Burning cryptocurrency reduces the total supply by permanently removing tokens from circulation, which can increase scarcity and potentially drive up value. Minting creates new tokens, expanding the supply and enabling network growth, often used in proof-of-stake systems to reward participants. The balance between burn and mint strategies plays a crucial role in maintaining a stable and sustainable cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Table of Comparison
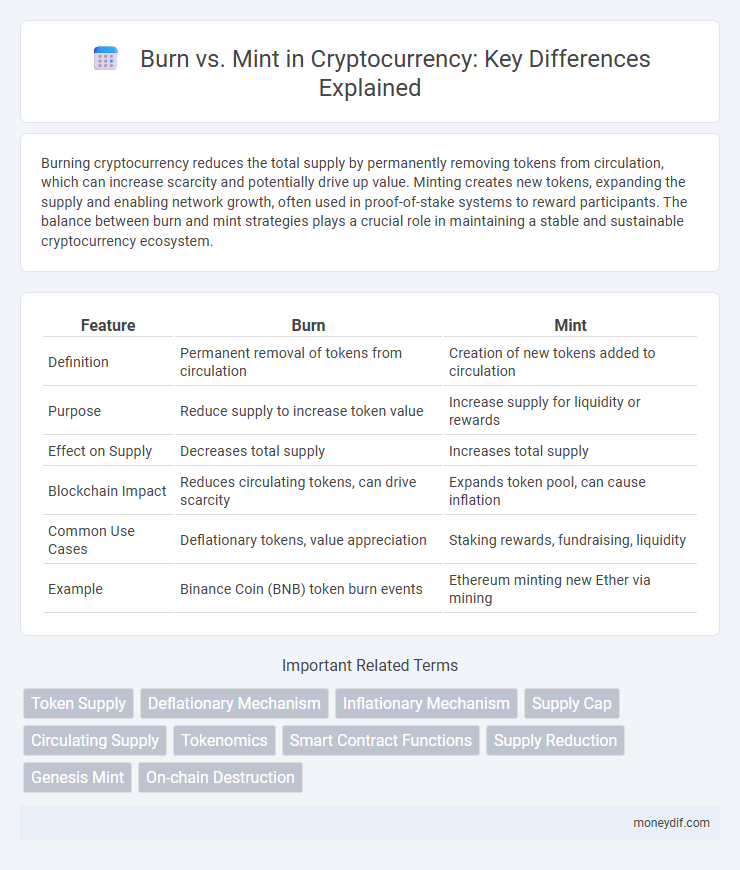
| Feature | Burn | Mint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent removal of tokens from circulation | Creation of new tokens added to circulation |
| Purpose | Reduce supply to increase token value | Increase supply for liquidity or rewards |
| Effect on Supply | Decreases total supply | Increases total supply |
| Blockchain Impact | Reduces circulating tokens, can drive scarcity | Expands token pool, can cause inflation |
| Common Use Cases | Deflationary tokens, value appreciation | Staking rewards, fundraising, liquidity |
| Example | Binance Coin (BNB) token burn events | Ethereum minting new Ether via mining |
Understanding the Concepts: What Are Token Burns and Mints?
Token burns reduce the total supply of a cryptocurrency by permanently removing tokens from circulation, often to increase scarcity and potentially boost value. Token mints refer to the creation of new tokens, expanding the total supply to reward participants or fund network activities. Balancing burns and mints impacts tokenomics, influencing asset inflation, deflation, and market perception.
The Purpose Behind Burning and Minting Cryptocurrencies
Burning cryptocurrencies reduces the total supply by permanently removing tokens from circulation, aiming to increase scarcity and potentially boost value. Minting creates new tokens, expanding the supply to reward participants, incentivize network security, or support ecosystem growth. These mechanisms balance token supply dynamics to maintain economic stability and drive project sustainability in the blockchain environment.
How Token Burns Impact Supply and Demand Dynamics
Token burns reduce the total supply by permanently removing tokens from circulation, creating scarcity that can increase demand and potentially drive up prices. Minting, on the other hand, increases supply by introducing new tokens, which can dilute value and reduce scarcity. The balance between burning and minting directly influences market dynamics, affecting token price stability and investor sentiment.
Minting: Creating New Tokens and Its Economic Implications
Minting in cryptocurrency refers to the process of creating new tokens, which increases the total supply available in the market. This mechanism can stimulate network growth and adoption by rewarding participants, such as miners or validators, for securing the blockchain. However, excessive minting may lead to inflation, reducing token value and impacting overall market dynamics.
Comparing Burn and Mint Mechanisms Across Popular Blockchains
Burn and mint mechanisms serve opposite functions in cryptocurrency supply management, with burning permanently removing tokens from circulation to reduce supply, while minting creates new tokens to increase supply. Ethereum employs burning through EIP-1559's base fee mechanism, effectively reducing ETH supply, whereas blockchains like Binance Smart Chain and Solana utilize minting to reward validators and increase token circulation. These opposing processes influence tokenomics differently, with burning promoting scarcity and potential value appreciation, and minting supporting network security and operational incentives.
