Token burn reduces the total supply of a cryptocurrency, increasing scarcity and potentially driving up its value by permanently removing tokens from circulation. Token mint involves creating new tokens, which can expand the supply to support network growth or incentivize users but may dilute the value if not managed properly. Understanding the balance between token burn and token mint is crucial for maintaining the economic stability and long-term viability of a blockchain project.
Table of Comparison
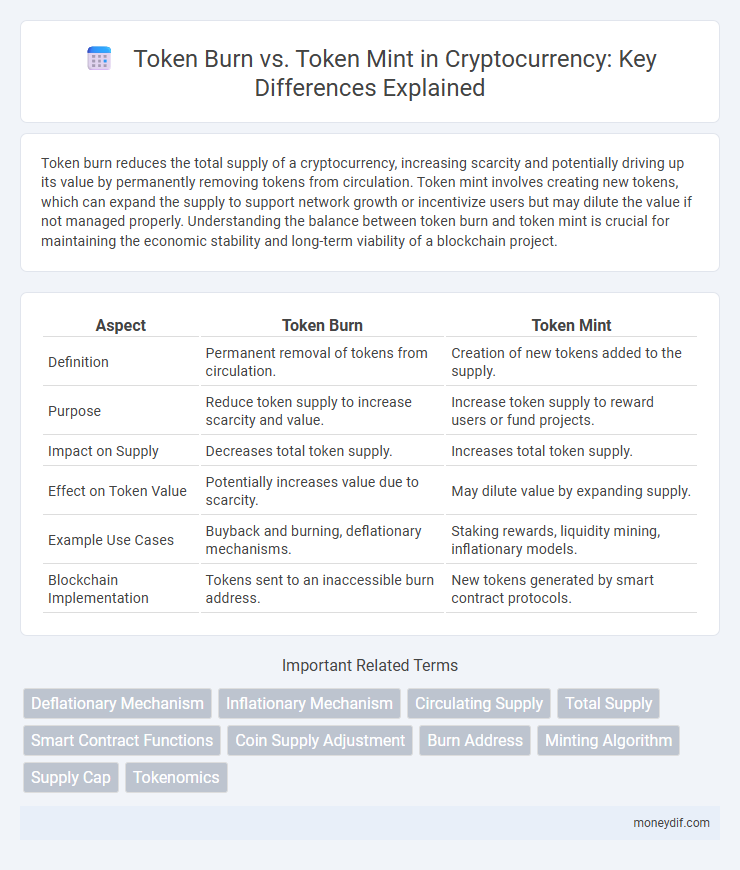
| Aspect | Token Burn | Token Mint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent removal of tokens from circulation. | Creation of new tokens added to the supply. |
| Purpose | Reduce token supply to increase scarcity and value. | Increase token supply to reward users or fund projects. |
| Impact on Supply | Decreases total token supply. | Increases total token supply. |
| Effect on Token Value | Potentially increases value due to scarcity. | May dilute value by expanding supply. |
| Example Use Cases | Buyback and burning, deflationary mechanisms. | Staking rewards, liquidity mining, inflationary models. |
| Blockchain Implementation | Tokens sent to an inaccessible burn address. | New tokens generated by smart contract protocols. |
Understanding Token Burn: Definition and Purpose
Token burn refers to the permanent removal of a certain number of tokens from circulation, effectively reducing the total supply to increase scarcity and potentially drive up value. This process is often implemented by sending tokens to a verifiably unspendable address, ensuring they cannot be retrieved or exchanged. Token burns can enhance network security, incentivize long-term holding, and align with deflationary economic models in cryptocurrency ecosystems.
What is Token Minting in Cryptocurrency?
Token minting in cryptocurrency refers to the process of creating new tokens and adding them to the total circulating supply. This mechanism is often used in blockchain networks to incentivize participation, validate transactions, or reward miners and stakers. Unlike token burning, which reduces supply to increase scarcity, minting expands the token supply to support network growth and functionality.
Key Differences Between Token Burn and Token Mint
Token burn permanently removes tokens from circulation, reducing total supply and potentially increasing scarcity and value, while token mint creates new tokens, expanding the supply to fund projects or incentivize users. Token burn is often used to control inflation and enhance tokenomics, whereas token minting can lead to dilution and requires careful management to avoid devaluation. These opposing mechanisms directly affect a cryptocurrency's market dynamics, supply management, and investor confidence.
