Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing transaction fees. Cross-chain bridges facilitate asset transfers between separate blockchain networks by locking tokens on one chain and minting equivalent tokens on another, increasing interoperability but introducing smart contract risks. Both technologies play crucial roles in expanding decentralized finance capabilities while balancing security and user experience.
Table of Comparison
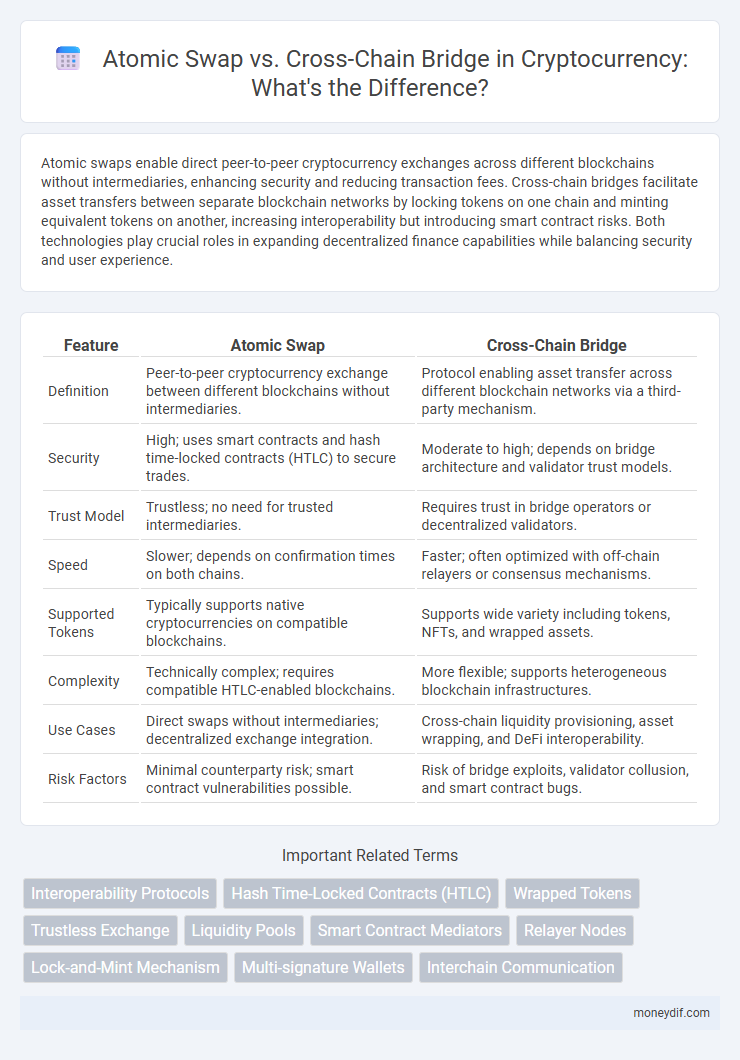
| Feature | Atomic Swap | Cross-Chain Bridge |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchange between different blockchains without intermediaries. | Protocol enabling asset transfer across different blockchain networks via a third-party mechanism. |
| Security | High; uses smart contracts and hash time-locked contracts (HTLC) to secure trades. | Moderate to high; depends on bridge architecture and validator trust models. |
| Trust Model | Trustless; no need for trusted intermediaries. | Requires trust in bridge operators or decentralized validators. |
| Speed | Slower; depends on confirmation times on both chains. | Faster; often optimized with off-chain relayers or consensus mechanisms. |
| Supported Tokens | Typically supports native cryptocurrencies on compatible blockchains. | Supports wide variety including tokens, NFTs, and wrapped assets. |
| Complexity | Technically complex; requires compatible HTLC-enabled blockchains. | More flexible; supports heterogeneous blockchain infrastructures. |
| Use Cases | Direct swaps without intermediaries; decentralized exchange integration. | Cross-chain liquidity provisioning, asset wrapping, and DeFi interoperability. |
| Risk Factors | Minimal counterparty risk; smart contract vulnerabilities possible. | Risk of bridge exploits, validator collusion, and smart contract bugs. |
Introduction to Atomic Swaps and Cross-Chain Bridges
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, relying on smart contracts to ensure secure, trustless trades. Cross-chain bridges facilitate asset transfers between distinct blockchain networks by locking tokens on one chain and minting equivalent tokens on another, enhancing interoperability with some reliance on bridge operators. Both technologies address blockchain fragmentation but differ in decentralization, security models, and transaction speed.
How Atomic Swaps Work: A Technical Overview
Atomic swaps enable trustless peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges by utilizing hashed time-locked contracts (HTLCs) that ensure either both parties complete the trade or the transaction is automatically reversed. A cryptographic hash locks the tokens on both blockchains, requiring the revelation of a secret key to unlock the funds, preventing double spending or fraud. This decentralized mechanism eliminates the need for third-party intermediaries while maintaining security and atomicity across incompatible blockchain networks.
Understanding Cross-Chain Bridges: Mechanisms and Architecture
Cross-chain bridges enable interoperability by connecting distinct blockchain networks, allowing seamless asset transfers and data exchange while maintaining security through mechanisms like multi-signature schemes and decentralized validators. Their architecture typically involves smart contracts, relayers, and consensus protocols that validate and verify transactions across chains, ensuring trustless communication. Atomic swaps differ by facilitating direct peer-to-peer token exchanges without intermediaries, relying on hashed time-locked contracts (HTLCs) that enforce conditional transfers between chains.
