On-chain transactions occur directly on the blockchain, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability by recording every transaction on the public ledger. Off-chain transactions happen outside the blockchain, enabling faster and cheaper transfers by avoiding network congestion and fees while relying on trusted intermediaries. Balancing these methods enhances scalability, privacy, and overall efficiency in cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
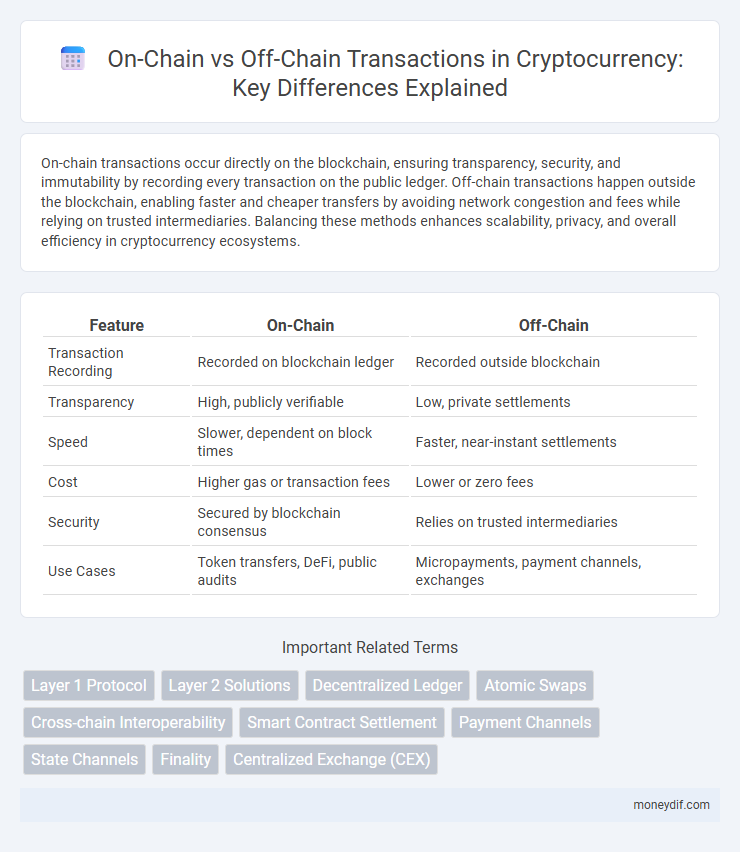
| Feature | On-Chain | Off-Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Recording | Recorded on blockchain ledger | Recorded outside blockchain |
| Transparency | High, publicly verifiable | Low, private settlements |
| Speed | Slower, dependent on block times | Faster, near-instant settlements |
| Cost | Higher gas or transaction fees | Lower or zero fees |
| Security | Secured by blockchain consensus | Relies on trusted intermediaries |
| Use Cases | Token transfers, DeFi, public audits | Micropayments, payment channels, exchanges |
Introduction to On-Chain vs Off-Chain Transactions
On-chain transactions occur directly on the blockchain, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability as each transaction is recorded and verified by the network. In contrast, off-chain transactions are conducted outside the blockchain, offering faster and cheaper transfers but relying on third-party intermediaries or trust-based mechanisms. The choice between on-chain and off-chain solutions impacts scalability, transaction speed, and the level of decentralization in cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Key Differences Between On-Chain and Off-Chain Solutions
On-chain solutions record transactions directly on a blockchain, ensuring transparency, immutability, and decentralization, but often face scalability and speed limitations due to network congestion. Off-chain solutions process transactions outside the blockchain to enhance speed, reduce fees, and increase scalability, yet they may sacrifice some level of trustlessness and security. Key differences include transaction finality, with on-chain offering permanent settlement and off-chain relying on later blockchain reconciliation or trust agreements.
Advantages of On-Chain Transactions
On-chain transactions provide enhanced security by recording every transaction on a decentralized blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability. These transactions enable direct peer-to-peer transfers without intermediaries, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing trust. The public ledger also facilitates easier auditing and regulatory compliance, making on-chain solutions ideal for high-value or sensitive cryptocurrency exchanges.
Benefits of Off-Chain Transactions
Off-chain transactions reduce blockchain congestion by processing transfers outside the main network, resulting in faster and cheaper payments. They enhance privacy as transaction details are not recorded on the public ledger, minimizing data exposure. Furthermore, off-chain solutions like payment channels improve scalability and enable real-time micropayments critical for widespread cryptocurrency adoption.
Security Considerations: On-Chain vs Off-Chain
On-chain transactions offer enhanced security by leveraging decentralized blockchain consensus mechanisms, ensuring immutability and transparency. Off-chain transactions reduce blockchain congestion but rely on third-party intermediaries, introducing potential risks such as trust vulnerabilities and reduced auditability. Balancing security considerations involves evaluating the trade-offs between decentralized verification and operational efficiency in transaction processing.