Impact of Token Burn on Crypto Supply and Value
Token burn permanently removes a specific amount of cryptocurrency tokens from circulation, effectively reducing the total supply and creating scarcity. This decreased supply often leads to increased demand and can enhance the token's market value over time. By contrast, token minting increases supply, which may dilute value unless matched by proportional demand growth.
The Role of Token Minting in Blockchain Ecosystems
Token minting plays a crucial role in blockchain ecosystems by enabling the creation of new tokens, which supports network growth, liquidity, and incentivization mechanisms. It allows protocols to manage supply dynamically, fund development, and reward participants, directly influencing token scarcity and value. Token minting contrasts with token burn, which reduces supply to increase scarcity and potentially boost token price.
Advantages of Token Burn for Investors and Projects
Token burn reduces the total supply of a cryptocurrency, which can increase scarcity and potentially drive up the token's value, benefiting investors by enhancing asset appreciation. For projects, token burns demonstrate commitment to long-term value, improve market perception, and can stabilize price volatility by managing circulating supply. By permanently removing tokens from circulation, burns help align supply-demand dynamics and incentivize holding among token holders.
Risks and Challenges of Token Minting
Token minting in cryptocurrency introduces risks such as inflationary pressure, which can devalue existing tokens and destabilize the token economy. Over-minting may lead to loss of investor confidence and market manipulation concerns, challenging transparent governance. Smart contract vulnerabilities during minting processes expose platforms to security breaches and potential token supply exploits.
Real-World Examples of Token Burn Events
Token burn events, such as Binance Coin's (BNB) quarterly burns, systematically reduce token supply, enhancing scarcity and potentially driving up market value. Ethereum's occasional burns, introduced by the EIP-1559 upgrade, destroy a portion of gas fees to stabilize transaction costs and reduce inflation. These real-world examples show how token burns strategically influence cryptocurrency economics compared to token minting, which increases supply and can dilute value.
Regulatory Considerations: Token Burn vs Token Mint
Regulatory considerations surrounding token burn and token mint processes focus on compliance with securities laws and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. Token burns, which permanently remove tokens from circulation, may impact token supply and influence market value, raising scrutiny from regulators on market manipulation. Conversely, token minting increases circulation, potentially triggering disclosure requirements and affecting investor protection frameworks under financial regulatory bodies.
Future Trends: Evolving Tokenomics with Burning and Minting
Token burn reduces circulating supply, increasing scarcity and potentially enhancing token value, while token minting introduces new tokens, expanding supply to fund development or incentivize users. Future trends in tokenomics include dynamic burn-and-mint algorithms that adjust token supply in real-time based on market demand and network activity, promoting balanced ecosystem growth. These evolving mechanisms leverage smart contracts and decentralized governance to optimize token utility and long-term sustainability.
Important Terms
Deflationary Mechanism
Deflationary mechanisms reduce token supply by implementing token burns, permanently removing tokens from circulation to increase scarcity and value. In contrast, token minting expands supply by creating new tokens, which can dilute value unless balanced by effective burn strategies or demand growth.
Inflationary Mechanism
The inflationary mechanism in cryptocurrency involves token minting, increasing supply and potentially decreasing token value, while token burning reduces supply by permanently removing tokens, often aiming to counteract inflation and support price stability. Balancing minting and burning activities influences the token's scarcity, market demand, and overall economic sustainability within blockchain ecosystems.
Circulating Supply
Token burns reduce circulating supply by permanently removing tokens, while token mints increase circulating supply by creating new tokens.
Total Supply
Total supply fluctuates as token burns permanently reduce circulating tokens while token mints increase the overall supply, directly impacting scarcity and token value.
Smart Contract Functions
Smart contract functions for token burn and token mint manage token supply by permanently destroying tokens to reduce circulation or creating new tokens to increase total supply, respectively, impacting token scarcity and market value.
Coin Supply Adjustment
Coin supply adjustment involves reducing tokens through token burn to decrease circulation or increasing tokens via token mint to expand supply.
Burn Address
A burn address permanently removes tokens from circulation by sending them to an irretrievable wallet, effectively reducing total supply, whereas token minting creates new tokens, increasing the overall supply.
Minting Algorithm
The Minting Algorithm controls token supply by generating new tokens during minting and reducing circulating tokens through token burn mechanisms for value stabilization.
Supply Cap
Supply cap limits total token availability by controlling token minting and accelerating scarcity through strategic token burn mechanisms.
Tokenomics
Token burn reduces circulating supply to increase token scarcity and potential value, while token minting expands supply to support network growth or incentivize users.
Token burn vs token mint Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com