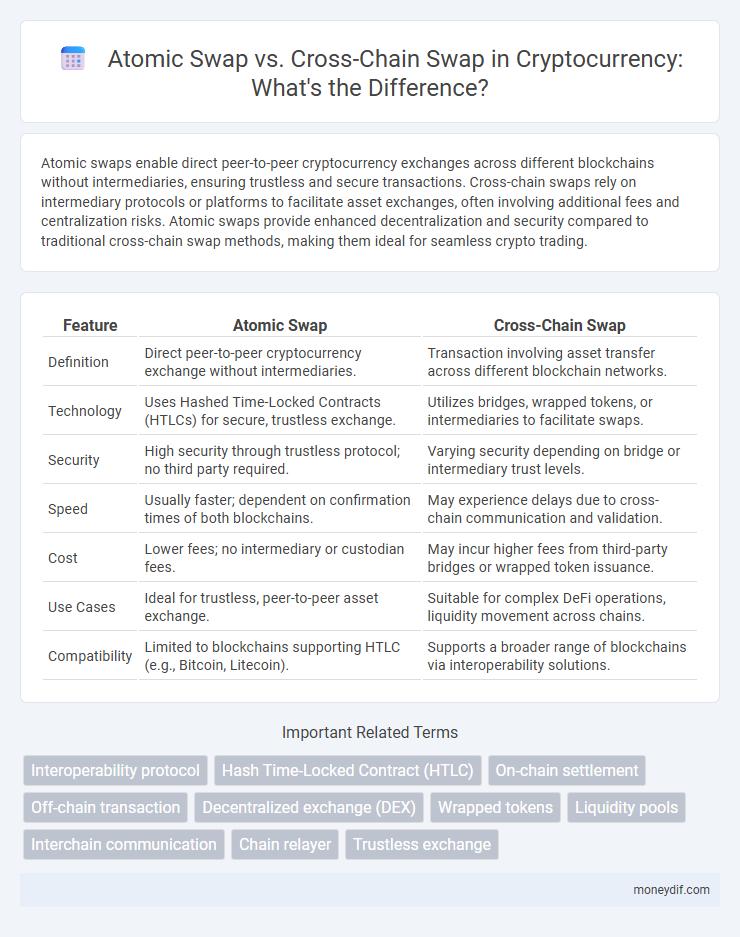
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, ensuring trustless and secure transactions. Cross-chain swaps rely on intermediary protocols or platforms to facilitate asset exchanges, often involving additional fees and centralization risks. Atomic swaps provide enhanced decentralization and security compared to traditional cross-chain swap methods, making them ideal for seamless crypto trading.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Atomic Swap | Cross-Chain Swap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchange without intermediaries. | Transaction involving asset transfer across different blockchain networks. |
| Technology | Uses Hashed Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs) for secure, trustless exchange. | Utilizes bridges, wrapped tokens, or intermediaries to facilitate swaps. |
| Security | High security through trustless protocol; no third party required. | Varying security depending on bridge or intermediary trust levels. |
| Speed | Usually faster; dependent on confirmation times of both blockchains. | May experience delays due to cross-chain communication and validation. |
| Cost | Lower fees; no intermediary or custodian fees. | May incur higher fees from third-party bridges or wrapped token issuance. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for trustless, peer-to-peer asset exchange. | Suitable for complex DeFi operations, liquidity movement across chains. |
| Compatibility | Limited to blockchains supporting HTLC (e.g., Bitcoin, Litecoin). | Supports a broader range of blockchains via interoperability solutions. |
Understanding Atomic Swaps: Definition and Mechanism
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges between different blockchains without intermediaries, using hashed timelock contracts (HTLCs) to ensure transaction security and trustlessness. This mechanism allows simultaneous, irreversible asset transfers, eliminating counterparty risk by enforcing atomicity--that is, either both sides complete the swap or neither does. Understanding atomic swaps is crucial as they facilitate decentralized trading and interoperability across distinct blockchain networks without relying on centralized exchanges.
