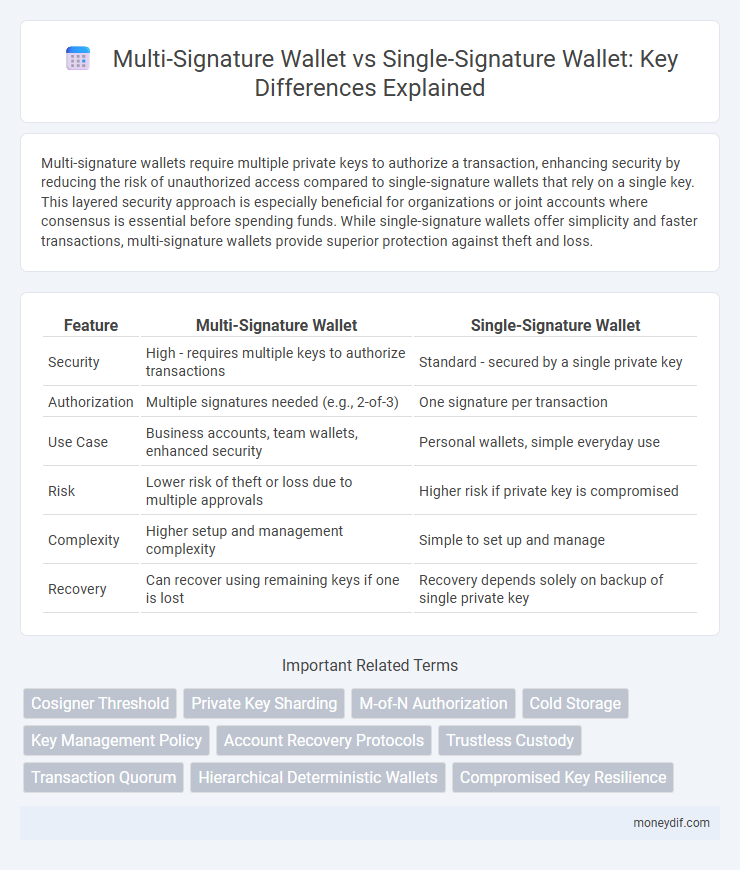
Multi-signature wallets require multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, enhancing security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access compared to single-signature wallets that rely on a single key. This layered security approach is especially beneficial for organizations or joint accounts where consensus is essential before spending funds. While single-signature wallets offer simplicity and faster transactions, multi-signature wallets provide superior protection against theft and loss.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Multi-Signature Wallet | Single-Signature Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High - requires multiple keys to authorize transactions | Standard - secured by a single private key |
| Authorization | Multiple signatures needed (e.g., 2-of-3) | One signature per transaction |
| Use Case | Business accounts, team wallets, enhanced security | Personal wallets, simple everyday use |
| Risk | Lower risk of theft or loss due to multiple approvals | Higher risk if private key is compromised |
| Complexity | Higher setup and management complexity | Simple to set up and manage |
| Recovery | Can recover using remaining keys if one is lost | Recovery depends solely on backup of single private key |
Introduction to Crypto Wallets: Single vs Multi-Signature
Single-signature wallets require one private key to authorize transactions, offering simplicity but limited security in managing cryptocurrency assets. Multi-signature wallets increase security by requiring multiple private keys, often from different participants, to approve any transaction, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or theft. These wallets cater to organizational use cases where collective approval is necessary, enhancing control and accountability in crypto asset management.
Understanding Single-Signature Wallets
Single-signature wallets require only one private key to authorize transactions, providing straightforward access and simplicity for individual users. They are highly convenient for daily use but offer limited security compared to multi-signature wallets that demand multiple approvals. These wallets are ideal for personal use cases where ease of access is prioritized over enhanced security measures.
Exploring Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature wallets require multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, enhancing security compared to single-signature wallets that rely on one key. These wallets reduce the risk of unauthorized access by distributing control among multiple parties, making them ideal for organizational or joint accounts. By implementing multi-signature technology, users benefit from increased protection against theft, fraud, and accidental loss of keys.
Security Differences: Multi-Sig vs Single-Sig
Multi-signature wallets require multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, significantly enhancing security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access or theft compared to single-signature wallets, which rely on a single key. Single-signature wallets are more vulnerable to hacking or key loss since one compromised key grants full access, whereas multi-sig wallets distribute control across multiple parties or devices for added protection. The added complexity of multi-signature wallets provides robust defense against phishing, malware, and insider threats, making them ideal for institutional or joint account management.
Ease of Use: User Experience Compared
Single-signature wallets offer straightforward access with one private key, making them highly user-friendly for individuals seeking simplicity. Multi-signature wallets require multiple approvals, which enhances security but can complicate the transaction process and slow down decision-making. Users must balance ease of use with security needs when choosing between these wallet types.