Token Burns vs. Mints: Effects on Token Value and Price Volatility
Token burns reduce the circulating supply by permanently removing tokens from circulation, which can increase scarcity and potentially boost token value. Mints introduce new tokens into the market, increasing supply and often leading to price dilution and higher volatility. The balance between burns and mints is crucial for maintaining token stability and investor confidence in cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Key Examples: Notable Burn and Mint Events in Crypto History
Notable burn events include Binance Coin's quarterly token burns, reducing supply and increasing value, while Ethereum's EIP-1559 introduced a burn mechanism to destroy a portion of transaction fees, effectively decreasing ETH supply. Key mint events include Bitcoin's periodic halving, which controls new BTC issuance by reducing block rewards, and Ethereum's transition to Proof of Stake with the Beacon Chain, enabling controlled minting of new ETH tokens. These events significantly impact token economics, influencing scarcity, inflation, and overall market dynamics in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Regulatory Considerations for Token Burns and Minting
Regulatory considerations for token burns and minting center on compliance with securities laws and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. Token burns reduce circulating supply to potentially influence market value but must avoid manipulative practices that attract regulatory scrutiny. Minting new tokens requires transparent disclosure to ensure investor protection and prevent unregistered offerings under financial regulations.
How Burn and Mint Functions Affect Governance and Community
Burning cryptocurrency reduces the total supply, increasing scarcity and potentially boosting token value, which empowers holders by enhancing their voting power within decentralized governance systems. Minting creates new tokens, expanding the supply and diluting ownership, yet it can incentivize community participation and fund development initiatives through inflationary rewards. Both mechanisms dynamically influence governance decisions and community engagement by adjusting token distribution and economic incentives.
Future Trends in Token Supply Management: Burn vs. Mint
Future trends in token supply management emphasize a dynamic balance between burning and minting mechanisms to stabilize cryptocurrency value and incentivize user participation. Advanced algorithms and decentralized governance models enable adaptive token burn rates and minting schedules, optimizing scarcity and circulation in response to market demand. Innovations such as programmable supply adjustments and real-time analytics enhance transparency and efficiency in managing token inflation and deflation.
Important Terms
Token Supply
Token supply dynamics are influenced by the processes of burning and minting, where burning permanently reduces the number of tokens in circulation, enhancing scarcity, while minting generates new tokens, increasing total supply and potentially diluting value. Managing the balance between burn and mint activities is crucial for maintaining tokenomics stability, investor confidence, and long-term project sustainability.
Deflationary Mechanism
Deflationary mechanisms reduce token supply through burning, permanently removing tokens from circulation to increase scarcity and value, while minting creates new tokens that can offset deflation by expanding supply. Balancing burn and mint processes is crucial for maintaining tokenomics stability and preventing hyperinflation or excessive deflation in cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Inflationary Mechanism
The inflationary mechanism in blockchain ecosystems involves a balance between minting new tokens and burning existing ones to control the total supply and maintain token value stability. Minting increases supply to incentivize network participation, while burning reduces supply to counteract inflation and preserve purchasing power.
Supply Cap
A supply cap limits the total number of tokens that can exist, directly impacting the balance between minting new tokens and burning existing ones to control inflation and scarcity. By enforcing a hard cap on supply, project issuers can ensure that minting does not exceed a predefined maximum, while strategic token burns reduce circulating supply to increase token value.
Circulating Supply
Circulating supply represents the total number of tokens currently available and tradable in the market, directly impacted by burn and mint mechanisms. Token burns reduce circulating supply by permanently removing tokens, while minting increases supply by creating new tokens, influencing scarcity and market value.
Tokenomics
Tokenomics involves analyzing the mechanisms of token supply management, where burning tokens reduces the circulating supply to potentially increase value by creating scarcity, while minting tokens increases supply to support network growth or incentivize participation. Balancing burn and mint rates is crucial for maintaining token stability, preventing inflation or deflation, and ensuring long-term ecosystem sustainability.
Smart Contract Functions
Smart contract functions for burning tokens permanently remove them from circulation by reducing the total supply, enhancing scarcity and value. Mint functions create new tokens, increasing the total supply and enabling expansion or rewards within blockchain networks.
Supply Reduction
Supply reduction in cryptocurrency is achieved through burning tokens, permanently removing them from circulation to decrease total supply, while minting involves creating new tokens, increasing the supply. Strategic token burn mechanisms enhance scarcity and value, contrasting with minting processes that can dilute supply and affect price stability.
Genesis Mint
Genesis Mint involves creating new digital assets through a controlled minting process that often impacts the circulating supply and market dynamics. The burn mechanism reduces token supply by permanently removing tokens from circulation, balancing the inflation caused by minting and potentially increasing asset scarcity and value.
On-chain Destruction
On-chain destruction involves permanently removing tokens from circulation by sending them to an irrecoverable address, reducing supply and potentially increasing token value. Burn and mint operations represent opposing mechanisms where burning decreases token supply, enhancing scarcity, while minting creates new tokens, expanding circulation and impacting inflation dynamics.
Burn vs Mint Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com