A segregated wallet stores user funds separately, enhancing security by isolating assets and reducing the risk of loss due to breaches or mismanagement. In contrast, a pooled wallet combines all users' funds into a single balance, simplifying transactions but increasing vulnerability to collective loss. Choosing between segregated and pooled wallets depends on the priority of security versus operational convenience.
Table of Comparison
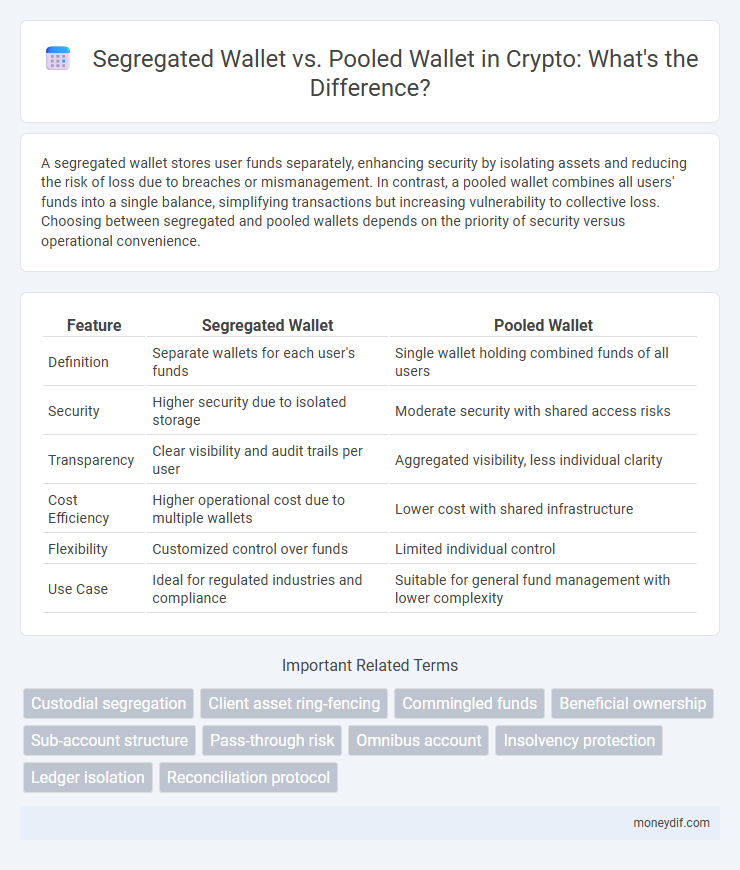
| Feature | Segregated Wallet | Pooled Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separate wallets for each user's funds | Single wallet holding combined funds of all users |
| Security | Higher security due to isolated storage | Moderate security with shared access risks |
| Transparency | Clear visibility and audit trails per user | Aggregated visibility, less individual clarity |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational cost due to multiple wallets | Lower cost with shared infrastructure |
| Flexibility | Customized control over funds | Limited individual control |
| Use Case | Ideal for regulated industries and compliance | Suitable for general fund management with lower complexity |
Introduction to Segregated and Pooled Wallets
Segregated wallets store user funds in individual accounts, ensuring enhanced security and clear ownership, while pooled wallets aggregate multiple users' funds into a single account for operational efficiency. Segregated wallets minimize risks related to fund commingling and simplify auditing processes, making them ideal for platforms prioritizing compliance. Pooled wallets, commonly used by exchanges, optimize transaction costs but require robust internal controls to manage user balances accurately.
Defining Segregated Wallets: Structure and Functionality
Segregated wallets are designed to keep individual customer funds separate from the company's operational accounts, enhancing security and regulatory compliance. Each wallet operates independently, ensuring transparent tracking and preventing the commingling of assets. This structure minimizes the risk of loss in case of insolvency or cyberattacks, providing clients with assured protection of their digital assets.
Understanding Pooled Wallets: Features and Mechanisms
Pooled wallets aggregate multiple users' funds into a single account, enhancing transaction efficiency and reducing operational costs. These wallets employ advanced reconciliation mechanisms to track individual balances accurately, ensuring transparency despite the shared pool. Security protocols and compliance measures are critical in pooled wallets to mitigate risks associated with collective fund management and regulatory requirements.
Key Differences Between Segregated and Pooled Wallets
Segregated wallets store each user's funds separately, enhancing security and reducing the risk of cross-user loss during breaches or insolvency, while pooled wallets combine multiple users' funds in a single account to simplify management and improve liquidity. Segregated wallets provide clearer audit trails and regulatory compliance, as individual balances are distinctly recorded, whereas pooled wallets require complex reconciliation processes due to aggregated holdings. The choice between segregated and pooled wallets impacts transparency, risk exposure, and operational efficiencies in cryptocurrency asset management.
