Hot wallets provide quick and convenient access to cryptocurrency for frequent trading but carry higher risks due to online exposure. Cold wallets store assets offline, significantly reducing the risk of hacking and unauthorized access, making them ideal for long-term storage. Choosing between hot and cold wallets depends on the balance between security needs and accessibility preferences for managing digital assets.
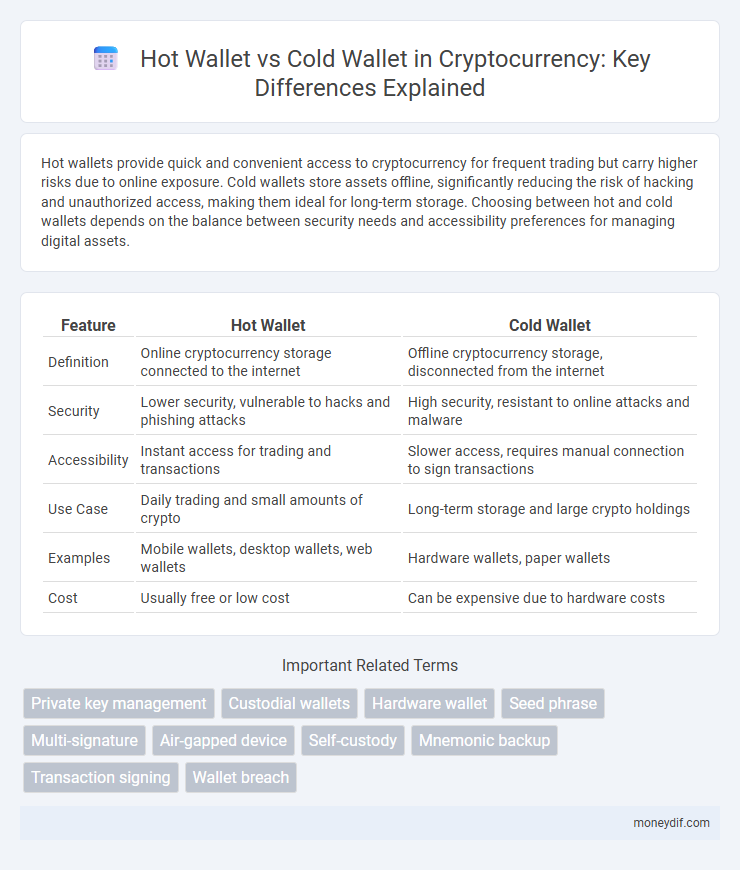
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hot Wallet | Cold Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Online cryptocurrency storage connected to the internet | Offline cryptocurrency storage, disconnected from the internet |
| Security | Lower security, vulnerable to hacks and phishing attacks | High security, resistant to online attacks and malware |
| Accessibility | Instant access for trading and transactions | Slower access, requires manual connection to sign transactions |
| Use Case | Daily trading and small amounts of crypto | Long-term storage and large crypto holdings |
| Examples | Mobile wallets, desktop wallets, web wallets | Hardware wallets, paper wallets |
| Cost | Usually free or low cost | Can be expensive due to hardware costs |
Introduction to Cryptocurrency Wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets serve as essential tools for securely storing and managing digital assets, categorized primarily into hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets are connected to the internet, offering quick access and convenience for frequent transactions but are more vulnerable to cyber attacks. Cold wallets operate offline, providing enhanced security against hacking, making them ideal for long-term storage of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
What Is a Hot Wallet?
A hot wallet is a cryptocurrency storage solution connected to the internet, enabling quick access and seamless transactions for digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It typically includes mobile apps, desktop applications, or web-based platforms, prioritizing convenience but posing higher security risks due to potential online vulnerabilities. Users often rely on hot wallets for active trading or frequent transfers, balancing ease of use with the need for strong security measures such as two-factor authentication and encryption.
What Is a Cold Wallet?
A cold wallet is a type of cryptocurrency storage that keeps private keys offline, enhancing security by isolating assets from internet-based threats like hacking and phishing. Examples include hardware wallets and paper wallets, which significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access or theft. Cold wallets are essential for long-term holders prioritizing safety over quick access to funds.
Key Differences: Hot Wallets vs Cold Wallets
Hot wallets provide real-time access to cryptocurrencies through internet-connected devices, enabling quick transactions but posing higher cybersecurity risks. Cold wallets store private keys offline on hardware devices or paper, significantly reducing vulnerability to hacking and malware attacks. Users typically choose hot wallets for daily trading and cold wallets for long-term asset security and backup.
