On-chain wallets store private keys and transaction data directly on the blockchain, ensuring enhanced transparency and security through decentralized verification. Off-chain wallets manage keys and transactions outside the blockchain, offering faster transaction speeds and reduced fees but relying on third-party intermediaries. Choosing between on-chain and off-chain wallets depends on the user's priorities for security versus convenience and transaction cost.
Table of Comparison
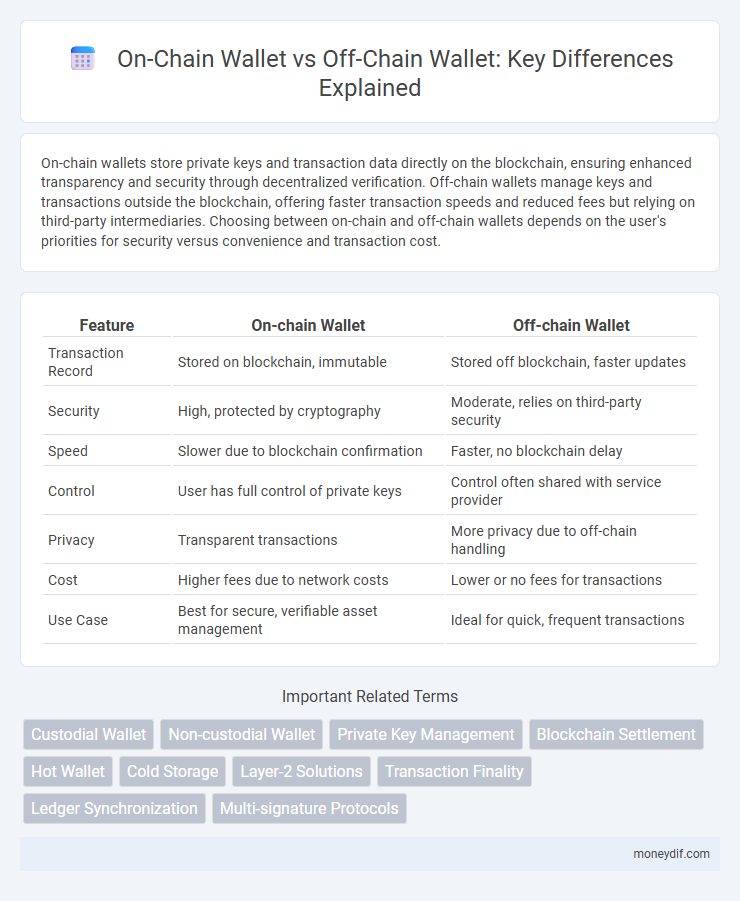
| Feature | On-chain Wallet | Off-chain Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Record | Stored on blockchain, immutable | Stored off blockchain, faster updates |
| Security | High, protected by cryptography | Moderate, relies on third-party security |
| Speed | Slower due to blockchain confirmation | Faster, no blockchain delay |
| Control | User has full control of private keys | Control often shared with service provider |
| Privacy | Transparent transactions | More privacy due to off-chain handling |
| Cost | Higher fees due to network costs | Lower or no fees for transactions |
| Use Case | Best for secure, verifiable asset management | Ideal for quick, frequent transactions |
Introduction to On-chain and Off-chain Wallets
On-chain wallets store cryptocurrency keys directly on the blockchain, ensuring full control, transparency, and security through decentralized ledger technology. Off-chain wallets manage keys and transactions outside the blockchain, offering faster processing and reduced fees but relying on third-party custodians or centralized servers. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting a wallet based on security preferences and transaction needs.
Core Differences Between On-chain and Off-chain Wallets
On-chain wallets store cryptocurrencies directly on the blockchain, providing enhanced security and full control over private keys, while off-chain wallets hold assets outside the blockchain, often relying on third-party custodians for convenience and faster transactions. On-chain transactions are transparent, irreversible, and traceable on the blockchain ledger, whereas off-chain transactions occur off the blockchain, allowing for quicker settlement but reduced transparency and increased counterparty risk. Core differences include control over assets, transaction speed, security levels, and dependency on blockchain confirmation processes.
How On-chain Wallets Work
On-chain wallets operate by directly interacting with the blockchain, allowing users to send, receive, and store cryptocurrency through cryptographic keys stored on the blockchain ledger. Transactions made with on-chain wallets are recorded publicly and immutably on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and security. These wallets require users to manage private keys, giving full control over funds without intermediaries.
How Off-chain Wallets Operate
Off-chain wallets manage cryptocurrency transactions without recording them directly on the blockchain, enabling faster and lower-cost transfers by avoiding network congestion and fees. They rely on centralized servers or trusted third parties to maintain transaction records and balances, offering enhanced privacy and scalability compared to on-chain wallets. Users benefit from seamless, instant transactions while sacrificing some decentralization and security inherent to blockchain-based on-chain wallets.
Security Features: On-chain vs Off-chain
On-chain wallets store private keys directly on the blockchain, providing enhanced security through decentralized validation and immutability, reducing the risk of centralized hacks. Off-chain wallets, often custodial, keep private keys on centralized servers, which can create vulnerabilities to data breaches but offer faster transactions and easier recovery options. Choosing between on-chain and off-chain wallets depends on prioritizing security decentralization versus convenience and speed.
