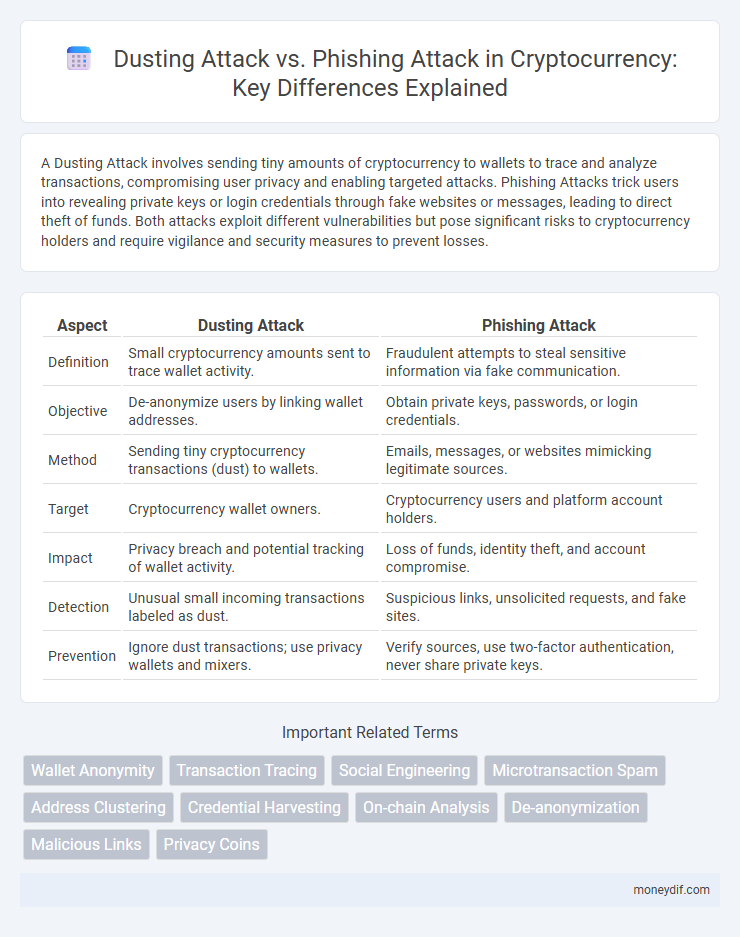
A Dusting Attack involves sending tiny amounts of cryptocurrency to wallets to trace and analyze transactions, compromising user privacy and enabling targeted attacks. Phishing Attacks trick users into revealing private keys or login credentials through fake websites or messages, leading to direct theft of funds. Both attacks exploit different vulnerabilities but pose significant risks to cryptocurrency holders and require vigilance and security measures to prevent losses.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dusting Attack | Phishing Attack |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small cryptocurrency amounts sent to trace wallet activity. | Fraudulent attempts to steal sensitive information via fake communication. |
| Objective | De-anonymize users by linking wallet addresses. | Obtain private keys, passwords, or login credentials. |
| Method | Sending tiny cryptocurrency transactions (dust) to wallets. | Emails, messages, or websites mimicking legitimate sources. |
| Target | Cryptocurrency wallet owners. | Cryptocurrency users and platform account holders. |
| Impact | Privacy breach and potential tracking of wallet activity. | Loss of funds, identity theft, and account compromise. |
| Detection | Unusual small incoming transactions labeled as dust. | Suspicious links, unsolicited requests, and fake sites. |
| Prevention | Ignore dust transactions; use privacy wallets and mixers. | Verify sources, use two-factor authentication, never share private keys. |
Understanding Dusting Attacks in Cryptocurrency
Dusting attacks in cryptocurrency involve sending tiny amounts of crypto to numerous wallets to trace and de-anonymize users by analyzing transaction patterns. These attacks exploit the blockchain's transparency, enabling attackers to link wallet addresses and potentially identify individuals behind pseudonymous accounts. Protecting against dusting requires vigilance in managing wallet interactions and utilizing privacy-focused tools or wallets that prevent address clustering.
