Software wallets offer enhanced security by storing private keys locally on a device, reducing exposure to online threats. Web wallets provide convenient access from any internet-connected device but are more vulnerable to phishing attacks and server breaches. Choosing between them depends on balancing security needs and accessibility preferences.
Table of Comparison
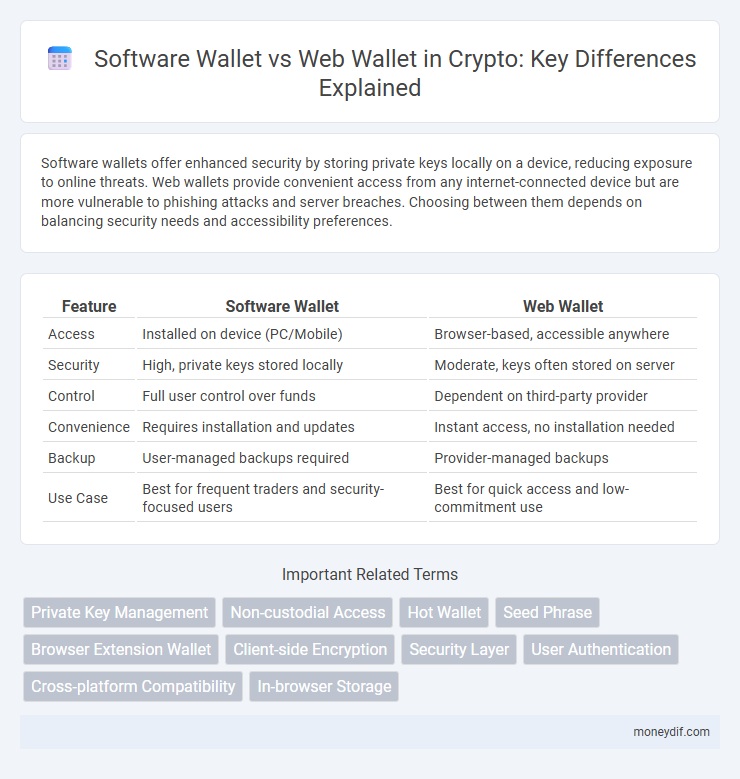
| Feature | Software Wallet | Web Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Installed on device (PC/Mobile) | Browser-based, accessible anywhere |
| Security | High, private keys stored locally | Moderate, keys often stored on server |
| Control | Full user control over funds | Dependent on third-party provider |
| Convenience | Requires installation and updates | Instant access, no installation needed |
| Backup | User-managed backups required | Provider-managed backups |
| Use Case | Best for frequent traders and security-focused users | Best for quick access and low-commitment use |
Overview of Software Wallets and Web Wallets
Software wallets are applications installed on desktop or mobile devices, offering users enhanced security by storing private keys locally and enabling offline access to cryptocurrencies. Web wallets operate through internet browsers, providing convenient access without installation but relying on third-party servers, which can pose higher security risks due to potential vulnerabilities. Both wallet types support key cryptocurrency functions such as sending, receiving, and storing digital assets, but differ significantly in security, accessibility, and control.
Key Differences Between Software and Web Wallets
Software wallets store private keys locally on a device, offering enhanced security and offline access, whereas web wallets keep keys on remote servers, prioritizing convenience with any-device accessibility. Software wallets typically require manual updates and backups, increasing user control, while web wallets depend on third-party providers for maintenance and may be more exposed to cyber threats. Choosing between these wallet types involves balancing security needs against ease of use and accessibility.
Security Features: Software Wallets vs Web Wallets
Software wallets provide enhanced security by storing private keys locally on a user's device, reducing exposure to online threats and phishing attacks. Web wallets, while convenient, rely heavily on third-party servers that increase vulnerability to hacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Advanced encryption and offline storage in software wallets offer superior protection compared to web wallets' dependency on internet connectivity and centralized server security.
Ease of Use and User Experience Comparison
Software wallets offer robust security and offline access, providing users with enhanced control and faster transaction capabilities compared to web wallets. Web wallets enable convenient access through any internet browser without installation, simplifying usage but often relying on third-party security measures. The user experience in software wallets typically involves a steeper learning curve due to setup and maintenance requirements, whereas web wallets prioritize accessibility and simplicity for casual users.
