SegWit (Segregated Witness) improves Bitcoin's scalability by separating transaction signatures from the main block data, reducing block size and enabling faster confirmations. The Lightning Network builds on SegWit's enhancements by facilitating off-chain, instant transactions through payment channels, significantly increasing transaction throughput and reducing fees. Together, SegWit and the Lightning Network address Bitcoin's performance limitations, making micropayments and high-frequency transactions more feasible.
Table of Comparison
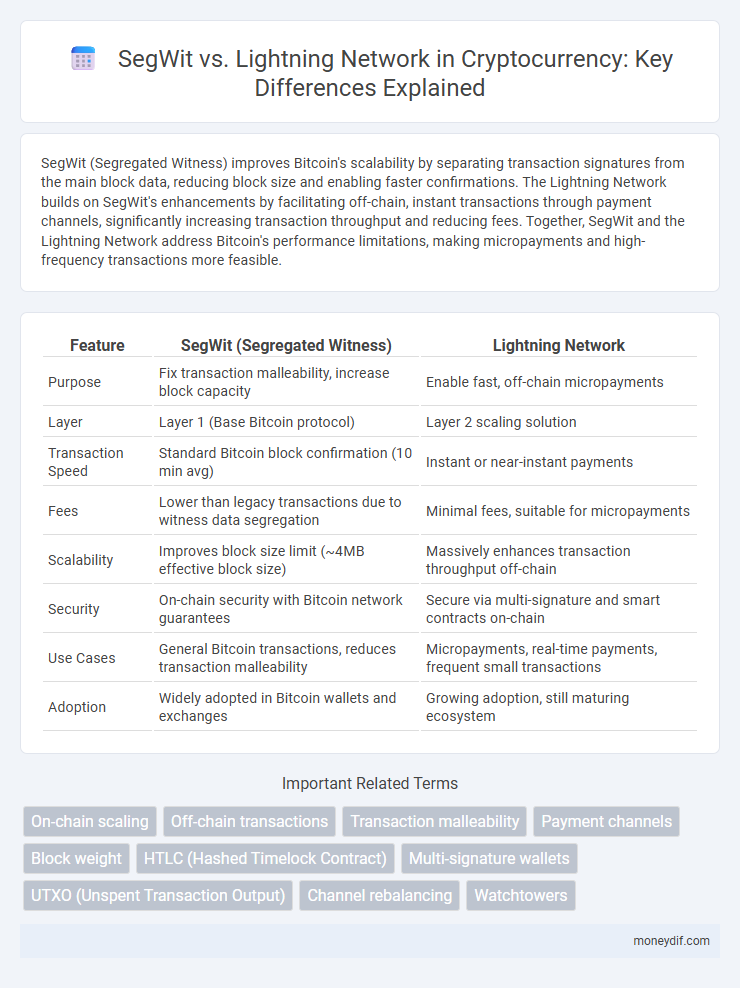
| Feature | SegWit (Segregated Witness) | Lightning Network |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Fix transaction malleability, increase block capacity | Enable fast, off-chain micropayments |
| Layer | Layer 1 (Base Bitcoin protocol) | Layer 2 scaling solution |
| Transaction Speed | Standard Bitcoin block confirmation (10 min avg) | Instant or near-instant payments |
| Fees | Lower than legacy transactions due to witness data segregation | Minimal fees, suitable for micropayments |
| Scalability | Improves block size limit (~4MB effective block size) | Massively enhances transaction throughput off-chain |
| Security | On-chain security with Bitcoin network guarantees | Secure via multi-signature and smart contracts on-chain |
| Use Cases | General Bitcoin transactions, reduces transaction malleability | Micropayments, real-time payments, frequent small transactions |
| Adoption | Widely adopted in Bitcoin wallets and exchanges | Growing adoption, still maturing ecosystem |
Understanding SegWit: Definition and Purpose
Segregated Witness (SegWit) is a protocol upgrade for Bitcoin that separates transaction signatures from the main blockchain, increasing block capacity and enhancing transaction malleability fixes. By removing signature data from transactions, SegWit boosts scalability and enables second-layer solutions like the Lightning Network. This foundational change improves transaction speed and reduces fees, facilitating more efficient cryptocurrency payments.
Lightning Network Explained: How It Works
The Lightning Network is a second-layer solution built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain to enable faster, low-cost transactions by creating off-chain payment channels between users. It operates by opening a multi-signature wallet where participants can conduct multiple instant transactions without broadcasting each to the main blockchain, only settling the final balance on-chain. This mechanism significantly reduces congestion, lowers transaction fees, and scales Bitcoin for everyday microtransactions and instant payments.
Key Differences Between SegWit and Lightning Network
SegWit (Segregated Witness) primarily addresses Bitcoin's scalability by separating transaction signatures from transaction data, enabling larger block sizes without increasing block weight. The Lightning Network builds on this by enabling off-chain, instant micropayments through payment channels, significantly reducing transaction fees and times. While SegWit enhances on-chain capacity and malleability fixes, the Lightning Network facilitates scalable, low-cost transactions off-chain, complementing SegWit's improvements.
