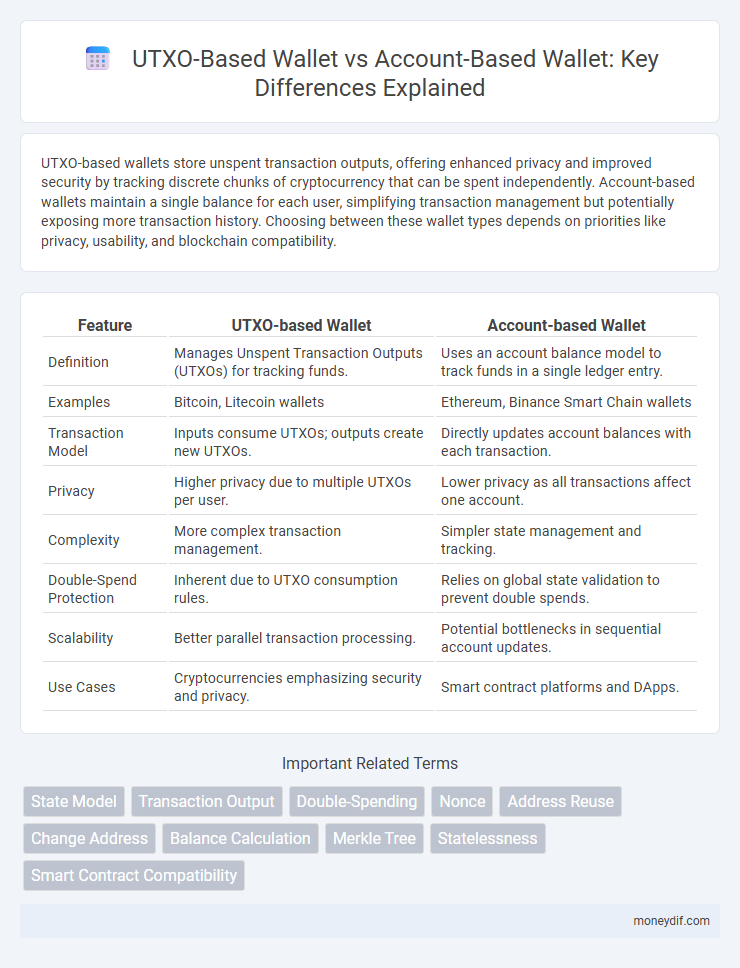
UTXO-based wallets store unspent transaction outputs, offering enhanced privacy and improved security by tracking discrete chunks of cryptocurrency that can be spent independently. Account-based wallets maintain a single balance for each user, simplifying transaction management but potentially exposing more transaction history. Choosing between these wallet types depends on priorities like privacy, usability, and blockchain compatibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UTXO-based Wallet | Account-based Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manages Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs) for tracking funds. | Uses an account balance model to track funds in a single ledger entry. |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Litecoin wallets | Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain wallets |
| Transaction Model | Inputs consume UTXOs; outputs create new UTXOs. | Directly updates account balances with each transaction. |
| Privacy | Higher privacy due to multiple UTXOs per user. | Lower privacy as all transactions affect one account. |
| Complexity | More complex transaction management. | Simpler state management and tracking. |
| Double-Spend Protection | Inherent due to UTXO consumption rules. | Relies on global state validation to prevent double spends. |
| Scalability | Better parallel transaction processing. | Potential bottlenecks in sequential account updates. |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies emphasizing security and privacy. | Smart contract platforms and DApps. |
Understanding UTXO-Based Wallets
UTXO-based wallets manage funds by tracking unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs) rather than account balances, enabling precise control over individual inputs and outputs. Each UTXO represents a discrete chunk of cryptocurrency that can be spent entirely or partially in new transactions, enhancing privacy and making auditing more transparent. This approach contrasts with account-based wallets by offering improved scalability and reducing the risk of double-spending through clear state validation.
Overview of Account-Based Wallets
Account-based wallets store balances as a single value linked to a user's address, simplifying transaction verification by updating account states directly on the blockchain. This model, used by platforms like Ethereum, allows for efficient smart contract interactions and easier user experience since there is no need to track multiple unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs). Account-based wallets enable streamlined management of assets and permissions, supporting more complex financial applications and decentralized finance protocols.
Key Differences Between UTXO and Account Models
UTXO-based wallets track individual unspent transaction outputs, enabling precise accounting and enhanced privacy through coin selection and change management. Account-based wallets maintain a single balance per address, simplifying transactions but reducing granularity and privacy. The UTXO model excels in parallel transaction verification, while the account model offers straightforward state management on blockchains like Ethereum.