Accessibility: Software Wallets vs Web Wallets
Software wallets offer enhanced security by storing private keys locally on a user's device, limiting accessibility to the device itself, which can restrict convenience but reduce exposure to online threats. Web wallets provide superior accessibility by allowing users to access their funds from any internet-enabled device through a browser, facilitating on-the-go transactions but increasing vulnerability to phishing and hacking. Choosing between software and web wallets depends on balancing the need for quick, universal access against the priority of robust security measures.
Private Key Management and Control
Software wallets offer enhanced private key management by storing keys locally on the user's device, granting full control and reducing dependence on third-party services. In contrast, web wallets store private keys on centralized servers, increasing vulnerability to hacking and limiting user control. Prioritizing software wallets improves security and ensures direct access to private keys without intermediary risks.
Supported Cryptocurrencies and Multi-Asset Functionality
Software wallets typically support a wider range of cryptocurrencies and offer robust multi-asset functionality, enabling users to manage various digital assets securely on their devices. Web wallets, while more accessible, often provide limited support for diverse tokens and fewer features for handling multiple asset types simultaneously. Selecting between software and web wallets depends on the need for extensive cryptocurrency compatibility and advanced multi-asset management capabilities.
Backup and Recovery Options
Software wallets offer robust backup and recovery options by allowing users to securely store private keys or seed phrases locally, often enabling encrypted backups and offline storage. Web wallets, while convenient for accessibility, typically rely on cloud-based backup systems that may expose users to higher risks if the service provider experiences downtime or security breaches. Prioritizing wallets with clear, user-controlled recovery methods ensures stronger protection against data loss and unauthorized access.
Suitability for Different User Types
Software wallets offer enhanced security and control, making them ideal for experienced users and cryptocurrency holders prioritizing asset protection. Web wallets provide easy accessibility and convenience, suited for beginners and users seeking quick, on-the-go transactions without complex setup. Choosing between software and web wallets depends on individual needs for security, usability, and device compatibility.
Pros and Cons of Software Wallets and Web Wallets
Software wallets offer enhanced security by storing private keys locally on a device, reducing exposure to online threats, but they require device maintenance and risk loss from hardware failure. Web wallets provide convenient access from any internet-enabled device without installation, facilitating quick transactions but depend heavily on third-party servers, increasing vulnerability to hacking and phishing attacks. Choosing between software and web wallets involves balancing ease of use, security measures, and control over private keys.
Important Terms
Private Key Management
Private key management in software wallets offers enhanced security through local key storage, while web wallets store keys on remote servers, increasing vulnerability to online attacks.
Non-custodial Access
Non-custodial access in software wallets ensures users retain full control over private keys, enhancing security compared to web wallets that often rely on third-party servers for key management.
Hot Wallet
Hot wallets include both software wallets, which store private keys on devices, and web wallets, which manage keys through online browsers, offering varying trade-offs between security and accessibility.
Seed Phrase
A seed phrase securely backs up private keys in software wallets, offering enhanced control and offline storage compared to web wallets that store keys on centralized servers vulnerable to online attacks.
Browser Extension Wallet
Browser extension wallets provide a secure software wallet experience by storing private keys locally, unlike web wallets that manage keys on remote servers, enhancing user control and reducing vulnerability to online attacks.
Client-side Encryption
Client-side encryption enhances software wallets by securely encrypting private keys locally, unlike web wallets which often rely on server-side security, increasing vulnerability to breaches.
Security Layer
Software wallets offer enhanced security through local key storage and offline access, whereas web wallets rely on online servers, increasing vulnerability to phishing and hacking attacks.
User Authentication
Software wallets provide enhanced security through local key storage for user authentication, while web wallets offer convenience with server-side authentication but increased vulnerability to online attacks.
Cross-platform Compatibility
Software wallets offer enhanced security through local key storage while web wallets provide seamless cross-platform compatibility by enabling access from any internet-connected device.
In-browser Storage
Software wallets store private keys locally on a device using in-browser storage technologies like IndexedDB or LocalStorage, while web wallets store keys on remote servers accessed through the browser, impacting security and user control.
Software wallet vs Web wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com