Hash rate measures the speed at which a cryptocurrency network processes transactions by solving complex algorithms, reflecting the number of hashes computed per second. Hash power refers to the computational strength or capacity that miners collectively contribute to support and secure the blockchain. A higher hash rate or hash power indicates greater network security and mining efficiency against potential attacks.
Table of Comparison
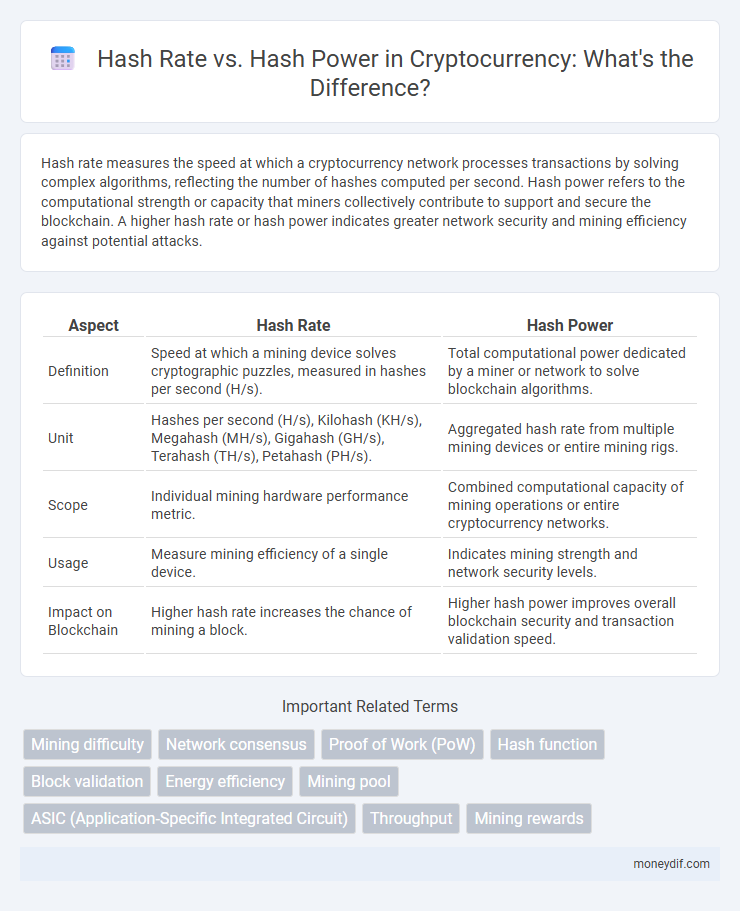
| Aspect | Hash Rate | Hash Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Speed at which a mining device solves cryptographic puzzles, measured in hashes per second (H/s). | Total computational power dedicated by a miner or network to solve blockchain algorithms. |
| Unit | Hashes per second (H/s), Kilohash (KH/s), Megahash (MH/s), Gigahash (GH/s), Terahash (TH/s), Petahash (PH/s). | Aggregated hash rate from multiple mining devices or entire mining rigs. |
| Scope | Individual mining hardware performance metric. | Combined computational capacity of mining operations or entire cryptocurrency networks. |
| Usage | Measure mining efficiency of a single device. | Indicates mining strength and network security levels. |
| Impact on Blockchain | Higher hash rate increases the chance of mining a block. | Higher hash power improves overall blockchain security and transaction validation speed. |
Understanding Hash Rate and Hash Power
Hash rate measures the number of hash computations a cryptocurrency network performs per second, indicating its processing speed and security level. Hash power refers to the computational capacity contributed by individual miners or mining pools to solve complex algorithms, directly impacting mining efficiency. Understanding the distinction between hash rate as a network metric and hash power as individual contribution is essential for evaluating mining performance and network robustness.
Key Differences Between Hash Rate and Hash Power
Hash rate measures the number of hash computations a device or network performs per second, reflecting speed and efficiency in verifying blockchain transactions. Hash power refers to the total computational capacity dedicated to mining cryptocurrencies, indicating the overall strength of a mining operation or network. Understanding the distinction aids in analyzing mining performance and network security in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
How Hash Rate Affects Blockchain Security
Hash rate, measuring the number of hashes computed per second, directly impacts blockchain security by determining the computational power protecting the network from attacks. A higher hash rate increases the difficulty for malicious actors to execute a 51% attack, ensuring transaction integrity and preventing double-spending. Consequently, blockchain networks with elevated hash rates maintain enhanced resilience against manipulation and unauthorized alterations.
