Token burn decreases the total supply of a cryptocurrency by permanently removing tokens from circulation, which can increase scarcity and potentially drive up value. Token minting creates new tokens, expanding the supply and often used to incentivize network participation or reward holders. Balancing token burn and minting is crucial for maintaining a stable and healthy token economy.
Table of Comparison
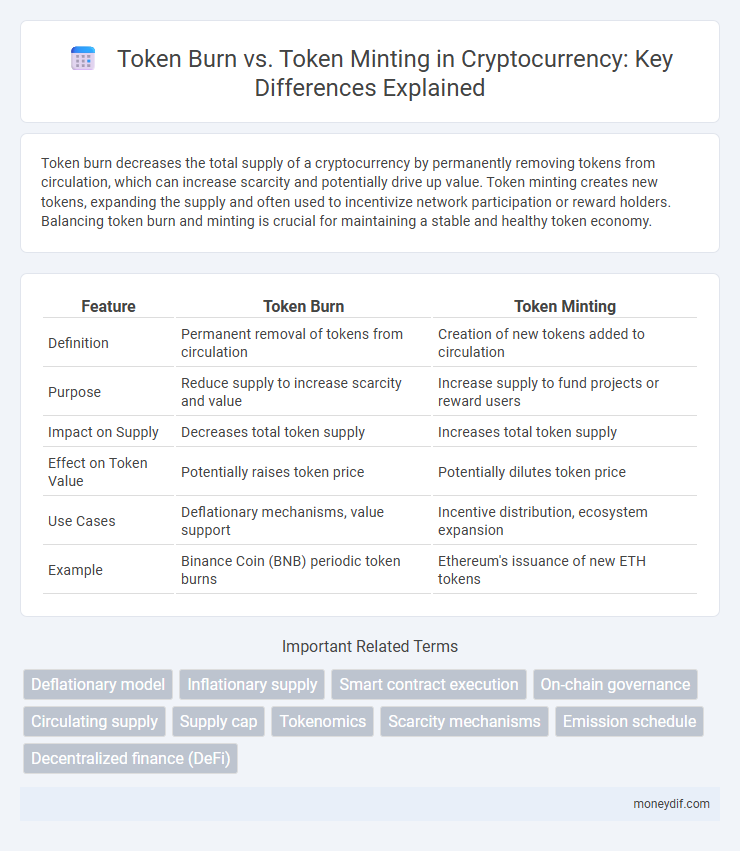
| Feature | Token Burn | Token Minting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent removal of tokens from circulation | Creation of new tokens added to circulation |
| Purpose | Reduce supply to increase scarcity and value | Increase supply to fund projects or reward users |
| Impact on Supply | Decreases total token supply | Increases total token supply |
| Effect on Token Value | Potentially raises token price | Potentially dilutes token price |
| Use Cases | Deflationary mechanisms, value support | Incentive distribution, ecosystem expansion |
| Example | Binance Coin (BNB) periodic token burns | Ethereum's issuance of new ETH tokens |
Understanding Tokenomics: Burn vs Mint
Token burn reduces the total supply of a cryptocurrency by permanently removing tokens from circulation, enhancing scarcity and potentially increasing value. Token minting creates new tokens, expanding supply and often used for rewarding users or funding development. Understanding the balance between burn and mint mechanisms is essential for analyzing a token's inflation, deflation, and overall economic model.
What Is Token Burning in Cryptocurrency?
Token burning in cryptocurrency refers to the process of permanently removing a specific number of tokens from circulation, reducing the total supply and potentially increasing the token's value. This mechanism is often executed by sending tokens to an inaccessible wallet address, known as a burn address, where they cannot be retrieved or spent. Token burning contrasts with token minting, which involves creating new tokens and adding them to the circulating supply, often leading to inflationary effects.
The Mechanics of Minting Tokens
Token minting involves creating new cryptocurrency tokens and adding them to the circulating supply, often governed by smart contracts on blockchain platforms like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. This process increases token supply, affecting market liquidity and potentially diluting existing token value if not managed properly. Minting is typically executed to reward network participants, fund projects, or expand ecosystem functionality while adhering to predefined protocol rules.
Supply Control: Impact of Burning and Minting
Token burn reduces the circulating supply by permanently removing tokens, creating scarcity that can increase value and stabilize the market. Token minting increases supply, often to fund development or reward participants, which can dilute token value if overused. Effective supply control balances token burning and minting to maintain price stability and incentivize ecosystem growth.
Deflationary Effects of Token Burn
Token burn reduces the total supply of a cryptocurrency by permanently removing tokens from circulation, creating scarcity that can increase token value. This deflationary mechanism contrasts with token minting, which increases supply and can dilute value. Blockchain projects use token burns to incentivize holding and stabilize the token economy by managing inflation effectively.