Exploring Phishing Attacks in Crypto Transactions
Phishing attacks in cryptocurrency transactions exploit social engineering tactics to trick users into revealing their private keys or login credentials, often through fake websites or fraudulent emails. These attacks target vulnerabilities in user behavior rather than technical system flaws, resulting in unauthorized access to wallets and loss of funds. Understanding the mechanics and prevention of phishing is crucial for enhancing security measures in digital asset management.
Key Differences Between Dusting and Phishing Attacks
Dusting attacks involve sending tiny amounts of cryptocurrency to wallets to analyze transaction patterns and deanonymize users, while phishing attacks trick victims into revealing private keys or login credentials through fraudulent websites or messages. Dusting exploits blockchain transparency and data analysis, whereas phishing relies on social engineering and deception techniques. The primary distinction lies in dusting's indirect surveillance approach versus phishing's direct theft of sensitive information.
How Dusting Attacks Compromise Wallet Privacy
Dusting attacks compromise wallet privacy by sending tiny amounts of cryptocurrency, called "dust," to multiple wallet addresses to trace and link these addresses together through blockchain analysis. Attackers use this technique to de-anonymize users, revealing transaction patterns and wallet associations, which can lead to targeted phishing attacks or identity exposure. Unlike phishing attacks that deceive users into revealing private keys or login credentials, dusting attacks silently gather data, undermining privacy without immediate loss of funds.
Social Engineering Tactics in Crypto Phishing
Dusting attacks subtly trace cryptocurrency transactions by sending tiny amounts of coins to wallets, exposing ownership patterns through blockchain analysis. Phishing attacks exploit social engineering tactics, deceiving individuals into revealing private keys or login credentials via fraudulent emails, fake websites, or deceptive messages. These attacks leverage trust manipulation and urgent prompts to compromise digital wallets and cryptocurrency exchanges.
Identifying Signs of Dusting Attacks on Your Wallet
Dusting attacks involve sending tiny amounts of cryptocurrency to numerous wallets to trace and deanonymize users through transaction analysis, whereas phishing attacks trick victims into revealing private keys or credentials via fake websites or messages. Signs of a dusting attack on your wallet include unexpected small deposits from unknown addresses, unusual transaction patterns, and increased unsolicited network activity linked to your wallet. Monitoring transaction history and enabling alerts for small incoming amounts can help identify and mitigate dusting threats early.
Common Phishing Methods Targeting Crypto Users
Common phishing methods targeting cryptocurrency users include fake wallet apps, fraudulent exchange websites, and deceptive email campaigns designed to steal private keys and login credentials. Attackers often impersonate legitimate platforms or services to trick users into providing sensitive information or authorizing unauthorized transactions. Awareness of these tactics is crucial for securing digital assets against identity theft and financial loss.
Preventive Measures Against Dusting and Phishing
To prevent dusting attacks, users should regularly monitor wallet activity, avoid sharing public keys unnecessarily, and use wallets with built-in dust filtering features. Phishing attack prevention includes employing two-factor authentication, verifying URLs before entering sensitive information, and using hardware wallets to secure private keys offline. Maintaining updated security software and awareness of suspicious communication further reduces the risk of falling victim to both attacks.
Real-World Examples of Dusting vs Phishing Attacks
Dusting attacks involve sending tiny amounts of cryptocurrency to numerous wallets to trace activity and de-anonymize users, exemplified by the 2020 dusting campaign targeting Bitcoin holders. Phishing attacks exploit social engineering to steal credentials or private keys, as seen in the 2022 MetaMask phishing scam where attackers impersonated wallet login pages. These real-world cases underscore the importance of vigilant wallet monitoring and using hardware wallets for enhanced security.
Enhancing Security: Protecting Crypto Assets from Attacks
Dusting attacks exploit tiny cryptocurrency transactions to trace and deanonymize wallet users, while phishing attacks use deceptive communications to steal private keys and login credentials. Strengthening security involves implementing multi-factor authentication, utilizing hardware wallets, and regularly monitoring wallet activity for suspicious transactions. Educating users about recognizing phishing attempts and avoiding unsolicited links or downloads significantly reduces the risk of compromising crypto assets.