The Role of Hash Power in Cryptocurrency Mining
Hash power represents the computational strength that miners use to solve complex cryptographic puzzles essential for validating transactions and securing the blockchain network. A higher hash power increases the likelihood of successfully mining new cryptocurrency blocks, directly impacting mining efficiency and profitability. The hash rate quantifies this power, measuring how many hashes a miner or network can compute per second, serving as a critical metric for assessing network security and mining competition.
Measuring Hash Rate vs Hash Power: Metrics Explained
Measuring hash rate involves quantifying the number of cryptographic calculations performed per second, typically expressed in hashes per second (H/s), kilohashes (KH/s), or terahashes (TH/s). Hash power refers to the computational capacity of a mining system or network, indicating its ability to solve complex algorithms and validate transactions within a blockchain. Understanding the distinction between hash rate as a raw performance metric and hash power as an aggregate capability is crucial for evaluating mining efficiency and network security in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Impact of Hash Rate and Hash Power on Network Decentralization
Hash rate measures the speed at which a cryptocurrency miner solves computational puzzles, directly influencing the security and efficiency of blockchain networks. Higher hash power, representing the total computational capacity within the network, promotes decentralization by distributing mining efforts across numerous participants, reducing risks of centralization. Concentration of hash rate in a few entities threatens network decentralization, increasing vulnerability to 51% attacks and undermining trust in blockchain integrity.
Hash Rate, Hash Power, and Mining Profitability
Hash rate represents the speed at which a cryptocurrency network processes transactions and solves complex algorithms, directly influencing mining efficiency and profitability. Hash power, often used interchangeably, specifically denotes the computational strength of mining hardware contributing to the network's overall hash rate. Higher hash rate and hash power levels increase the likelihood of successfully mining blocks, boosting mining rewards and enhancing profitability for miners in competitive environments.
Factors Influencing Hash Rate and Hash Power
Hash rate and hash power are critical metrics in cryptocurrency mining, reflecting the speed at which a miner can process transactions and solve complex cryptographic puzzles. Factors influencing hash rate and hash power include the hardware efficiency of mining rigs, such as ASICs or GPUs, the network difficulty level set by the blockchain protocol, and the overall mining pool's computational resources. Energy consumption and technological advancements in mining equipment also significantly impact the consistency and capacity of hash rate and hash power within a given network.
Hash Rate vs Hash Power: Implications for Investors
Hash rate measures the speed at which a cryptocurrency network processes transactions, expressed in hashes per second, while hash power refers to the total computational capacity contributing to mining efforts. Investors analyze hash rate to gauge network security and mining difficulty, which directly influence coin value stability and long-term profitability. Understanding the distinction between hash rate and hash power helps investors assess the mining ecosystem's health and make informed decisions about cryptocurrency investments.
Future Trends in Hash Rate and Hash Power
Future trends in hash rate and hash power indicate a significant increase driven by advancements in mining hardware and energy-efficient technologies. The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms in mining operations is expected to optimize hash power utilization, boosting overall network security and transaction speed. Decentralized mining pools and renewable energy adoption will further propel sustainable growth in global hash rate, enhancing cryptocurrency resilience and scalability.
Important Terms
Mining difficulty
Mining difficulty dynamically adjusts to maintain block time consistency by correlating with hash rate, where increased hash power requires higher difficulty for secure blockchain validation.
Network consensus
Network consensus reliability depends on hash rate as a measure of computational speed, while hash power represents the total computational capacity contributing to blockchain security.
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work (PoW) consensus relies on hash rate as the measure of computational speed, whereas hash power refers to the total combined processing capability available for mining.
Hash function
Hash rate measures the number of hash calculations performed per second by a mining device, while hash power refers to the overall computational capacity contributing to blockchain network security.
Block validation
Block validation efficiency depends on hash rate, which measures the computational speed, while hash power refers to the total mining capacity contributing to network security.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency in cryptocurrency mining is maximized by optimizing the hash rate-to-hash power ratio, ensuring higher computational output per unit of energy consumed.
Mining pool
Mining pools combine individual miners' hash power to collectively achieve a higher hash rate, increasing the probability of successfully mining cryptocurrency blocks.
ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit)
ASICs deliver significantly higher hash rates than general-purpose hardware by using optimized hash power tailored for specific cryptographic algorithms.
Throughput
Throughput measures the number of transactions processed per second, directly influenced by hash rate, which quantifies the computational speed contributing to overall hash power in blockchain networks.
Mining rewards
Mining rewards increase proportionally with higher hash rate as greater hash power improves the likelihood of successfully solving cryptographic puzzles on the blockchain.
Hash rate vs hash power Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com