SegWit’s Impact on Bitcoin Scalability
SegWit (Segregated Witness) significantly enhances Bitcoin scalability by increasing block size limits and reducing transaction malleability, enabling more efficient data storage. This protocol upgrade allows more transactions per block, improving throughput and lowering fees compared to pre-SegWit blocks. While Lightning Network facilitates off-chain microtransactions for scalability, SegWit remains essential for optimizing on-chain transaction capacity and security.
Lightning Network’s Role in Instant Payments
The Lightning Network significantly enhances Bitcoin's scalability by enabling instant, low-cost micropayments through off-chain transactions. By creating a network of payment channels, it reduces blockchain congestion and transaction fees, facilitating near-instant settlement times. This layer-two solution addresses Bitcoin's inherent latency, making it viable for everyday retail and peer-to-peer payments.
Security Implications: SegWit vs Lightning Network
SegWit enhances Bitcoin security by fixing transaction malleability, enabling more reliable verification and reducing risks of double-spending attacks on the main chain. The Lightning Network introduces off-chain payment channels that offer faster transactions but shift some security trust to multi-signature contracts and network routing, creating potential vulnerabilities like channel breaches or routing attacks. SegWit's on-chain improvements complement Lightning's off-chain scalability, yet users must weigh the trade-offs between on-chain security guarantees and off-chain operational risks inherent in Lightning Network channels.
Transaction Fees: Comparing Cost Efficiency
SegWit reduces transaction fees by optimizing block space and decreasing the size of individual transactions, directly lowering costs on the Bitcoin network. Lightning Network further enhances cost efficiency by enabling off-chain, instant microtransactions with minimal fees, ideal for frequent small payments. Comparing both, SegWit provides immediate fee reductions on-chain, while Lightning Network offers scalability and near-zero fees for continuous transactions.
Adoption and Integration in the Crypto Ecosystem
SegWit adoption has accelerated transaction throughput and reduced fees by enabling block size optimization on the Bitcoin blockchain, becoming a foundational upgrade widely integrated into wallets and exchanges since its activation in 2017. The Lightning Network, designed for off-chain micropayments, complements SegWit by facilitating instant, low-cost transactions, with growing integration evident through an expanding network of nodes and merchant adoption. Both technologies play critical roles in scaling Bitcoin, with SegWit serving as a prerequisite for Lightning Network channels, driving enhanced liquidity and interoperability within the crypto ecosystem.
Limitations and Challenges of SegWit and Lightning
SegWit faces limitations such as partial adoption hindering network scalability and compatibility issues with legacy wallets and exchanges. The Lightning Network struggles with challenges like liquidity management, routing efficiency, and the complexity of maintaining open payment channels. Both technologies require continuous development to overcome security concerns and wider user acceptance for mainstream cryptocurrency transactions.
The Future of Bitcoin: SegWit and Lightning Network Synergy
SegWit, by optimizing Bitcoin's transaction structure, reduces block size constraints and lowers fees, paving the way for enhanced scalability. The Lightning Network leverages this foundation to enable instant, off-chain micropayments, significantly boosting transaction speed and reducing network congestion. Together, their synergy promises a more efficient, scalable Bitcoin ecosystem capable of supporting mass adoption and complex financial applications.
Important Terms
On-chain scaling
On-chain scaling through SegWit improves block capacity by reducing signature data size, while the Lightning Network enhances scalability by enabling off-chain, instant, and low-fee micropayments.
Off-chain transactions
Off-chain transactions reduce blockchain congestion and enhance scalability by recording transactions outside the main chain, with SegWit enabling efficient off-chain solutions through transaction malleability fixes and increased block capacity. The Lightning Network builds upon SegWit by creating a decentralized network of payment channels that support instant, low-fee microtransactions without waiting for on-chain confirmations.
Transaction malleability
SegWit reduces transaction malleability by separating signature data from transaction IDs, enabling the Lightning Network to securely and efficiently implement off-chain payment channels.
Payment channels
Payment channels enable off-chain Bitcoin transactions, where SegWit reduces transaction malleability to improve channel security, while the Lightning Network leverages these channels for instant, scalable micropayments.
Block weight
Block weight, defined by the SegWit protocol, increases the maximum block capacity to 4 million weight units, facilitating more transactions within a single block by separating signature data from transaction data. The Lightning Network operates off-chain, minimizing on-chain block weight usage by enabling instant, low-fee micropayments through payment channels, thereby reducing overall blockchain congestion and improving transaction scalability.
HTLC (Hashed Timelock Contract)
HTLCs enable secure, trustless payment channels in the Lightning Network by leveraging SegWit's transaction malleability fixes to facilitate instant, cross-chain atomic swaps.
Multi-signature wallets
Multi-signature wallets enhance security in SegWit transactions by requiring multiple signatures to authorize spending, while Lightning Network utilizes multi-signature addresses to enable fast, off-chain microtransactions and reduce on-chain congestion.
UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output)
SegWit optimizes UTXO management by reducing transaction size and enabling scalability, while the Lightning Network leverages off-chain UTXOs for faster, low-fee micropayments.
Channel rebalancing
Channel rebalancing enhances Lightning Network efficiency by optimizing SegWit-enabled payment channels to reduce on-chain transaction costs and improve liquidity distribution.
Watchtowers
Watchtowers enhance Lightning Network security by monitoring off-chain transactions and enforcing penalties for fraudulent SegWit channel closures.
SegWit vs Lightning Network Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com