Decentralized Finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, offering increased transparency and control over assets. Centralized Finance (CeFi) relies on traditional financial institutions or platforms that act as intermediaries, providing user-friendly services but often requiring trust in third parties. DeFi prioritizes censorship resistance and permissionless access, while CeFi emphasizes regulatory compliance and customer support.
Table of Comparison
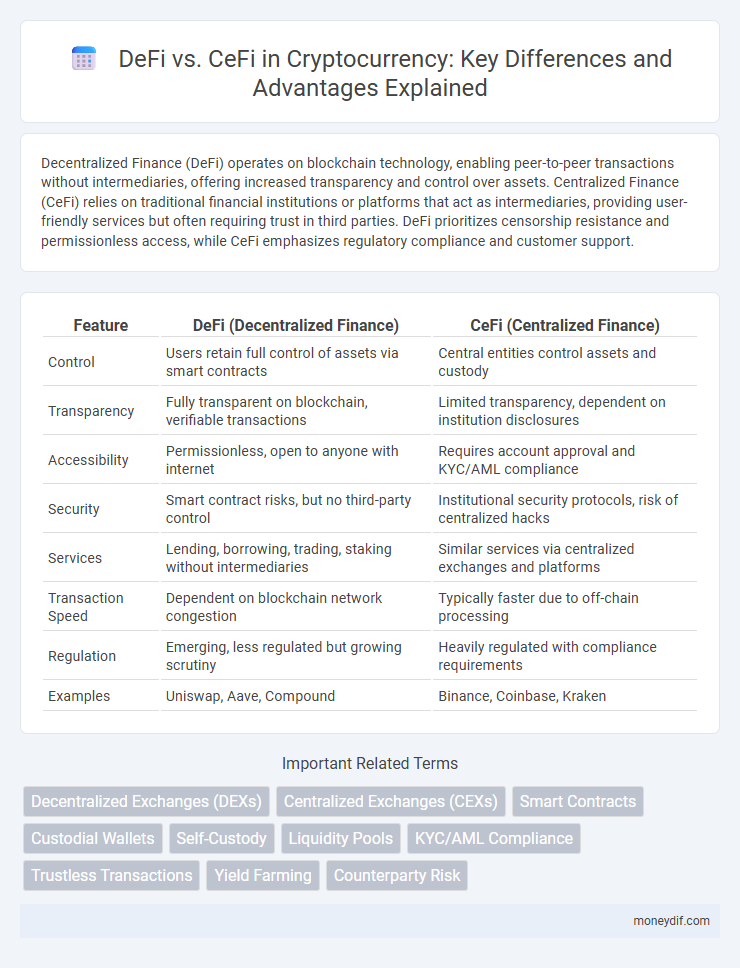
| Feature | DeFi (Decentralized Finance) | CeFi (Centralized Finance) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Users retain full control of assets via smart contracts | Central entities control assets and custody |
| Transparency | Fully transparent on blockchain, verifiable transactions | Limited transparency, dependent on institution disclosures |
| Accessibility | Permissionless, open to anyone with internet | Requires account approval and KYC/AML compliance |
| Security | Smart contract risks, but no third-party control | Institutional security protocols, risk of centralized hacks |
| Services | Lending, borrowing, trading, staking without intermediaries | Similar services via centralized exchanges and platforms |
| Transaction Speed | Dependent on blockchain network congestion | Typically faster due to off-chain processing |
| Regulation | Emerging, less regulated but growing scrutiny | Heavily regulated with compliance requirements |
| Examples | Uniswap, Aave, Compound | Binance, Coinbase, Kraken |
Understanding DeFi and CeFi: Key Definitions
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, promoting transparency and accessibility. Centralized Finance (CeFi) involves traditional financial institutions or centralized platforms that control users' assets and transactions, offering regulated services and customer support. Understanding the key differences between DeFi and CeFi reveals contrasting approaches to security, control, and user autonomy in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Core Differences Between DeFi and CeFi
DeFi operates on decentralized blockchain networks, enabling peer-to-peer financial services without intermediaries, whereas CeFi relies on centralized institutions to manage and control assets and transactions. DeFi offers greater transparency and user control through smart contracts, while CeFi provides faster transactions and customer support due to centralized oversight. Security mechanisms differ as DeFi depends on cryptographic protocols, whereas CeFi implements regulatory compliance and traditional security frameworks.
Security and Trust Models in DeFi vs CeFi
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) operates on blockchain technology, providing enhanced transparency and user control by eliminating central intermediaries, which reduces single points of failure and censorship risk. Centralized Finance (CeFi) relies on trusted institutions to manage assets and transactions, offering user-friendly interfaces but exposing users to potential risks like custodial breaches and regulatory shutdowns. Security in DeFi depends on smart contract integrity and protocol audits, while CeFi's trust model hinges on institutional reputation and regulatory compliance.
Accessibility and Inclusivity Comparison
DeFi platforms offer greater accessibility by enabling anyone with an internet connection and a digital wallet to participate in financial services without traditional bureaucratic barriers. CeFi relies on centralized authorities that often require identity verification and geographic restrictions, limiting access for underserved or unbanked populations. Consequently, DeFi's permissionless nature fosters inclusivity by democratizing access to loans, savings, and trading globally.
User Experience: Interfaces and Usability
DeFi platforms offer decentralized interfaces that provide users with full control over their assets but often feature complex navigation and require a higher learning curve. CeFi platforms prioritize user-friendly, intuitive interfaces with streamlined onboarding processes, appealing to beginners by offering familiar financial services with customer support. Enhanced usability in CeFi fosters trust and accessibility, while DeFi emphasizes transparency and security at the cost of convenience.
