Stablecoins maintain a fixed value by being pegged to assets like the US dollar, offering price stability for transactions and savings. Utility tokens provide access to specific services or platforms within a blockchain ecosystem, often fluctuating in value based on demand and network usage. Choosing between stablecoins and utility tokens depends on whether price stability or platform functionality is the primary goal.
Table of Comparison
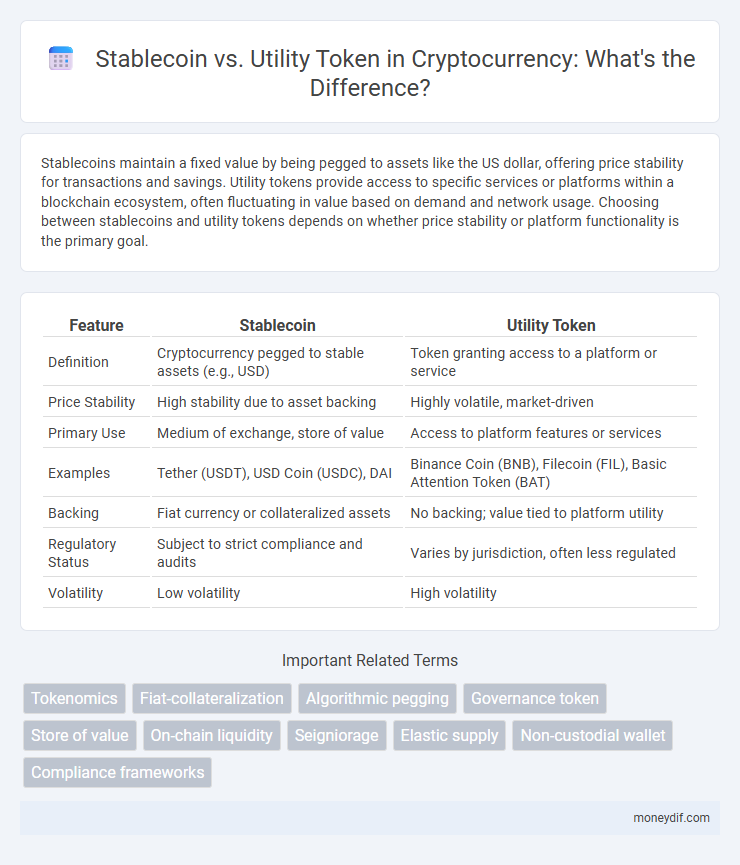
| Feature | Stablecoin | Utility Token |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptocurrency pegged to stable assets (e.g., USD) | Token granting access to a platform or service |
| Price Stability | High stability due to asset backing | Highly volatile, market-driven |
| Primary Use | Medium of exchange, store of value | Access to platform features or services |
| Examples | Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), DAI | Binance Coin (BNB), Filecoin (FIL), Basic Attention Token (BAT) |
| Backing | Fiat currency or collateralized assets | No backing; value tied to platform utility |
| Regulatory Status | Subject to strict compliance and audits | Varies by jurisdiction, often less regulated |
| Volatility | Low volatility | High volatility |
Understanding Stablecoins and Utility Tokens
Stablecoins are digital assets designed to maintain a stable value by being pegged to a reserve asset like the US dollar, providing price stability and reducing volatility in cryptocurrency markets. Utility tokens grant holders access to a specific product or service within a blockchain ecosystem, often functioning as a digital coupon or access key rather than a store of value. Understanding the fundamental differences between stablecoins and utility tokens is essential for investors and users navigating the cryptocurrency landscape and managing risk effectively.
Key Differences Between Stablecoins and Utility Tokens
Stablecoins maintain a stable value by being pegged to fiat currencies or assets, making them ideal for transactions and value storage in the cryptocurrency market. Utility tokens provide access to a product or service within a blockchain ecosystem, serving as a medium for participation rather than a value store. Key differences include their primary function, value stability, and regulatory considerations, with stablecoins often subject to stricter financial oversight.
Use Cases of Stablecoins in Crypto Ecosystem
Stablecoins provide a reliable medium of exchange and store of value within the crypto ecosystem by maintaining price stability pegged to assets like fiat currencies. Their use cases include facilitating seamless cross-border payments, serving as a hedge against volatility in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, and enabling efficient trading pairs on cryptocurrency exchanges. Unlike utility tokens, which grant access to specific platform services, stablecoins enhance transactional certainty and liquidity across various blockchain applications.
Applications of Utility Tokens in Blockchain Projects
Utility tokens serve as integral components in blockchain projects by granting holders access to specific services or features within a decentralized platform. They facilitate operations such as voting rights in governance, payment for transaction fees, and unlocking premium content or functionalities, driving user engagement and ecosystem growth. Unlike stablecoins, which primarily maintain price stability for trading and value storage, utility tokens emphasize enhancing platform usability and incentivizing participation.
Stability and Volatility: Comparing Price Behavior
Stablecoins maintain price stability by pegging their value to a reserve asset, such as the US dollar, minimizing volatility and enabling predictable transactions. Utility tokens exhibit higher volatility as their value is driven by network demand and usage within a specific blockchain ecosystem. Investors and users often prefer stablecoins for safeguarding assets against market fluctuations, while utility tokens offer potential for growth tied to the platform's adoption and development.
Regulatory Implications: Stablecoins vs Utility Tokens
Stablecoins face stricter regulatory scrutiny due to their pegged value and potential impact on financial stability, often requiring compliance with banking and securities laws. Utility tokens, generally used to access platform services, encounter lighter regulatory oversight but must still navigate rules to avoid classification as securities under frameworks like the SEC's Howey Test. Regulatory clarity varies globally, influencing the development, issuance, and adoption of both stablecoins and utility tokens in cryptocurrency markets.
