A public key in cryptocurrency is a cryptographic code that allows users to receive funds and can be shared openly without compromising security. In contrast, a private key is a secret code known only to the owner, enabling them to access and control their cryptocurrency assets securely. Protecting the private key is crucial because losing it means losing access to the associated digital wallet and funds permanently.
Table of Comparison
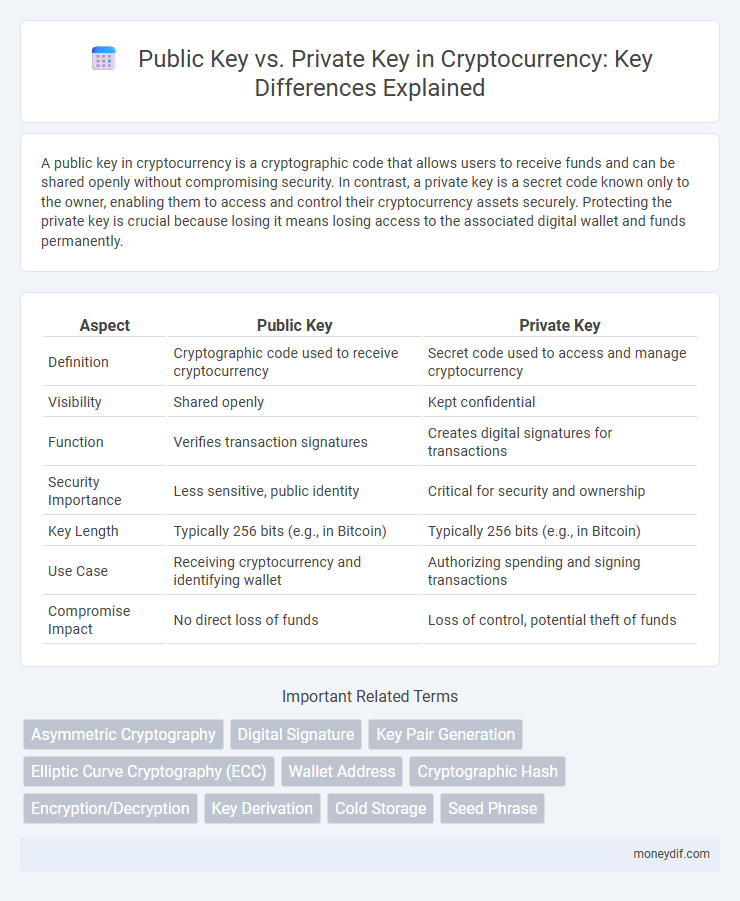
| Aspect | Public Key | Private Key |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptographic code used to receive cryptocurrency | Secret code used to access and manage cryptocurrency |
| Visibility | Shared openly | Kept confidential |
| Function | Verifies transaction signatures | Creates digital signatures for transactions |
| Security Importance | Less sensitive, public identity | Critical for security and ownership |
| Key Length | Typically 256 bits (e.g., in Bitcoin) | Typically 256 bits (e.g., in Bitcoin) |
| Use Case | Receiving cryptocurrency and identifying wallet | Authorizing spending and signing transactions |
| Compromise Impact | No direct loss of funds | Loss of control, potential theft of funds |
Introduction to Public and Private Keys in Cryptocurrency
Public and private keys are fundamental cryptographic components that secure cryptocurrency transactions, enabling users to send and receive digital assets with confidence. The public key acts as a digital address visible on the blockchain, while the private key functions as a secret code that authorizes access and control over the associated cryptocurrency funds. Mastery of these keys ensures secure, transparent, and verifiable ownership within decentralized networks.
Understanding the Role of Public Keys
Public keys in cryptocurrency function as unique digital addresses that enable secure transaction verification without exposing sensitive information. They play a crucial role in blockchain technology by allowing users to receive funds and verify signatures, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of transactions. Unlike private keys, public keys can be shared openly to facilitate trustless interactions in decentralized networks.
The Function and Importance of Private Keys
Private keys in cryptocurrency serve as the essential cryptographic tool for authorizing transactions, providing exclusive access to a user's digital assets and ensuring security via asymmetric encryption. Their uniqueness and secrecy are critical because anyone with the private key can control the associated cryptocurrency wallet, making key management vital for preventing unauthorized access and theft. Without the private key, funds remain inaccessible, underscoring its fundamental role in protecting ownership and enabling secure blockchain interactions.
How Public and Private Keys Work Together
Public and private keys operate as a cryptographic pair, enabling secure transactions in cryptocurrency networks. The public key acts as an address for receiving funds, while the private key authorizes spending by digitally signing transactions. This asymmetric encryption ensures transaction authenticity and user control without exposing the private key.
Security Implications: Protecting Your Private Key
Public keys serve as your cryptocurrency wallet's address, enabling secure transactions without revealing sensitive information, while private keys act as the crucial secret codes granting access and control of your digital assets. Protecting your private key is paramount to prevent unauthorized access, theft, or loss of funds, as any compromise directly endangers the security of your cryptocurrency holdings. Employing hardware wallets, encrypted backups, and secure offline storage methods significantly reduces the risk of exposure and enhances overall asset protection.