What are Cross-Chain Swaps? Key Concepts Explained
Cross-chain swaps enable the direct exchange of different cryptocurrencies across separate blockchains without relying on a centralized intermediary, enhancing security and reducing transaction costs. These swaps utilize smart contracts and hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs) to ensure atomicity, meaning either both parties complete the swap successfully or the transaction is canceled. This mechanism contrasts with atomic swaps, which typically involve direct peer-to-peer exchanges on compatible blockchains, whereas cross-chain swaps accommodate diverse blockchain protocols and tokens.
Atomic Swap vs Cross-Chain Swap: Core Differences
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries by utilizing hashed time-locked contracts (HTLCs) to ensure trustless and simultaneous transaction completion. Cross-chain swaps, often facilitated by third-party platforms or decentralized exchanges (DEXs), offer broader compatibility with various blockchain ecosystems but may introduce counterparty risk and longer settlement times. The core difference lies in atomic swaps' trustless, on-chain execution versus cross-chain swaps' reliance on intermediaries or off-chain mechanisms for asset interchange.
Security Features: Comparing Atomic and Cross-Chain Swaps
Atomic swaps utilize hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs) to ensure trustless, secure exchanges without intermediaries, minimizing counterparty risk. Cross-chain swaps may involve third-party protocols or intermediaries, introducing potential vulnerabilities and lessening the security compared to atomic swaps. Both methods aim to facilitate seamless asset exchange across different blockchains, but atomic swaps offer stronger guarantees through cryptographic enforcement.
Transaction Speed and Efficiency: Which Swap Wins?
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer exchanges of cryptocurrencies without intermediaries, ensuring faster settlement times and reduced transaction fees compared to cross-chain swaps, which often rely on third-party platforms or escrow services. Cross-chain swaps, while offering broader asset compatibility across different blockchains, typically involve longer confirmation times and higher computational overhead, impacting overall efficiency. Evaluating transaction speed and operational cost, atomic swaps tend to outperform cross-chain swaps in delivering swift and cost-effective decentralized asset exchanges.
Supported Blockchains and Token Compatibility
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer exchanges between two different cryptocurrencies on separate blockchains without intermediaries, supporting coins that adhere to compatible hash time-locked contract (HTLC) standards such as Bitcoin and Litecoin. Cross-chain swaps expand compatibility by using intermediary networks or protocols like Polkadot or Cosmos, allowing for token exchanges across a broader range of blockchains including Ethereum-based ERC-20 tokens and other non-HTLC-compatible assets. This results in atomic swaps being limited to blockchains with HTLC support, while cross-chain swaps provide enhanced token compatibility through interoperable bridges and relay chains.
User Experience: Complexity and Accessibility
Atomic swaps offer a seamless and trustless method for exchanging cryptocurrencies directly between users without intermediaries, enhancing security but often requiring advanced technical knowledge and compatible wallets. Cross-chain swaps provide a more accessible user experience by leveraging intermediaries or platforms that simplify complex processes, though they may introduce additional trust risks and fees. User experience in atomic swaps is optimized for security-conscious users with technical skills, while cross-chain swaps prioritize ease of use and broader accessibility for everyday traders.
Use Cases: When to Choose Atomic or Cross-Chain Swaps
Atomic swaps are ideal for direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, particularly useful in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and small-scale trades between compatible blockchains like Bitcoin and Litecoin. Cross-chain swaps excel in complex scenarios requiring asset exchanges across multiple, diverse blockchain networks, supporting larger transactions or integrations within broader blockchain ecosystems, such as enterprise-level supply chain solutions or multi-asset decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Choosing atomic swaps suits users seeking fast, trustless exchanges on a limited number of chains, while cross-chain swaps are preferred for interoperability and scalability in multi-chain environments.
Risks and Limitations of Each Swap Method
Atomic swaps face risks such as the reliance on smart contract security, potential loss of funds from incorrect contract execution, and limited support across blockchain platforms due to lack of interoperability standards. Cross-chain swaps encounter vulnerabilities related to intermediary trust, increased transaction complexity, and slower processing times stemming from the need to coordinate multiple blockchain confirmations. Both swap methods are constrained by scalability challenges and may incur higher fees depending on network congestion and protocol implementation.
