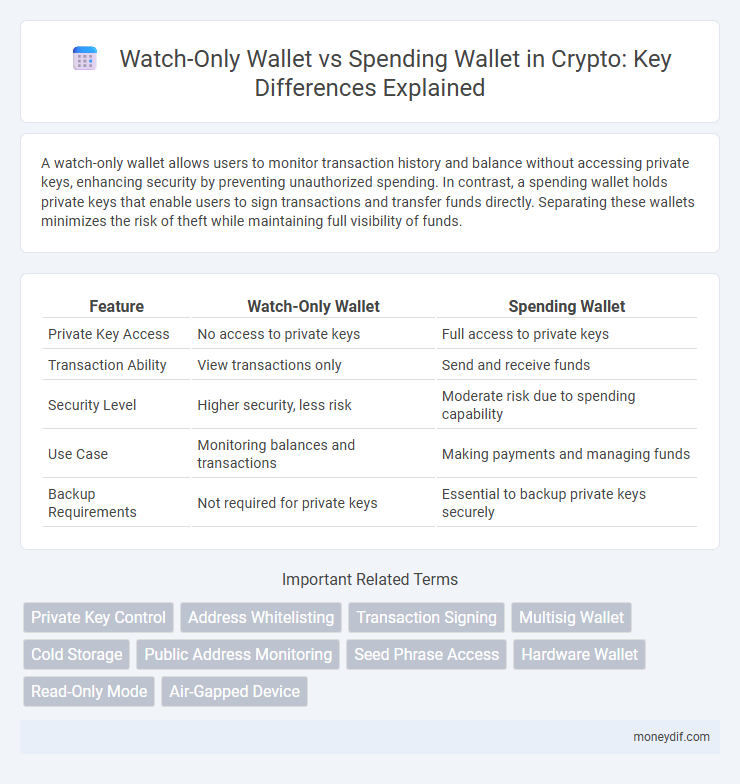
A watch-only wallet allows users to monitor transaction history and balance without accessing private keys, enhancing security by preventing unauthorized spending. In contrast, a spending wallet holds private keys that enable users to sign transactions and transfer funds directly. Separating these wallets minimizes the risk of theft while maintaining full visibility of funds.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Watch-Only Wallet | Spending Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Private Key Access | No access to private keys | Full access to private keys |
| Transaction Ability | View transactions only | Send and receive funds |
| Security Level | Higher security, less risk | Moderate risk due to spending capability |
| Use Case | Monitoring balances and transactions | Making payments and managing funds |
| Backup Requirements | Not required for private keys | Essential to backup private keys securely |
Introduction to Wallet Types: Watch-Only vs Spending
Watch-only wallets allow users to monitor cryptocurrency balances and transactions without access to private keys, ensuring heightened security by preventing unauthorized spending. Spending wallets hold private keys, enabling users to authorize transactions and manage funds actively. Understanding the distinction between watch-only and spending wallets is essential for effective asset management and security in cryptocurrency environments.
What Is a Watch-Only Wallet?
A watch-only wallet is a digital wallet that allows users to monitor cryptocurrency balances and transaction history without having access to private keys, ensuring funds cannot be spent or transferred. It provides enhanced security by enabling users to track assets while preventing unauthorized spending or hacking attempts. This type of wallet is ideal for portfolio tracking and auditing purposes where transaction visibility is needed without compromising asset control.
What Is a Spending Wallet?
A spending wallet is a type of cryptocurrency wallet designed to store private keys that enable users to actively send and receive funds. Unlike watch-only wallets, which allow users to monitor balances and transactions without the ability to spend, spending wallets provide full access for executing transactions on the blockchain. These wallets are essential for managing daily crypto activities such as payments, transfers, and trading, ensuring the security of private keys through encryption and backup options.
Key Differences Between Watch-Only and Spending Wallets
Watch-only wallets allow users to monitor cryptocurrency balances and transactions without access to private keys, ensuring enhanced security and reduced risk of unauthorized spending. Spending wallets hold private keys, enabling users to initiate transactions and manage funds directly, but they require robust security measures to prevent theft. Key differences include access permissions, security levels, and functional capabilities related to transaction authorization and asset control.