How Transactions Work: UTXO vs Account-Based
UTXO-based wallets track individual unspent transaction outputs, requiring users to select and combine these outputs as inputs for new transactions, which enhances privacy and enables complex transaction types like coin mixing. Account-based wallets maintain a single balance per address, updating this balance directly with each transaction, simplifying state management but offering less privacy. The UTXO model allows for parallel transaction validation, whereas account-based systems process transactions sequentially, impacting scalability and concurrency.
Security Implications of Each Wallet Type
UTXO-based wallets offer enhanced privacy and security by using discrete unspent transaction outputs, minimizing traceability and reducing the risk of double spending. Account-based wallets simplify tracking and managing balances but are more susceptible to replay attacks and require robust protection for private keys to prevent unauthorized access. Choosing between these wallet types depends on the desired balance between transparency, ease of use, and security resilience.
Privacy Considerations: UTXO vs Account-Based Wallets
UTXO-based wallets enhance privacy by obfuscating transaction history through discrete unspent outputs, making it difficult to trace funds across multiple transactions. Account-based wallets, used in platforms like Ethereum, maintain a single balance with publicly visible transaction history, which can be more susceptible to tracking and linking activities. Privacy-conscious users often prefer UTXO models like Bitcoin due to their superior anonymity features compared to the transparent nature of account-based systems.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
UTXO-based wallets excel in parallel transaction processing, enhancing scalability through independent unspent outputs that reduce computational overhead. Account-based wallets streamline state management by maintaining singular account balances, which simplifies real-time updates but may introduce bottlenecks under high transaction volumes. UTXO models are better suited for high-throughput scenarios, whereas account-based wallets often prioritize ease of use and straightforward transaction histories over peak performance.
Popular Cryptocurrencies Using Each Model
Popular cryptocurrencies using UTXO-based wallets include Bitcoin (BTC) and Litecoin (LTC), leveraging the UTXO model for enhanced security and transaction traceability. Ethereum (ETH) exemplifies account-based wallets, facilitating smart contracts and seamless balance management through a global state. Understanding the distinctions between UTXO and account-based models is crucial for users navigating wallet compatibility and transaction processing across different blockchain networks.
Use Cases Suited for UTXO and Account-Based Wallets
UTXO-based wallets excel in use cases requiring enhanced privacy, precise transaction control, and offline or hardware wallet compatibility, commonly seen in Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash ecosystems. Account-based wallets are better suited for applications demanding smooth user experience, compatibility with smart contracts, and efficient balance tracking, typical in Ethereum and similar blockchain networks. Choosing between UTXO and account-based wallets depends on prioritizing transaction transparency versus ease of use and programmability.
Choosing the Right Wallet Model for Your Needs
UTXO-based wallets provide enhanced privacy and security by managing unspent transaction outputs individually, ideal for users prioritizing transaction traceability and precise fund control. Account-based wallets offer simpler user experiences with streamlined transaction management, better suited for frequent transfers and smart contract interactions. Selecting the right wallet model depends on whether you value granular control and anonymity or convenience and ease of use in everyday transactions.
Important Terms
State Model
The state model in UTXO-based wallets tracks unspent transaction outputs to ensure transaction validity, whereas account-based wallets maintain balances linked to single accounts, streamlining transaction management and state updates.
Transaction Output
Transaction Output in UTXO-based wallets represents unspent transaction outputs recorded on the blockchain, enabling precise tracking of individual coin ownership, while Account-based wallets maintain a single balance reflecting cumulative transactions without tracking individual outputs.
Double-Spending
UTXO-based wallets prevent double-spending by individually tracking unspent transaction outputs, while account-based wallets rely on balance states, making UTXO models inherently more secure against double-spending risks.
Nonce
Nonce ensures transaction order and uniqueness in account-based wallets, while UTXO-based wallets rely on unspent outputs instead of nonces for transaction validation.
Address Reuse
Address reuse in UTXO-based wallets reduces privacy and increases traceability risks, whereas account-based wallets inherently manage a single address, simplifying transactions but lowering anonymity.
Change Address
Changing an address in UTXO-based wallets requires managing multiple unspent transaction outputs for balance reconciliation, unlike account-based wallets that update a single account state for address changes.
Balance Calculation
UTXO-based wallets calculate balance by aggregating unspent transaction outputs associated with the wallet's addresses, while account-based wallets maintain a single balance updated by each transaction affecting the account.
Merkle Tree
Merkle Trees enhance UTXO-based wallets by enabling efficient verification of transaction outputs, while account-based wallets rely on different state management without direct use of Merkle Trees for output tracking.
Statelessness
Statelessness in UTXO-based wallets enables enhanced privacy and parallel transaction validation compared to account-based wallets, which maintain continuous account states and balances.
Smart Contract Compatibility
Smart contract compatibility varies as UTXO-based wallets emphasize transaction outputs for enhanced security and privacy, while account-based wallets streamline contract interaction through simplified state management and direct balance tracking.
UTXO-based Wallet vs Account-based Wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com