Public Key Cryptography in Blockchain Transactions
Public key cryptography in blockchain transactions utilizes a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key, enabling secure and transparent verification of digital signatures. The public key acts as an address for receiving cryptocurrency, allowing anyone to send funds or verify transaction authenticity without exposing the private key. This asymmetric encryption method ensures that only the holder of the private key can authorize transfers, protecting user assets and maintaining the integrity of the blockchain ledger.
Generating and Managing Cryptocurrency Keys
Generating cryptocurrency keys involves creating a unique pair of cryptographic keys: a public key, which serves as a wallet address for receiving funds, and a private key, which authorizes transactions and must remain confidential. Efficiently managing these keys includes securely storing the private key using hardware wallets or encrypted backups to prevent unauthorized access and ensure recovery. Public keys are openly shared across the blockchain network to facilitate transparent and verifiable transactions without compromising security.
Common Misconceptions About Public and Private Keys
Public and private keys are fundamental components of cryptocurrency security, yet many users mistakenly believe public keys should be kept secret like private keys. The public key is designed to be shared openly to receive funds, while the private key must remain confidential to authorize transactions and access wallets. Misunderstanding this distinction can lead to poor security practices and potential loss of digital assets.
Key Recovery and Backup Best Practices
Public key cryptography in cryptocurrency relies on a pair of keys: the public key, which is openly shared for transaction verification, and the private key, kept confidential to authorize access to funds. Effective key recovery and backup best practices involve securely storing private keys offline in hardware wallets or encrypted backups, ensuring they are inaccessible to unauthorized users yet retrievable in emergencies. Utilizing multi-signature wallets and mnemonic seed phrases enhances security and facilitates key recovery without compromising asset control.
Future Developments in Cryptocurrency Key Technology
Public and private key technologies remain fundamental to cryptocurrency security, with emerging developments focusing on quantum-resistant algorithms to counter future cyber threats. Innovations in multi-party computation and threshold signatures aim to enhance private key management by distributing control, reducing risks of single-point failures. Future advancements prioritize seamless integration with decentralized identity systems to strengthen authentication while preserving user privacy.
Important Terms
Asymmetric Cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography uses a pair of mathematically linked keys--public key for encryption and private key for decryption--to ensure data confidentiality and secure communication. The public key is openly distributed to encrypt messages, while the private key remains secret, enabling only the key owner to decrypt and access the original information.
Digital Signature
A digital signature uses a private key to create a unique encrypted hash of a message, ensuring data integrity and authentication, while the corresponding public key enables recipients to verify the signature's validity without exposing the private key. This asymmetric cryptography mechanism secures electronic transactions by confirming the sender's identity and preventing tampering.
Key Pair Generation
Key pair generation involves creating a matched set of cryptographic keys: a public key for encryption or signature verification and a private key for decryption or digital signing. This asymmetric cryptography process ensures secure communication by allowing data encrypted with the public key to be decrypted only by the corresponding private key, maintaining confidentiality and authentication.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) utilizes a pair of mathematically linked keys: a public key derived from multiplying a private key by a predefined elliptic curve point, enabling secure encryption and digital signatures. The private key is a confidential random number, while the public key is openly shared, ensuring that only the private key holder can decrypt messages or generate valid signatures.
Wallet Address
A wallet address is a hashed representation of the public key used in blockchain transactions, enabling users to receive cryptocurrencies without exposing their private key. The private key remains confidential and is essential for signing transactions, ensuring secure access and control over the associated wallet funds.
Cryptographic Hash
Cryptographic hash functions generate fixed-size outputs from input data, ensuring data integrity by producing unique hashes that change drastically with any input modification. In public key cryptography, private keys sign data while public keys verify these signatures, often incorporating cryptographic hashes to securely link the original message with its digital signature.
Encryption/Decryption
Public key encryption uses a paired system where the public key encrypts data and the private key decrypts it, ensuring secure communication without sharing the private key. Private key encryption, also known as symmetric encryption, relies on a single secret key for both encryption and decryption, requiring secure key exchange methods to maintain confidentiality.
Key Derivation
Key derivation transforms initial cryptographic material into secure keys, enabling safe encryption and decryption processes. In public key cryptography, the private key generates the public key through a one-way mathematical function, ensuring that only the private key holder can derive the corresponding secret information.
Cold Storage
Cold storage securely isolates private keys from internet access, preventing unauthorized exposure during cryptocurrency transactions. Public keys enable wallet addresses for receiving funds, while corresponding private keys stored offline in cold storage authorize signing and spending digital assets.
Seed Phrase
A seed phrase is a human-readable representation of the private key used to generate a public key in cryptocurrency wallets, enabling secure access and recovery of digital assets. Unlike the public key, which is shared to receive funds, the private key derived from the seed phrase must remain confidential to prevent unauthorized transactions.
Public Key vs Private Key Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com