Security Comparison: Atomic Swap vs Cross-Chain Bridge
Atomic swaps offer superior security compared to cross-chain bridges by enabling direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without relying on intermediaries, minimizing the risk of hacks and custodial failures. Cross-chain bridges, while facilitating interoperability between different blockchain networks, are more vulnerable to security breaches due to centralized validators or smart contract exploits, as evidenced by multiple bridge-related hacks resulting in significant financial losses. The trustless nature and on-chain execution of atomic swaps make them a more secure option for cross-chain asset exchanges, reducing attack surfaces inherent in bridge architectures.
Speed and Efficiency: Transaction Times Explored
Atomic swaps offer faster transaction times by enabling direct peer-to-peer exchanges without intermediaries, significantly reducing delays. Cross-chain bridges often incur longer processing times due to the need for intermediary verification and security protocols across different blockchains. Efficiency in atomic swaps is enhanced by eliminating reliance on third-party validators, while bridges provide broader compatibility at the expense of speed.
Decentralization Levels: Trustless vs Trusted Solutions
Atomic swaps enable fully trustless cryptocurrency exchanges by executing peer-to-peer trades directly on the blockchain using smart contracts, eliminating intermediaries and reducing counterparty risk. Cross-chain bridges often rely on trusted intermediaries or validators to facilitate asset transfers between different blockchains, introducing varying degrees of centralization and potential vulnerabilities. The higher decentralization level in atomic swaps enhances security and trustlessness, while cross-chain bridges offer greater scalability and usability at the cost of increased trust dependencies.
Supported Assets: Flexibility Across Networks
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer exchanges of cryptocurrencies without intermediaries, supporting assets primarily on blockchains with native atomic swap functionality like Bitcoin and Litecoin. Cross-chain bridges offer broader flexibility by connecting multiple blockchain networks, allowing diverse asset transfers including tokens from Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and others. The choice depends on whether users prioritize decentralized, trustless trades or extensive asset compatibility across varied blockchain ecosystems.
Fees and Costs: Comparing Transaction Expenses
Atomic swaps typically incur lower fees as they execute directly between users on-chain without intermediaries, reducing transaction expenses. Cross-chain bridges often involve higher costs due to multiple transactions, smart contract interactions, and potential liquidity provider fees. Choosing between the two depends on balancing fee efficiency with interoperability and speed requirements.
Use Cases: When to Use Atomic Swaps or Cross-Chain Bridges
Atomic swaps are ideal for peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trades without intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing transaction fees. Cross-chain bridges enable seamless asset transfers across different blockchain networks, making them suitable for liquidity sharing and DeFi applications. Use atomic swaps for direct, trustless exchanges and cross-chain bridges for complex interoperability and multi-chain ecosystem integration.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Interoperability Solutions
Atomic swaps and cross-chain bridges are poised to transform cryptocurrency interoperability by enabling seamless asset transfers across diverse blockchain ecosystems. Future developments emphasize enhancing security protocols, reducing transaction costs, and improving speed to foster broader adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Innovations such as layer-2 scaling solutions and decentralized governance models will drive the evolution of these technologies, promoting trustless, efficient, and scalable cross-chain interactions.
Important Terms
Interoperability Protocols
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, while cross-chain bridges facilitate asset transfers between distinct blockchain networks by connecting them through interoperable protocols.
Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLC)
Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLC) enable trustless atomic swaps by ensuring secure, conditional transfers across blockchains without relying on centralized cross-chain bridges, minimizing counterparty risk and enhancing interoperability.
Wrapped Tokens
Wrapped tokens enable seamless value transfer through atomic swaps, offering trustless, direct asset exchanges across blockchains, while cross-chain bridges facilitate broader interoperability by locking and minting tokens but may introduce centralized risks.
Trustless Exchange
Trustless exchanges utilize atomic swaps to enable secure, peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trades without intermediaries, contrasting with cross-chain bridges that rely on intermediaries to facilitate asset transfers between different blockchains.
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools enable seamless asset exchange by providing decentralized funds for atomic swaps, whereas cross-chain bridges rely on trust-minimized protocols to transfer assets across different blockchains.
Smart Contract Mediators
Smart Contract Mediators facilitate trustless asset exchanges by enabling atomic swaps with on-chain verification, offering enhanced security compared to cross-chain bridges that rely on external validators.
Relayer Nodes
Relayer nodes facilitate secure and efficient communication in atomic swaps by validating and transmitting transaction data without intermediaries, while cross-chain bridges rely on relayer nodes to enable asset transfers between different blockchains through trusted or decentralized mechanisms.
Lock-and-Mint Mechanism
The Lock-and-Mint mechanism securely enables token transfers by locking assets on the source chain and minting equivalent tokens on the destination chain, offering a trust-minimized alternative to atomic swaps and enhancing interoperability compared to traditional cross-chain bridges.
Multi-signature Wallets
Multi-signature wallets enhance security for atomic swaps by requiring multiple approvals for cross-chain transactions, contrasting with cross-chain bridges that rely on centralized validators to facilitate asset transfers.
Interchain Communication
Interchain communication enables seamless atomic swaps and secure cross-chain bridges, facilitating trustless asset exchanges across diverse blockchain networks.
Atomic swap vs cross-chain bridge Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com