Inflationary Dynamics of Token Minting
Token minting increases the total supply of a cryptocurrency, leading to inflationary pressure that can reduce the token's value if demand does not keep pace. Inflationary dynamics caused by minting dilute existing token holdings and may impact investor confidence negatively. Effective supply management requires balancing token minting rates with market demand to maintain price stability.
Use Cases for Token Burning
Token burning is commonly used in cryptocurrency networks to reduce the total supply of tokens, thereby increasing scarcity and potentially boosting token value. Use cases include deflationary mechanisms in DeFi projects, reducing circulating supply after token sales, and as a method to reward holders by increasing the relative token ownership percentage. Burning tokens can also help maintain network security and integrity by removing tokens from the ecosystem that were obtained through hacks or fraudulent activities.
Real-World Applications of Token Minting
Token minting plays a critical role in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms by enabling the creation of new tokens to represent real-world assets such as commodities, real estate, or stocks, facilitating seamless digital ownership and trading. In supply chain management, token minting allows companies to generate verifiable digital tokens that track the provenance and authenticity of goods, enhancing transparency and trust. Moreover, gaming and metaverse ecosystems rely on token minting to create in-game assets and collectibles that users can own, trade, or monetize, driving user engagement and new economic models.
Token Burn and Mint Strategies in Major Projects
Token burn and mint strategies play crucial roles in managing supply dynamics in major cryptocurrency projects, influencing scarcity and value. Token burn involves permanently removing tokens from circulation, as seen in Binance Coin (BNB), to reduce supply and potentially increase price. Conversely, token minting, utilized in projects like Ethereum with its EIP-1559 mechanism, creates new tokens to incentivize network security and operations, balancing inflation and utility.
Evaluating Token Burn vs Minting for Investors
Token burn reduces circulating supply by permanently removing tokens, potentially increasing scarcity and value, which can benefit investors seeking price appreciation. Token minting increases supply by creating new tokens, possibly diluting value but supporting network growth and liquidity. Investors must evaluate burn and minting events based on their impact on tokenomics, market demand, and long-term project sustainability.
Important Terms
Deflationary model
A deflationary model reduces the total supply of tokens primarily through token burn mechanisms, where tokens are permanently removed from circulation to increase scarcity and value. This contrasts with token minting, which increases supply and can dilute value, making token burn strategies essential for sustaining token price appreciation in deflationary ecosystems.
Inflationary supply
Inflationary supply occurs when new tokens are minted, increasing the total supply and potentially diluting existing token value. Token burn reduces supply by permanently removing tokens, counteracting inflationary effects and helping to stabilize or increase the token's market value.
Smart contract execution
Smart contract execution governs token burn and token minting processes by enforcing predefined rules that either reduce the total token supply through burning or increase it by minting new tokens, directly impacting the token's scarcity and market value. These automated functions ensure transparency and security, preventing unauthorized token creation or destruction while maintaining blockchain integrity.
On-chain governance
On-chain governance directly influences token supply dynamics through mechanisms like token burn and token minting, where token holders vote to remove or create tokens, affecting scarcity and value. This decentralized decision-making process ensures transparent adjustments in tokenomics, balancing inflationary and deflationary pressures within the blockchain ecosystem.
Circulating supply
Circulating supply reflects the total number of tokens currently available in the market, directly influenced by token burn events that permanently remove tokens, reducing supply, and token minting processes that create new tokens, increasing supply. Monitoring these mechanisms is crucial for understanding token scarcity, inflation, and overall market dynamics in blockchain ecosystems.
Supply cap
The supply cap limits the maximum number of tokens that can exist, making token burn an effective mechanism to reduce circulating supply and potentially increase token value. Token minting, constrained by the supply cap, introduces new tokens into circulation but must be balanced with burns to maintain scarcity and control inflation.
Tokenomics
Token burn reduces token supply by permanently removing tokens from circulation, increasing scarcity and potentially boosting token value. Token minting creates new tokens, expanding supply and diluting existing token value, which impacts inflation and overall tokenomics balance.
Scarcity mechanisms
Scarcity mechanisms in blockchain ecosystems regulate token supply through token burn, which permanently removes tokens to create supply scarcity, enhancing value by reducing circulation. Conversely, token minting increases supply by generating new tokens, often diluting scarcity and potentially impacting token valuation and inflation dynamics.
Emission schedule
An emission schedule outlines the timing and quantity of token minting, controlling supply inflation by gradually releasing new tokens into circulation. Token burn mechanisms counterbalance this by permanently removing tokens from supply, reducing overall circulation and helping maintain token scarcity and value.
Decentralized finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems manage token supply dynamics through mechanisms like token burn and token minting to influence scarcity and inflation rates. Token burn reduces circulating supply by permanently removing tokens, enhancing value scarcity, whereas token minting increases supply, often to incentivize liquidity or governance participation.
token burn vs token minting Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com