Transaction Speed and Efficiency
On-chain wallets record transactions directly on the blockchain, ensuring high security but often experiencing slower transaction speeds due to network congestion and consensus mechanisms. Off-chain wallets process transactions outside the blockchain, enabling faster and more efficient transfers by reducing on-chain load and confirmation times. Choosing between them depends on the need for immediate transaction speed versus blockchain transparency and security.
User Experience and Accessibility
On-chain wallets provide users with direct control over their private keys and assets on the blockchain, ensuring higher security and transparency, but often require more technical knowledge and interaction with network fees, impacting user experience. Off-chain wallets enhance accessibility and ease of use by managing private keys and transactions within centralized platforms, offering faster transactions and simplified interfaces suitable for beginners, though they introduce dependence on third-party services and potential custodial risks. Prioritizing user experience, off-chain wallets are favored for everyday convenience, while on-chain wallets appeal to users valuing full control and decentralized security.
Use Cases for On-chain Wallets
On-chain wallets provide direct interaction with blockchain networks, enabling users to send, receive, and store cryptocurrencies securely while maintaining full control over private keys. Use cases for on-chain wallets include decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, where users can participate in lending, staking, and yield farming without intermediaries. These wallets also facilitate secure transactions in NFT marketplaces and support cross-chain asset transfers, making them essential for users engaging with decentralized ecosystems.
Use Cases for Off-chain Wallets
Off-chain wallets excel in scenarios requiring fast, low-cost transactions, such as micropayments and gaming platforms where on-chain fees would be prohibitive. They enable instant settlement by conducting transactions off the blockchain while maintaining security through periodic on-chain state updates. Businesses leverage off-chain wallets for scalable payment solutions, reducing network congestion and enhancing user experience in decentralized applications.
Choosing the Right Wallet for Your Needs
On-chain wallets store cryptocurrency keys directly on the blockchain, offering enhanced security and transparency but may incur higher transaction fees and slower processing times. Off-chain wallets, often custodial, facilitate faster transactions and lower costs by managing keys outside the blockchain, though they carry risks related to third-party control and potential loss of funds. Assessing priorities like control, transaction speed, security, and cost is essential for selecting the most suitable wallet tailored to individual requirements.
Important Terms
Custodial Wallet
A custodial wallet stores private keys on behalf of users, offering ease of access but relying on a third party for security, in contrast to on-chain wallets that provide full user control over private keys directly on the blockchain. Off-chain wallets manage assets off the blockchain, enabling faster transactions and scalability, yet they often lack the transparency and self-custody benefits inherent to on-chain wallets.
Non-custodial Wallet
Non-custodial wallets provide users full control over their private keys, ensuring complete ownership of on-chain assets without relying on third-party custody. Unlike off-chain wallets, which may store assets or transaction data off the blockchain for faster processing and lower fees, non-custodial on-chain wallets directly interact with blockchain networks, enhancing security and transparency.
Private Key Management
Private key management in on-chain wallets involves storing keys directly on a blockchain, enhancing security through decentralized verification but requiring users to safeguard keys themselves. Off-chain wallets manage private keys outside the blockchain environment, often relying on third-party custodians or hardware solutions that balance convenience with potential security trade-offs.
Blockchain Settlement
Blockchain settlement efficiency depends on whether transactions are processed through on-chain wallets, which offer decentralized security and transparency, or off-chain wallets, which provide faster, lower-cost settlements by conducting transactions outside the main blockchain.
Hot Wallet
Hot wallets are internet-connected digital wallets that enable real-time access to cryptocurrencies, making them ideal for frequent transactions but more vulnerable to cyber threats compared to cold storage. In contrast, on-chain wallets interact directly with blockchain networks to record transactions publicly, while off-chain wallets manage assets through third-party platforms, offering faster but less transparent transfers.
Cold Storage
Cold storage securely stores cryptocurrency private keys offline, significantly reducing exposure to cyberattacks compared to on-chain wallets that maintain keys directly on the blockchain, enhancing transaction transparency but increasing vulnerability. Off-chain wallets manage assets outside the public ledger, boosting transaction speed and privacy while posing greater risk of centralized control and potential hacking.
Layer-2 Solutions
Layer-2 solutions enhance blockchain scalability by processing transactions off the main Ethereum chain, reducing on-chain wallet congestion and gas fees while maintaining security through on-chain settlement. Off-chain wallets interact seamlessly with Layer-2 networks, enabling faster and cheaper transactions, whereas on-chain wallets conduct all operations directly on the base layer, ensuring maximum decentralization but higher costs.
Transaction Finality
Transaction finality in on-chain wallets ensures irreversible and verifiable settlement recorded on the blockchain ledger, providing enhanced security and transparency through consensus mechanisms. Off-chain wallets rely on third-party intermediaries for transaction validation, often resulting in faster processing but lacking the immutable and trustless finality inherent in on-chain solutions.
Ledger Synchronization
Ledger synchronization ensures consistent transaction records between on-chain wallets, which record every transaction on the blockchain, and off-chain wallets, which manage transactions privately to enhance speed and reduce costs.
Multi-signature Protocols
Multi-signature protocols enhance security by requiring multiple keys for transaction approval, with on-chain wallets executing these signatures transparently on the blockchain while off-chain wallets perform these validations privately to improve speed and reduce fees.
On-chain Wallet vs Off-chain Wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com