Security and Risks in Stablecoins and Utility Tokens
Stablecoins offer price stability by being pegged to assets like fiat currencies, reducing volatility risks but facing security challenges such as regulatory scrutiny and potential peg failures. Utility tokens, while integral for accessing platform services, expose holders to smart contract vulnerabilities and market speculation without inherent value backing. Both stablecoins and utility tokens require robust security measures and risk management strategies to mitigate fraud, hacking, and regulatory uncertainties.
Popular Examples of Stablecoins and Utility Tokens
Popular stablecoins like Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and Dai (DAI) maintain price stability by pegging their value to fiat currencies, making them essential for transactions and value storage in the crypto ecosystem. Utility tokens such as Ethereum (ETH), Binance Coin (BNB), and Chainlink (LINK) provide access to specific blockchain services, enabling smart contract execution and decentralized application interactions. These tokens drive platform functionality, while stablecoins prioritize financial stability within decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
How to Choose Between Stablecoins and Utility Tokens
Choosing between stablecoins and utility tokens depends on the intended use case and risk tolerance; stablecoins provide price stability by being pegged to fiat currencies, ideal for transactions and value preservation, while utility tokens grant access to specific blockchain platforms or services, offering potential for value appreciation but higher volatility. Assess the need for predictable value versus participation in decentralized ecosystems, considering factors such as liquidity, regulatory environment, and network utility. Understanding tokenomics and project fundamentals is crucial for informed decision-making in cryptocurrency investments.
The Future Outlook for Stablecoins and Utility Tokens
Stablecoins are expected to gain widespread adoption as digital currencies for everyday transactions due to their price stability and regulatory compliance, fostering integration with traditional financial systems. Utility tokens will continue to drive innovation within decentralized applications (dApps) and blockchain ecosystems by enabling access to specific services and governance rights. The evolving regulatory landscape and growing institutional interest will shape the future growth and differentiation between stablecoins and utility tokens in the cryptocurrency market.
Important Terms
Tokenomics
Tokenomics distinguishes stablecoins by their design to maintain a fixed value through collateral or algorithmic mechanisms, ensuring price stability for transactions and store of value purposes. Utility tokens typically provide access to a platform's services or features, with value fluctuating based on demand and network usage, driving ecosystem participation and incentivizing holder engagement.
Fiat-collateralization
Fiat-collateralization involves backing stablecoins with reserves of government-issued currency to maintain price stability, contrasting with utility tokens that derive value from their specific platform functions rather than fixed asset backing. Stablecoins like USDT and USDC rely on fiat reserves to minimize volatility, whereas utility tokens such as Ethereum's ETH grant access to decentralized applications and services without direct fiat collateral.
Algorithmic pegging
Algorithmic pegging stabilizes stablecoins by automatically adjusting their supply based on market demand, differentiating them from utility tokens, which primarily provide access to a platform or service without inherent price stabilization mechanisms. This mechanism ensures stablecoins maintain a consistent value peg, typically to fiat currencies, crucial for transactional reliability in decentralized finance.
Governance token
Governance tokens grant holders voting rights and influence over stablecoin protocol parameters, enhancing decentralized decision-making within the ecosystem. Utility tokens primarily enable access to platform services, while governance tokens focus on protocol management, distinguishing their roles in blockchain governance and stablecoin stability.
Store of value
Stablecoins serve as a reliable store of value by maintaining price stability through pegging to assets like fiat currencies, making them suitable for preserving purchasing power. Utility tokens, in contrast, primarily provide access to a platform's services and lack inherent value stability, limiting their effectiveness as a store of value.
On-chain liquidity
On-chain liquidity for stablecoins ensures seamless trading and reduced volatility by maintaining consistent value pegged to fiat currencies, whereas utility tokens often experience higher liquidity fluctuations due to demand variability linked to platform usage. Efficient on-chain liquidity management leverages automated market makers (AMMs) and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) to facilitate token swaps and enhance user participation in DeFi ecosystems.
Seigniorage
Seigniorage in the context of stablecoins refers to the profit generated from issuing digital currency pegged to fiat assets, leveraging the difference between the reserve backing and the token's market value; utility tokens, in contrast, do not generate seigniorage as their value is derived from access to a platform or service rather than asset backing. Stablecoins maintain price stability and provide predictable seigniorage revenue, whereas utility tokens fluctuate with network demand and usage without direct monetary issuance benefits.
Elastic supply
Elastic supply mechanisms adjust the token quantity to stabilize value, often implemented in stablecoins to maintain price parity with fiat currencies. Utility tokens typically have fixed supplies and rely on demand-driven value rather than supply elasticity for price stability.
Non-custodial wallet
Non-custodial wallets enable users to maintain full control over their private keys while securely storing stablecoins, which are pegged to fiat currencies to reduce volatility, and utility tokens that provide access to specific blockchain services or applications. These wallets facilitate seamless transactions and direct interaction with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, enhancing security and autonomy compared to custodial solutions.
Compliance frameworks
Compliance frameworks for stablecoins emphasize adherence to financial regulations, anti-money laundering (AML), and know your customer (KYC) standards due to their direct link to fiat currency and payment systems. Utility tokens primarily follow securities laws and consumer protection regulations, focusing on preventing fraud and ensuring transparency in providing access to a platform or service.
stablecoin vs utility token Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com