be individually backed up to prevent loss of funds, increasing the risk compared to HD wallets that simplify recovery through a single seed phrase. Non-HD wallets lack hierarchical key management, which can result in less efficient transaction handling and reduced privacy.
Key Features of HD Wallets
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets generate a tree-like structure of keys from a single master seed, enabling efficient backup and recovery through a single mnemonic phrase. They support the creation of multiple addresses without exposing the master key, enhancing security and privacy for users. HD wallets streamline transaction management and improve address generation flexibility compared to Non-HD wallets, which generate random, independent keys.
Key Characteristics of Non-HD Wallets
Non-HD wallets generate a fixed set of private keys independently, lacking the ability to derive multiple addresses from a single seed. Each key in a non-HD wallet must be backed up individually, increasing the risk of loss if any key is misplaced. These wallets provide straightforward management but lack scalability and enhanced privacy features inherent in Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets.
Security Comparison: HD Wallet vs Non-HD Wallet
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets enhance security by generating a tree of cryptographic keys from a single seed phrase, enabling easy backup and recovery while minimizing exposure of private keys. Non-HD wallets require managing multiple independent private keys, increasing the risk of key loss or compromise without simplified recovery options. HD wallets' structured key derivation significantly reduces vulnerability to breaches compared to the scattered key management in non-HD wallets.
Backup and Recovery Differences
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets generate a master seed that enables the creation of multiple private keys from a single backup phrase, simplifying recovery and reducing the risk of loss. Non-HD wallets require individual backups for each private key, increasing the complexity and vulnerability during backup and recovery processes. The streamlined seed-based backup in HD wallets enhances security by allowing users to restore all accounts from one source, unlike non-HD wallets where loss of one key equates to permanent asset loss.
Privacy Implications of HD and Non-HD Wallets
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets enhance privacy by generating a new public address for every transaction from a single seed, minimizing address reuse and making it harder to link transactions to a single user. Non-HD wallets reuse addresses or require manual key management, increasing the risk of address clustering and exposure of transaction history. Using an HD wallet significantly reduces traceability on blockchain networks, improving user anonymity and security.
Use Cases: When to Choose HD or Non-HD Wallets
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets are ideal for users requiring enhanced security and convenience, allowing the generation of multiple private keys from a single seed phrase, making them perfect for long-term storage and managing numerous addresses. Non-HD wallets are better suited for simple, one-off transactions or users who prioritize straightforward wallet recovery without the need for extensive key management. Choose HD wallets for scalability and backup efficiency, while non-HD wallets fit cases needing minimal setup and direct key control.
Future Trends in Wallet Technology
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets enable automatic generation of a tree of key pairs from a single seed, enhancing security and ease of backup compared to Non-HD wallets that rely on individual keys. Future trends in wallet technology emphasize integration with multi-chain support, improved user privacy through zero-knowledge proofs, and advanced recovery options leveraging biometric data. Adoption of HD wallets combined with decentralized identity frameworks is anticipated to drive innovation in seamless, secure access to digital assets across diverse blockchain ecosystems.
Important Terms
BIP32
BIP32 defines Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets that generate a tree of key pairs from a single seed, enabling easier backup and improved key management compared to Non-HD wallets that use independent keys without a structured derivation path.
Extended Public Key (xPub)
Extended Public Keys (xPub) enable Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets to generate a tree of public addresses from a single master key, unlike Non-HD wallets which require individual private keys for each address.
Seed Phrase
A Seed Phrase securely generates all private keys in a Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallet, enabling easy backup and recovery, whereas Non-HD wallets require managing each private key individually without such hierarchical structure.
Master Private Key
The Master Private Key in a Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallet enables the generation of a tree of cryptographic keys from a single seed, enhancing key management and backup compared to Non-HD wallets that rely on independent, unrelated private keys.
Address Derivation Path
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets use address derivation paths to generate a structured tree of cryptographic keys from a single seed, whereas Non-HD wallets generate independent keys without a standardized path system.
Nonce Management
Nonce management in Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets enables efficient and secure transaction ordering by deriving unique nonces for each address, compared to Non-HD wallets where nonce tracking requires manual or external synchronization.
Mnemonic Recovery
Mnemonic recovery provides a user-friendly method to restore hierarchical deterministic (HD) wallets by generating a master seed that enables the regeneration of all child keys, unlike non-HD wallets which require backing up each private key individually for recovery.
Single Key Wallet
Single Key Wallets using Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) technology generate a tree of keys from a single seed, enabling easier backup and enhanced security by allowing multiple addresses without exposing the private key. Non-HD wallets rely on separate private keys for each address, increasing the risk of loss or compromise and complicating the backup process.
UTXO Tracking
UTXO tracking in Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets enhances security and privacy by generating a new address for each transaction, while non-HD wallets reuse addresses, making UTXO management less efficient and more susceptible to privacy risks.
Keypool Refresh
Keypool Refresh in Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets automatically regenerates unused addresses to maintain security and privacy, unlike Non-HD wallets which rely on static key management and lack dynamic address generation.
Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallet vs Non-HD wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com