Yield Opportunities: Earning in DeFi vs CeFi
DeFi platforms offer higher yield opportunities by enabling users to earn interest through decentralized lending, staking, and liquidity mining with fewer intermediaries and more control over assets. CeFi institutions provide more stable returns by offering fixed interest rates on deposits and yield products backed by regulated entities, appealing to risk-averse investors. Liquidity in DeFi is often more volatile but can result in greater profits, while CeFi yields prioritize security and consistency.
Regulatory Landscape: Compliance and Risks
DeFi operates with decentralized protocols, often lacking comprehensive regulatory oversight, which exposes users to smart contract vulnerabilities and potential legal ambiguities. CeFi platforms comply with established financial regulations, implementing KYC/AML processes that reduce fraud risks but may limit user privacy and accessibility. Regulatory authorities increasingly scrutinize both sectors, aiming to balance innovation with consumer protection and systemic risk management.
Popular Platforms: Leading DeFi and CeFi Examples
Leading DeFi platforms like Uniswap, Aave, and Compound offer decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading services without intermediaries, emphasizing transparency and user control. In contrast, popular CeFi platforms such as Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken provide centralized cryptocurrency exchange services with regulatory compliance, customer support, and enhanced security features. The choice between DeFi and CeFi depends on users' preferences for decentralization, trust models, and ease of use within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Future Trends: The Evolution of DeFi and CeFi
DeFi platforms are increasingly integrating advanced interoperability protocols to enhance cross-chain transactions, positioning themselves for broader adoption and scalability. Meanwhile, CeFi institutions are adopting blockchain-based compliance tools and expanding hybrid models that combine traditional financial services with decentralized features. Future trends also indicate a convergence where DeFi's transparency and CeFi's regulatory frameworks merge, fostering a more secure and accessible financial ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Option: Which Fits Your Needs?
Deciding between DeFi and CeFi depends on your priorities for control, security, and accessibility. DeFi platforms offer decentralized protocols enabling peer-to-peer transactions and greater transparency, while CeFi relies on centralized intermediaries providing user-friendly interfaces and customer support. Assess your comfort with risk, desire for autonomy, and the need for regulatory protections to choose the best fit for your cryptocurrency goals.
Important Terms
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) operate on blockchain networks enabling peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, enhancing security and user control compared to centralized exchanges (CeFi) which manage assets through centralized authority. DeFi platforms leverage DEXs to offer transparent, permissionless financial services, contrasting with CeFi's reliance on traditional custodial models and regulatory oversight.
Centralized Exchanges (CEXs)
Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) operate with a central authority managing user funds and transactions, contrasting with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that use smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. CEXs typically offer higher liquidity and faster trade execution compared to CeFi's decentralized protocols but require users to trust the exchange's security and regulatory compliance.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate and enforce agreements on DeFi platforms using blockchain technology, enhancing transparency and reducing the need for intermediaries. Unlike CeFi institutions, which rely on centralized control and manual processes, DeFi smart contracts enable trustless, permissionless financial services with improved efficiency and lower costs.
Custodial Wallets
Custodial wallets in DeFi often require users to rely on third-party platforms that manage private keys, contrasting with CeFi custodial wallets where centralized entities hold and secure assets, offering easier access but less user control. The choice between DeFi and CeFi custodial wallets impacts security, transparency, and control, with DeFi promoting decentralization and CeFi providing streamlined user experience through centralized custody.
Self-Custody
Self-custody in DeFi empowers users with full control over their digital assets through private keys, eliminating reliance on centralized intermediaries typical in CeFi platforms. This enhanced autonomy reduces counterparty risk and fosters trustless transactions, pivotal for secure, decentralized financial services.
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools in DeFi enable decentralized trading by pooling tokens in smart contracts, offering continuous liquidity without intermediaries, while CeFi relies on centralized order books and market makers to provide liquidity, often resulting in less transparency and higher fees. DeFi's automated market makers (AMMs) optimize liquidity provision through algorithmic pricing, contrasting with CeFi's traditional financial mechanisms governed by centralized institutions.
KYC/AML Compliance
KYC/AML compliance in DeFi remains challenging due to its decentralized nature and lack of centralized control, limiting effective identity verification and transaction monitoring. CeFi platforms implement stringent KYC/AML protocols with robust user identification and regulatory reporting, enhancing security but reducing user privacy compared to DeFi's pseudonymous environment.
Trustless Transactions
Trustless transactions in DeFi enable peer-to-peer exchanges without intermediaries, leveraging smart contracts on blockchain networks like Ethereum for secure, transparent execution. CeFi relies on centralized platforms to facilitate transactions, introducing counterparty risk and requiring users to trust third-party custodians.
Yield Farming
Yield farming in DeFi leverages decentralized protocols to maximize returns through liquidity mining, offering higher APYs but with increased smart contract risks and impermanent loss. In contrast, CeFi yield farming operates within centralized platforms providing more user-friendly interfaces and potentially lower risk, yet often yields lower returns due to centralized control and fees.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk in DeFi is minimized through smart contracts and decentralized protocols, reducing reliance on centralized intermediaries, whereas CeFi platforms expose users to higher counterparty risk due to centralized control and the potential for insolvency or fraud. DeFi's transparent blockchain mechanics enable real-time verification of assets, contrasting with CeFi's often opaque risk management practices.
DeFi vs CeFi Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com