Legacy address wallets use the original Bitcoin address format starting with "1," resulting in higher transaction fees and slower processing times compared to SegWit address wallets. SegWit wallets utilize addresses starting with "3" or "bc1," enabling faster transactions and reduced fees by optimizing block space and fixing transaction malleability. Choosing a SegWit address wallet enhances efficiency and cost-effectiveness in Bitcoin transactions.
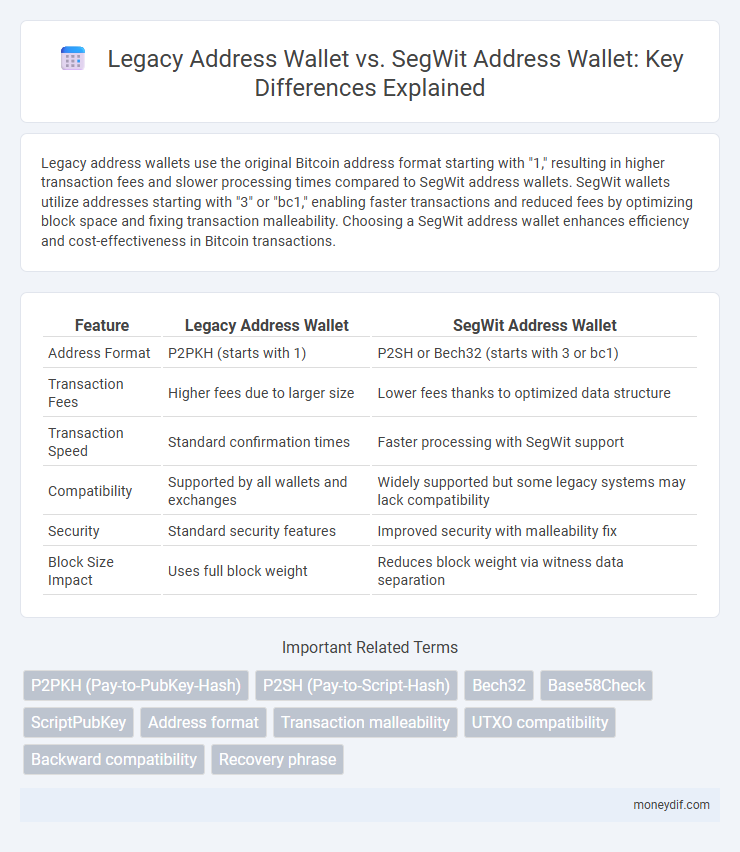
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Legacy Address Wallet | SegWit Address Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Address Format | P2PKH (starts with 1) | P2SH or Bech32 (starts with 3 or bc1) |
| Transaction Fees | Higher fees due to larger size | Lower fees thanks to optimized data structure |
| Transaction Speed | Standard confirmation times | Faster processing with SegWit support |
| Compatibility | Supported by all wallets and exchanges | Widely supported but some legacy systems may lack compatibility |
| Security | Standard security features | Improved security with malleability fix |
| Block Size Impact | Uses full block weight | Reduces block weight via witness data separation |
Introduction to Cryptocurrency Wallet Address Types
Legacy address wallets use the original Bitcoin address format starting with "1," offering broad compatibility but higher transaction fees and slower speeds. SegWit address wallets utilize the newer format beginning with "3" or "bc1," enabling reduced transaction size that lowers fees and increases network efficiency. Understanding these address types is crucial for optimizing transaction costs and ensuring wallet compatibility across different cryptocurrency networks.
What is a Legacy Address Wallet?
A Legacy Address Wallet uses traditional Bitcoin addresses starting with the number "1," representing the original format for Bitcoin transactions. These wallets are compatible with all Bitcoin services but incur higher transaction fees and slower confirmation times due to larger transaction sizes. SegWit adoption is recommended as it optimizes transaction efficiency and lowers fees by utilizing a new address format starting with "3" or "bc1.
What is a SegWit Address Wallet?
A SegWit address wallet utilizes Segregated Witness technology to separate transaction signatures from the payload data, enabling faster confirmations and lower fees compared to legacy address wallets. This wallet type supports Bech32 address formats, enhancing transaction efficiency and reducing the risk of malleability attacks. SegWit wallets improve scalability and are compatible with most modern Bitcoin applications, making them a preferred choice for optimized cryptocurrency transactions.
Technical Differences Between Legacy and SegWit Addresses
Legacy address wallets use the original Bitcoin address format, starting with a "1," which results in larger transaction sizes due to storing the full signature data on-chain. SegWit address wallets leverage Segregated Witness technology, using addresses starting with "3" (P2SH) or "bc1" (Bech32), which separate signature data from the transaction, reducing size and lowering fees. The technical improvements in SegWit enhance scalability and enable advanced features like batch transactions and Lightning Network compatibility, which are not supported by legacy addresses.
Transaction Fees: Legacy vs SegWit Wallets
Legacy address wallets (starting with "1") typically incur higher transaction fees due to larger transaction sizes and less efficient data encoding. SegWit address wallets (starting with "3" or "bc1") reduce transaction size by separating signature data, resulting in lower fees and faster confirmations. Using SegWit addresses improves network scalability and cost-efficiency for Bitcoin transactions.
Transaction Speed and SegWit Efficiency
SegWit address wallets significantly enhance transaction speed by reducing data size through the segregation of signature data, resulting in faster block confirmation times compared to legacy address wallets. Legacy address transactions tend to be larger and slower due to the inclusion of all signature data within the main block, leading to higher fees and delayed processing. SegWit wallets also improve network efficiency by enabling more transactions per block, optimizing blockchain scalability and reducing congestion.