Transaction Speed and Scalability
On-chain transactions occur directly on the blockchain, ensuring high security but often facing limitations in transaction speed and scalability due to network congestion and block size constraints. Off-chain solutions, such as payment channels and sidechains, enable faster and more scalable transactions by processing transfers outside the main blockchain while periodically settling on-chain to maintain security. This balance allows cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum to enhance throughput and reduce latency without compromising decentralization.
Fees and Cost Comparison
On-chain transactions incur higher fees due to network congestion and miner incentives, often ranging from a few cents to several dollars depending on blockchain activity. Off-chain transactions significantly reduce costs by settling trades off the main ledger, enabling faster and cheaper transfers without occupying blockchain space. This cost-efficient approach is preferred for microtransactions and frequent transfers, minimizing fees while maintaining security through eventual on-chain settlement.
Use Cases: When to Use On-Chain or Off-Chain
On-chain transactions are ideal for use cases requiring transparency, immutability, and decentralized validation, such as high-value asset transfers and official record-keeping. Off-chain solutions suit scenarios demanding faster processing and lower fees, like microtransactions, gaming, and scalability-focused applications. Choosing between on-chain and off-chain depends on priorities such as security, cost, and speed tailored to the specific business or technical requirements of the cryptocurrency use case.
Risks and Challenges of Each Approach
On-chain transactions leverage blockchain's security and immutability but face scalability issues and higher fees, increasing transaction latency during network congestion. Off-chain solutions offer faster, low-cost transfers by handling transactions outside the blockchain, yet they introduce risks such as reduced transparency, reliance on third-party intermediaries, and potential vulnerabilities to fraud or censorship. Both approaches demand careful evaluation of trade-offs between decentralization, speed, cost, and security in cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Future Trends in On-Chain and Off-Chain Development
Future trends in on-chain development emphasize scalability solutions like layer 2 protocols and sharding to enhance transaction throughput and reduce fees, fostering broader decentralized finance (DeFi) adoption. Off-chain developments prioritize interoperability and cross-chain communication through technologies such as bridges and sidechains, enabling seamless asset transfers and data sharing between diverse blockchain networks. Hybrid models combining on-chain security and off-chain speed are gaining traction, aiming to balance transparency with efficiency in blockchain ecosystems.
Important Terms
Layer 1 Protocol
Layer 1 protocol serves as the foundational blockchain architecture, handling on-chain transactions directly on the main blockchain, ensuring security and decentralization. Off-chain solutions complement Layer 1 by processing transactions outside the main chain, enhancing scalability and reducing network congestion without compromising the core protocol's integrity.
Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 solutions enhance blockchain scalability by processing transactions off-chain while anchoring final states on-chain, reducing congestion and gas fees. This hybrid approach balances the security of on-chain settlement with the efficiency of off-chain execution, enabling faster and more cost-effective decentralized applications.
Decentralized Ledger
Decentralized ledger technology ensures transparent and tamper-resistant record-keeping by distributing data across multiple nodes, enabling secure on-chain transactions that are permanently recorded on the blockchain. Off-chain solutions, while improving scalability and reducing transaction costs, handle data or operations outside the blockchain network but often require trusted intermediaries or mechanisms to maintain integrity and synchronization with the on-chain ledger.
Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps enable trustless, direct cryptocurrency exchanges between parties on-chain, ensuring security and transparency through blockchain consensus. Off-chain atomic swaps utilize payment channels or second-layer solutions to facilitate faster, lower-cost transactions while maintaining the atomicity of cross-chain trades.
Cross-chain Interoperability
Cross-chain interoperability enables seamless communication and asset transfers between different blockchain networks, bridging on-chain activities that occur directly on blockchains with off-chain processes that take place outside the blockchain environment. This integration enhances transaction efficiency and scalability while maintaining security by leveraging on-chain consensus and off-chain data handling mechanisms.
Smart Contract Settlement
Smart contract settlement enhances transaction efficiency by automating contract execution directly on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability in on-chain processes. Off-chain settlement reduces blockchain congestion and lowers transaction costs by handling complex computations or agreements externally while anchoring final outcomes on-chain for security and auditability.
Payment Channels
Payment channels enable multiple transactions to be conducted off-chain, significantly reducing on-chain congestion and lowering transaction fees. By locking funds in a smart contract on-chain and executing numerous off-chain payments instantly, they enhance scalability and speed without compromising blockchain security.
State Channels
State channels enable off-chain transactions by allowing participants to conduct multiple exchanges privately without immediately recording each action on the blockchain, reducing on-chain congestion and gas fees. By settling only the final state on-chain, they combine the security of on-chain verification with the efficiency of off-chain processing.
Finality
Finality in blockchain refers to the point at which a transaction is irreversibly recorded on the ledger, with on-chain finality achieved through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake ensuring immediate and trustless confirmation. Off-chain finality relies on external systems such as payment channels or sidechains, offering faster transaction processing but requiring trust in intermediaries for eventual settlement on the main chain.
Centralized Exchange (CEX)
Centralized Exchanges (CEX) conduct most transactions off-chain within their own ledgers, enabling faster trade execution and lower fees compared to on-chain transactions. However, users rely on the CEX's custody and trust since asset transfers between wallets only occur on-chain during deposits and withdrawals.
On-chain vs Off-chain Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com