Security Implications: Segregated vs Pooled Wallets
Segregated wallets enhance security by isolating individual user funds, reducing the risk of widespread loss from a single breach or insolvency event. Pooled wallets, while offering operational efficiency, increase vulnerability since all users share a common address and private keys, potentially exposing the entire pool to hacking or mismanagement risks. Choosing segregated wallets aligns with stringent compliance standards and offers greater transparency in asset custody.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Segregated wallets enhance compliance by isolating client funds, reducing risks of commingling and simplifying asset traceability, which aligns with regulatory mandates such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) requirements. Pooled wallets, while operationally efficient, pose greater challenges for regulators due to aggregated funds, increasing complexity in auditing and potential exposure to liquidity risks under stringent financial regulations. Regulatory frameworks often favor segregated wallets to ensure transparent oversight, protect customer assets, and facilitate quicker resolution during insolvency or disputes.
Use Cases: When to Choose Segregated or Pooled Wallets
Segregated wallets ensure individual fund separation, making them ideal for scenarios requiring enhanced security, regulatory compliance, or clear audit trails, such as client fund management and escrow services. Pooled wallets aggregate multiple users' funds, optimizing transaction efficiency and reducing operational costs, suitable for high-volume payment processors and microtransaction platforms. Selecting between segregated and pooled wallets depends on balancing security needs with transaction speed and cost-effectiveness.
Cost and Operational Efficiency Comparison
Segregated wallets offer higher security by isolating funds, which reduces the risk of cross-contamination but typically involve higher operational costs due to the need for separate management and reconciliation processes. Pooled wallets enhance cost efficiency by consolidating multiple users' assets into a single account, simplifying management and reducing administrative overhead, though they may introduce complexities related to fund allocation and regulatory compliance. Financial institutions often choose pooled wallets to optimize transaction processing speeds and lower fees, while segregated wallets are favored when prioritizing transparency and individualized control.
Impact on User Experience and Transaction Speed
Segregated wallets enhance user experience by providing individualized security and faster access to funds, reducing congestion during high transaction volumes. Pooled wallets simplify management by aggregating multiple users' funds but may introduce delays due to shared transaction processing and increased verification times. Transaction speed in segregated wallets often outperforms pooled wallets, as isolated accounts minimize bottlenecks and enable quicker settlements.
Choosing the Right Wallet Type for Your Needs
Choosing between a segregated wallet and a pooled wallet depends on security priorities and transaction frequency. Segregated wallets offer enhanced security by keeping assets separate, reducing risk in case of a breach, while pooled wallets provide convenience and faster access by combining funds for multiple users. Evaluating factors like asset protection, ease of access, and fee structures helps determine the most suitable wallet type for individual or business requirements.
Important Terms
Custodial segregation
Custodial segregation ensures user funds are held in distinct segregated wallets rather than combined pooled wallets, enhancing asset security and regulatory compliance.
Client asset ring-fencing
Client asset ring-fencing ensures segregation by storing funds in segregated wallets, preventing commingling with pooled wallets used for operational liquidity.
Commingled funds
Commingled funds involve pooling investor assets into a single pooled wallet for collective investment management, whereas segregated wallets maintain individual investor assets separately to enhance security and regulatory compliance.
Beneficial ownership
Beneficial ownership in segregated wallets ensures individual asset protection and clear legal rights, while pooled wallets combine assets increasing operational efficiency but complicating individual ownership claims.
Sub-account structure
A sub-account structure enhances security and compliance by allowing segregated wallets to isolate user funds, whereas pooled wallets combine assets in a single account, increasing risk but improving liquidity management.
Pass-through risk
Pass-through risk is significantly reduced in segregated wallets compared to pooled wallets due to isolated asset management and minimized exposure to other users' liabilities.
Omnibus account
An omnibus account consolidates multiple clients' assets into a pooled wallet for streamlined management, contrasting with segregated wallets that individually separate each client's funds for enhanced security and compliance.
Insolvency protection
Insolvency protection is enhanced by segregated wallets, which isolate client funds from company assets, whereas pooled wallets combine funds and increase risk exposure during insolvency events.
Ledger isolation
Ledger isolation enhances security by ensuring segregated wallets keep private keys and transaction records distinct from pooled wallets, minimizing cross-contamination risks and improving auditability.
Reconciliation protocol
Reconciliation protocols ensure accurate transaction matching and fund allocation by verifying individual balances in segregated wallets versus aggregated funds in pooled wallets for enhanced financial integrity.
segregated wallet vs pooled wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com