Security Advantages of Watch-Only Wallets
Watch-only wallets enhance security by allowing users to monitor cryptocurrency balances and transaction history without exposing private keys, thus eliminating the risk of unauthorized spending. They provide a safe way to track assets on multiple devices without the threat of hacking or malware compromising spending capabilities. This separation of viewing and spending functions significantly reduces the attack surface for potential cyber threats.
Use Cases for Watch-Only Wallets
Watch-only wallets enable users to monitor cryptocurrency balances and transactions without risking fund security, making them ideal for auditing or portfolio tracking. They are especially useful for institutions or individuals who require visibility over multiple accounts without access to private keys. This enhances security by preventing unauthorized spending while maintaining real-time oversight of wallet activity.
Spending Wallets: Features and Functionalities
Spending wallets enable users to send and receive cryptocurrency with full access to private keys, ensuring complete control over transactions and asset management. These wallets support advanced functionalities such as transaction signing, multisignature capabilities, and real-time balance updates, enhancing security and flexibility. Designed for active use, spending wallets integrate seamlessly with decentralized applications, offering a comprehensive solution for day-to-day crypto spending and trading activities.
Managing Risk: When to Use Each Wallet Type
Watch-only wallets enhance security by allowing users to monitor balances and transactions without exposing private keys, minimizing the risk of unauthorized spending. Spending wallets store private keys necessary for transaction authorization, making them essential for active fund management but increasing exposure to potential theft. Employ watch-only wallets for risk-averse monitoring and spending wallets only when initiating transactions to balance security and usability effectively.
Best Practices for Wallet Security
Watch-only wallets enhance security by allowing users to monitor balances and transactions without exposing private keys, effectively reducing the risk of unauthorized spending. Spending wallets store private keys required for transaction signing, demanding strict protection methods such as hardware wallets or multi-factor authentication. Best practices recommend separating watch-only wallets for daily monitoring from spending wallets kept in highly secure environments to minimize potential attack vectors.
Choosing the Right Wallet for Your Needs
Watch-only wallets enhance security by allowing users to monitor transactions and balances without risking exposure to private keys, making them ideal for auditing and cold storage verification. Spending wallets provide full control over funds with access to private keys, enabling seamless transaction signing and fund transfers. Selecting the right wallet depends on your priority between security monitoring (watch-only) and active fund management (spending wallet).
Important Terms
Private Key Control
Private Key Control is essential in spending wallets, granting full transaction authority, while watch-only wallets lack private keys and only allow balance monitoring without spending capability.
Address Whitelisting
Address whitelisting enhances security by allowing only pre-approved addresses to interact with spending wallets, while watch-only wallets monitor transactions without permitting fund transfers.
Transaction Signing
Transaction signing requires a spending wallet holding private keys, while a watch-only wallet can monitor balances and transactions without authorizing spending.
Multisig Wallet
A multisig wallet enhances security by requiring multiple signatures for transactions, distinguishing watch-only wallets that monitor balances without spending capabilities from spending wallets authorized to execute transactions.
Cold Storage
Cold Storage securely stores cryptocurrency in a watch-only wallet, preventing unauthorized access and spending while maintaining transaction visibility, unlike spending wallets that allow direct fund transfers.
Public Address Monitoring
Public Address Monitoring enables tracking of incoming transactions and balances in watch-only wallets without exposing private keys required for spending wallets.
Seed Phrase Access
Seed phrase access grants full control and spending capabilities over a wallet, unlike watch-only wallets which provide transaction monitoring without private key or spending access.
Hardware Wallet
Hardware wallets securely store private keys for spending wallets while allowing watch-only wallets to monitor balances without exposing keys.
Read-Only Mode
Read-only mode enables secure monitoring of watch-only wallets without exposing private keys, unlike spending wallets that require access to private keys for transaction authorization.
Air-Gapped Device
An air-gapped device enhances security by isolating a spending wallet from online threats while a watch-only wallet allows transaction monitoring without exposing private keys.
watch-only wallet vs spending wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com