Future Prospects: The Evolution of Decentralized Swapping
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, while cross-chain swaps facilitate asset transfers via interoperability protocols involving multiple chains. Future prospects indicate advancements in cross-chain technology will enhance scalability, security, and efficiency, driving broader adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions. Integration of layer-2 scaling and smart contract innovations is expected to revolutionize decentralized swapping, reducing transaction costs and increasing real-time liquidity access.
Important Terms
Interoperability protocol
Interoperability protocols enable seamless digital asset exchange between distinct blockchain networks, with atomic swaps providing trustless, peer-to-peer transactions by ensuring either full execution or rollback without intermediaries. Cross-chain swaps utilize broader interoperability frameworks, often involving third-party intermediaries or smart contracts, to facilitate asset transfers across different chains with enhanced flexibility but increased complexity.
Hash Time-Locked Contract (HTLC)
Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs) enable trustless atomic swaps by using cryptographic hashlocks and timelocks to securely exchange assets across different blockchains without intermediaries, ensuring that either both parties complete the transaction or it is fully reverted. Cross-chain swaps utilize HTLCs to facilitate seamless and atomic transfer of tokens between separate blockchain networks, preserving transactional atomicity and preventing counterparty risk.
On-chain settlement
On-chain settlement ensures transaction finality directly on the blockchain, providing security and transparency for atomic swaps, which enable trustless exchange of assets between two parties without intermediaries. Cross-chain swaps facilitate interoperability by allowing asset transfers between different blockchains but often rely on off-chain mechanisms or intermediaries, potentially introducing latency or counterparty risk compared to fully on-chain atomic settlements.
Off-chain transaction
Off-chain transactions enable faster and cheaper asset exchanges by conducting trades outside the main blockchain, which is crucial for atomic swaps to securely execute trustless cross-chain exchanges without intermediaries. In contrast, cross-chain swaps facilitate asset transfers across different blockchains directly, relying on on-chain mechanisms that often involve longer settlement times and higher fees.
Decentralized exchange (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) utilize atomic swaps to enable trustless, peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading directly between wallets on different blockchains without intermediaries. Cross-chain swaps expand this capability by facilitating asset exchanges across multiple distinct blockchain networks, often employing interoperable protocols to maintain security and efficiency.
Wrapped tokens
Wrapped tokens enable seamless value transfer across different blockchains by representing assets from one chain on another, facilitating atomic swaps that execute trustless, simultaneous exchanges without intermediaries. Cross-chain swaps extend this interoperability by leveraging decentralized protocols to swap diverse assets across multiple blockchains, often using wrapped tokens for liquidity and efficiency in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Liquidity pools
Liquidity pools enable seamless asset exchange in decentralized finance by providing reserves that facilitate trades without intermediaries, crucial for both atomic swaps and cross-chain swaps. Atomic swaps execute instant peer-to-peer trades on a single blockchain using hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs), while cross-chain swaps leverage liquidity pools across multiple blockchains to enable asset interoperability and price discovery.
Interchain communication
Interchain communication enables seamless data and asset exchange across different blockchain networks, facilitating atomic swaps as trustless, peer-to-peer token exchanges without intermediaries. Cross-chain swaps, while similar, involve more complex mechanisms and may require intermediary chains or solutions like relayers, often trading off decentralization for broader compatibility.
Chain relayer
Chain relayers facilitate secure communication between blockchains by transmitting transaction proofs, enabling atomic swaps to execute trustless, simultaneous exchanges of tokens across different chains without intermediaries. Cross-chain swaps often leverage chain relayers but can include additional protocols or intermediaries to coordinate asset exchanges, sometimes sacrificing atomicity for broader interoperability.
Trustless exchange
Trustless exchanges enable secure peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries by utilizing atomic swaps, which guarantee simultaneous, irreversible asset exchanges across two blockchains. Cross-chain swaps extend this concept by facilitating transactions between multiple blockchain networks, enhancing liquidity and interoperability without relying on centralized exchanges.
atomic swap vs cross-chain swap Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com