Security Features and Risks
Hot wallets offer quick access to cryptocurrencies through internet connectivity but are vulnerable to hacking, phishing, and malware attacks due to constant online exposure. Cold wallets store private keys offline, significantly reducing risks of cyber theft and unauthorized access by isolating assets from internet threats. Users must balance the convenience of hot wallets with the enhanced security of cold wallets, especially for large or long-term holdings.
Ease of Access and Usability
Hot wallets offer seamless ease of access and user-friendly interfaces for frequent cryptocurrency transactions, making them ideal for daily use and quick trades. Cold wallets prioritize security by storing assets offline, which reduces accessibility and usability but significantly minimizes exposure to cyber threats. Choosing between hot and cold wallets involves balancing the convenience of instant access with the need for robust asset protection.
Cost Considerations for Wallet Choices
Hot wallets generally have lower upfront costs since they are often free or integrated with exchange platforms, but they may incur higher long-term risks and potential expenses due to security breaches. Cold wallets require an initial investment in hardware or physical storage devices, with costs varying between models, but offer enhanced security that can prevent costly losses from hacks. Evaluating these cost considerations against security needs helps determine the optimal wallet choice for cryptocurrency storage.
Ideal Use Cases for Hot and Cold Wallets
Hot wallets are ideal for frequent cryptocurrency traders and users requiring quick access to their digital assets, as they remain connected to the internet for instant transactions. Cold wallets, such as hardware wallets or paper wallets, are best suited for long-term investors prioritizing security, storing large amounts of cryptocurrency offline to protect against hacking. Combining both wallets allows users to manage daily transactions securely while safeguarding the majority of their holdings in cold storage.
How to Choose the Right Wallet for You
Choosing the right cryptocurrency wallet depends on security needs and transaction frequency; hot wallets offer convenient, quick access for frequent trading while cold wallets provide enhanced protection by storing assets offline. Evaluate risks associated with online connectivity and prioritize cold wallets for long-term storage of significant holdings to prevent hacking vulnerabilities. Balance usability and security by using hot wallets for daily transactions and cold wallets to safeguard large or infrequently accessed crypto assets.
Frequently Asked Questions About Crypto Wallets
Hot wallets are internet-connected crypto storage solutions, enabling quick access and transactions but exposing users to higher hacking risks, while cold wallets keep assets offline, offering enhanced security by protecting private keys from online threats. Common questions include which wallet type suits beginners, how to recover lost access, and ways to secure private keys effectively. Understanding the trade-offs between convenience and security is crucial for managing cryptocurrency holdings safely.
Important Terms
Private key management
Private key management involves securely storing cryptographic keys in hot wallets for frequent online access, while cold wallets keep keys offline to prevent unauthorized access and enhance security.
Custodial wallets
Custodial wallets are managed by third-party services that control private keys on behalf of users, often providing convenient access and recovery options typical of hot wallets, which are connected to the internet for real-time transactions. In contrast, cold wallets store private keys offline, offering enhanced security against online threats but typically lack the immediate accessibility features found in custodial hot wallets.
Hardware wallet
Hardware wallets provide enhanced security by storing private keys offline, contrasting with hot wallets that keep keys connected to the internet and are more vulnerable to cyber threats; cold wallets like hardware devices reduce hacking risks through physical isolation. This offline storage method ensures that transactions require physical confirmation, protecting digital assets from unauthorized access even if the connected device is compromised.
Seed phrase
A seed phrase securely backs up and restores a cold wallet's offline private keys, while hot wallets risk exposure due to their continuous internet connection.
Multi-signature
Multi-signature enhances security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions, making it an effective feature for both hot wallets, which offer online accessibility, and cold wallets, which provide offline storage.
Air-gapped device
Air-gapped devices are physical hardware systems isolated from any network connection, making them ideal for securely storing cryptocurrency private keys in cold wallets to prevent online hacking risks. Unlike hot wallets, which remain connected to the internet and are vulnerable to cyberattacks, air-gapped cold wallets ensure maximum security by eliminating exposure to external threats.
Self-custody
Self-custody involves individuals directly managing their cryptocurrency private keys, ensuring full control without relying on third-party services. Hot wallets offer convenient, internet-connected access ideal for frequent transactions, while cold wallets provide enhanced security by storing keys offline, minimizing exposure to hacking risks.
Mnemonic backup
Mnemonic backup securely preserves your private keys enabling recovery of hot wallets for frequent transactions and cold wallets for offline asset storage.
Transaction signing
Transaction signing in hot wallets offers quick, online authorization with higher security risks, whereas cold wallets enable offline signing, maximizing protection against cyber threats.
Wallet breach
A wallet breach often occurs in hot wallets due to their constant internet connectivity, making them more vulnerable to hacking and phishing attacks. Cold wallets, stored offline, provide enhanced security against breaches by isolating private keys from online threats.
Hot wallet vs cold wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com