Use Cases: When to Choose Single or Multi-Signature Wallets
Single-signature wallets are ideal for individuals or small businesses requiring fast, straightforward transactions with low security risk, such as personal savings or everyday spending. Multi-signature wallets are essential for organizations or joint accounts demanding enhanced security and shared control, like corporate funds management or joint investment accounts. Choosing between them depends on the need for transaction speed versus security, with multi-signature wallets providing strong fraud protection and single-signature wallets offering convenience.
Cost and Transaction Speed Analysis
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple approvals for transactions but often incur higher transaction fees due to increased data size and complexity on the blockchain. Single-signature wallets typically offer faster transaction processing with lower costs since only one signature is needed, reducing on-chain data load. Businesses prioritizing cost-efficiency and transaction speed may favor single-signature wallets, whereas those requiring advanced security might accept higher fees and slower confirmation times with multi-signature solutions.
Recovery and Backup: Multi-Sig vs Single-Sig
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple approvals for transactions, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access compared to single-signature wallets that rely on one key. Recovery in multi-sig wallets involves securing multiple private keys, enabling funds recovery if one key is lost, whereas single-sig wallets depend entirely on a single private key, making backup crucial and vulnerability higher in case of loss. Effective backup strategies in multi-sig wallets distribute keys across trusted parties or devices, improving resilience against theft and accidental loss.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Multi-signature wallets, utilized by companies like BitGo and Coinbase, enhance security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions, reducing the risk of single-point failures seen in single-signature wallets used commonly by individual users. Real-world cases such as the DAO hack in 2016 highlight single-signature wallet vulnerabilities, prompting many crypto custodians to adopt multi-signature solutions for improved asset protection. Case studies from institutional investors demonstrate that multi-signature wallets provide higher resilience against internal fraud and external hacking attempts compared to single-signature wallets.
Final Verdict: Which Wallet Suits Your Needs?
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions, making them ideal for businesses or groups managing shared funds. Single-signature wallets offer simplicity and faster access, suitable for individual users seeking convenient control over their assets. Evaluate your security needs and transaction frequency to decide between the robust protection of multi-signature wallets and the ease of single-signature wallets.
Important Terms
Cosigner Threshold
Cosigner threshold determines the minimum number of signatures required to authorize transactions in a multi-signature wallet, enhancing security compared to the single-signature wallet that requires only one signature.
Private Key Sharding
Private Key Sharding enhances security by splitting a single private key into multiple parts, requiring several shards to reconstruct the key, which contrasts with Multi-Signature Wallets that require multiple distinct private keys to authorize transactions. Unlike Single-Signature Wallets that depend solely on one private key, Private Key Sharding reduces the risk of a single point of failure while maintaining access control similarly to Multi-Signature Wallet setups.
M-of-N Authorization
M-of-N authorization enhances security by requiring multiple signatures to approve a transaction in multi-signature wallets, unlike single-signature wallets that depend on a sole private key.
Cold Storage
Cold storage provides enhanced security by keeping cryptocurrency keys offline, significantly reducing the risk of hacks compared to online storage solutions. Multi-signature wallets further increase protection by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions, whereas single-signature wallets rely on one key, making them more vulnerable to single points of failure.
Key Management Policy
Key Management Policy enforces strict control over cryptographic keys, enhancing security in Multi-Signature Wallets by requiring multiple approvals to access funds, unlike Single-Signature Wallets that depend on a single key, increasing vulnerability to key compromise. Implementing Multi-Signature Wallets within a robust Key Management Policy reduces the risk of unauthorized transactions and improves accountability through distributed key custody.
Account Recovery Protocols
Multi-signature wallets enhance account recovery protocols by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions, reducing the risk of total access loss compared to single-signature wallets, which rely on a single private key that, if lost, makes recovery nearly impossible. Incorporating multi-signature setups with decentralized key management systems strengthens security and improves recovery options in digital asset management.
Trustless Custody
Trustless custody enhances security by enabling multi-signature wallets to require multiple private keys for transaction approval, reducing the risk compared to single-signature wallets that rely on a single private key.
Transaction Quorum
Transaction quorum in multi-signature wallets requires a predefined number of signatures to authorize transactions, enhancing security compared to single-signature wallets that rely on only one signature for approval.
Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets
Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets enhance security and convenience by generating multiple private keys from a single seed, enabling efficient management of Multi-Signature Wallets that require multiple approvals versus the simpler Single-Signature Wallets with one key control.
Compromised Key Resilience
Compromised Key Resilience in multi-signature wallets enhances security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access compared to single-signature wallets, which rely on a single private key. This distributed key control mitigates the impact of a single compromised key, making multi-signature wallets a more robust solution for secure cryptocurrency management.
Multi-Signature Wallet vs Single-Signature Wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com