Security Implications: Legacy vs SegWit Wallets
Legacy address wallets use the older Pay-to-Public-Key-Hash (P2PKH) format, which lacks the enhanced security features found in SegWit wallets, such as reduced transaction malleability and lower risk of replay attacks. SegWit wallets leverage Pay-to-Witness-Public-Key-Hash (P2WPKH) addresses, enabling improved transaction verification and protecting against certain types of vulnerabilities inherent in legacy wallets. The adoption of SegWit also enhances scalability and lowers transaction fees while maintaining robust security protocols compared to legacy systems.
Compatibility with Exchanges and Wallets
Legacy address wallets use the original Bitcoin address format (P2PKH) and enjoy broad compatibility with most exchanges and wallets, ensuring seamless transactions. SegWit address wallets, with formats like P2SH and Bech32, enhance transaction efficiency and lower fees but may face partial support on older platforms. Choosing SegWit wallets is beneficial for future-proofing, though verifying exchange and wallet compatibility remains crucial for smooth operations.
Migrating from Legacy to SegWit Address Wallets
Migrating from Legacy to SegWit address wallets enhances transaction efficiency by reducing fees and increasing block capacity through Segregated Witness technology. SegWit wallets use addresses starting with "bc1" (native SegWit) or "3" (P2SH-wrapped SegWit), offering improved security and faster confirmation times compared to Legacy addresses beginning with "1." Transitioning involves consolidating funds from Legacy wallets into SegWit addresses, optimizing blockchain performance and future-proofing wallet usability.
Choosing the Right Address Type for Your Needs
Legacy Address Wallets start with a "1" and offer broad compatibility with most bitcoin services but incur higher transaction fees due to larger data sizes. SegWit Address Wallets, identifiable by starting with a "3" or "bc1," reduce transaction fees and increase scalability by optimizing block size and improving transaction malleability. Selecting between Legacy and SegWit depends on your priority for transaction cost efficiency and support across wallets and exchanges.
Important Terms
P2PKH (Pay-to-PubKey-Hash)
P2PKH (Pay-to-PubKey-Hash) is a transaction type used primarily by Legacy Address wallets, identified by addresses starting with '1', which store and spend Bitcoins using a hash of the user's public key. SegWit Address wallets, utilizing P2WPKH (Pay-to-Witness-Public-Key-Hash), improve upon P2PKH by segregating witness data to reduce transaction size and lower fees, often represented by addresses starting with 'bc1'.
P2SH (Pay-to-Script-Hash)
P2SH (Pay-to-Script-Hash) enables compatibility between Legacy Address Wallets and SegWit Address Wallets by allowing SegWit scripts to be embedded within legacy-style addresses for enhanced transaction efficiency and lower fees.
Bech32
Bech32 is a SegWit address format designed to improve error detection and efficiency compared to Legacy Address Wallets, which use Base58Check encoding and are more prone to transcription errors. SegWit Address Wallets reduce transaction fees and enable faster processing by separating signature data from transaction data, making Bech32 the preferred standard for modern Bitcoin wallets.
Base58Check
Base58Check encoding is a critical component in Legacy Address Wallets, using a checksum to prevent errors in Bitcoin addresses that typically start with '1.' SegWit Address Wallets, however, often use Bech32 encoding for addresses beginning with 'bc1,' which reduces transaction fees and improves scalability by separating witness data from the main block.
ScriptPubKey
ScriptPubKey defines the conditions needed to spend Bitcoin outputs, differing significantly between Legacy and SegWit address wallets; Legacy addresses use P2PKH scripts, which embed a public key hash directly, while SegWit addresses utilize P2WPKH or P2WSH scripts that offload signature data for enhanced scalability and lower transaction fees. SegWit ScriptPubKeys improve network efficiency by reducing transaction size and mitigating malleability issues, promoting faster confirmation times compared to the larger, more data-intensive ScriptPubKeys of Legacy wallets.
Address format
Legacy Address Wallets use the original Bitcoin address format starting with '1', while SegWit Address Wallets adopt newer formats such as P2SH addresses starting with '3' or Bech32 addresses starting with 'bc1', which improve transaction efficiency and lower fees. SegWit addresses enhance block capacity and reduce transaction malleability compared to Legacy addresses.
Transaction malleability
Transaction malleability refers to the ability to alter the transaction ID (TXID) of a Bitcoin transaction without changing its contents, which was a significant issue for Legacy Address Wallets (P2PKH and P2SH) due to the way signatures were structured. SegWit Address Wallets (starting with "bc1" or "3") separate the witness data from the transaction, effectively eliminating transaction malleability by making the TXID immune to signature changes and enhancing overall network efficiency.
UTXO compatibility
SegWit address wallets improve UTXO compatibility by enabling smaller transaction sizes and lower fees compared to legacy address wallets, enhancing blockchain efficiency.
Backward compatibility
Backward compatibility ensures SegWit address wallets can interact with legacy address wallets by supporting both old and new transaction formats, preserving seamless payment functionality. Legacy address wallets use P2PKH or P2SH formats, while SegWit wallets utilize bech32 addresses, offering reduced transaction fees and improved scalability without sacrificing compatibility.
Recovery phrase
Recovery phrases, also known as seed phrases, are crucial for restoring access to wallets and must correspond to the wallet type, as Legacy Address Wallets use traditional P2PKH (Pay-to-Pubkey-Hash) formats while SegWit Address Wallets utilize newer Bech32 or P2SH (Pay-to-Script-Hash) formats that provide better efficiency and lower transaction fees. Using a recovery phrase generated from a Legacy wallet may not restore SegWit addresses correctly, leading to potential access issues and requiring careful compatibility verification for successful wallet recovery.
Legacy Address Wallet vs SegWit Address Wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com