Important Terms
Wallet Anonymity
Wallet anonymity can be compromised by dusting attacks, where tiny amounts of cryptocurrency are sent to multiple wallets to trace user identities through transaction patterns, while phishing attacks trick users into revealing private keys or seed phrases, directly exposing wallet access. Protecting against both threats requires cautious handling of unknown transactions and robust security practices, including avoiding suspicious links and maintaining private information confidentiality.
Transaction Tracing
Transaction tracing leverages blockchain analysis to identify patterns indicative of dusting attacks, where small amounts of cryptocurrency are sent to wallets to track user activity, contrasting with phishing attacks that employ deceptive communication to steal credentials without direct transaction linkage. By monitoring transaction flows and wallet interactions, tracing tools expose dusting vectors to prevent privacy breaches, while detecting phishing relies more on behavioral analysis and network security measures.
Social Engineering
Social engineering exploits human psychology to manipulate individuals into revealing confidential information, with dusting attacks using small cryptocurrency transfers to trace wallet activity and identify potential targets, while phishing attacks deploy deceptive emails or websites to directly steal login credentials or personal data. Dusting attacks focus on blockchain privacy breaches through transaction analysis, whereas phishing attacks target user trust through fraudulent communication channels.
Microtransaction Spam
Microtransaction spam involves sending numerous minimal-value transactions to overwhelm a target's wallet, often linked with dusting attacks that trace users by mixing small amounts of cryptocurrency; phishing attacks instead focus on deceitfully obtaining private keys or login credentials to directly steal assets. Understanding the distinction is crucial for enhancing blockchain security against inconspicuous tracking versus explicit credential theft.
Address Clustering
Address clustering enhances cryptocurrency security by grouping related wallet addresses to detect suspicious patterns, crucial for identifying dusting attacks that distribute tiny amounts of coins to trace user transactions. By contrast, phishing attacks exploit social engineering to steal private keys or credentials, making address clustering less effective in preventing these direct fraud attempts.
Credential Harvesting
Credential harvesting tactics involve collecting user login information through methods like dusting attacks and phishing attacks, with dusting attacks targeting a wide range of low-value accounts using subtle login attempts, while phishing attacks rely on deceptive emails or websites to trick users into providing credentials. Both techniques aim to exploit vulnerabilities in user authentication, but dusting attacks often focus on automated credential stuffing across many accounts, whereas phishing attacks exploit social engineering to deceive individual users.
On-chain Analysis
On-chain analysis identifies patterns in blockchain transactions to detect suspicious activities such as dusting attacks, where tiny amounts of cryptocurrency are sent to trace and deanonymize wallets. Unlike phishing attacks that rely on social engineering to steal private keys or credentials, dusting attacks exploit transaction data on-chain to gather intelligence without direct user interaction.
De-anonymization
De-anonymization techniques exploit dusting attacks by sending tiny amounts of cryptocurrencies to many wallets, enabling attackers to trace transaction patterns and link identities across addresses. Phishing attacks de-anonymize users by deceiving them into revealing private keys or login credentials, allowing direct access to their wallets and personal data.
Malicious Links
Malicious links exploited in dusting attacks subtly distribute tiny amounts of cryptocurrency to multiple wallets to trace user transaction patterns, whereas phishing attack links aim to deceive users into revealing sensitive information or credentials. Both leverage deceptive URLs, but dusting attacks focus on blockchain analysis while phishing targets direct data theft.
Privacy Coins
Privacy coins like Monero and Zcash use advanced cryptographic techniques to protect user identities and transaction data, making dusting attacks--which involve spreading tiny amounts of cryptocurrency to trace wallet activity--less effective compared to transparent blockchains. Phishing attacks remain a significant threat across all cryptocurrencies as they exploit user trust and credentials rather than blockchain transparency, requiring robust user education and security measures beyond the inherent privacy features of these coins.
Dusting Attack vs Phishing Attack Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com