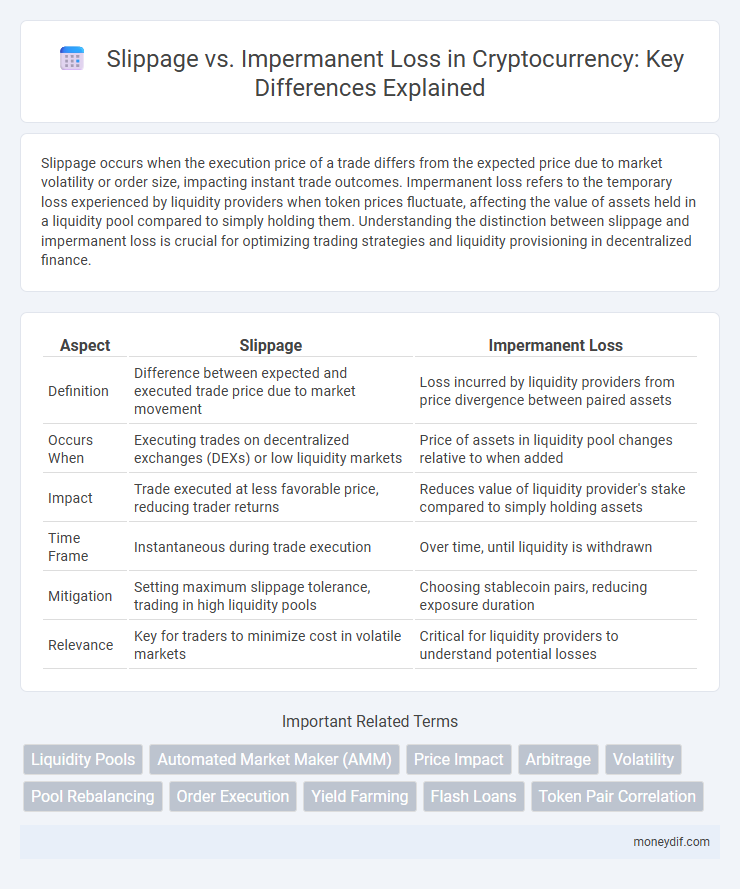
Slippage occurs when the execution price of a trade differs from the expected price due to market volatility or order size, impacting instant trade outcomes. Impermanent loss refers to the temporary loss experienced by liquidity providers when token prices fluctuate, affecting the value of assets held in a liquidity pool compared to simply holding them. Understanding the distinction between slippage and impermanent loss is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and liquidity provisioning in decentralized finance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Slippage | Impermanent Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Difference between expected and executed trade price due to market movement | Loss incurred by liquidity providers from price divergence between paired assets |
| Occurs When | Executing trades on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or low liquidity markets | Price of assets in liquidity pool changes relative to when added |
| Impact | Trade executed at less favorable price, reducing trader returns | Reduces value of liquidity provider's stake compared to simply holding assets |
| Time Frame | Instantaneous during trade execution | Over time, until liquidity is withdrawn |
| Mitigation | Setting maximum slippage tolerance, trading in high liquidity pools | Choosing stablecoin pairs, reducing exposure duration |
| Relevance | Key for traders to minimize cost in volatile markets | Critical for liquidity providers to understand potential losses |
Understanding Slippage in Cryptocurrency Trading
Slippage in cryptocurrency trading refers to the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual execution price, often occurring during periods of high volatility or low liquidity. It impacts traders by increasing costs and reducing profit margins, especially in decentralized exchanges where order books are limited. Understanding slippage is crucial for implementing effective trade strategies and using tools like limit orders to minimize unexpected losses.
What Is Impermanent Loss in DeFi?
Impermanent loss in DeFi refers to the temporary reduction in value experienced by liquidity providers when the price of their staked assets diverges from their initial deposit ratio in automated market makers (AMMs). This loss occurs because the AMM rebalances asset ratios to maintain liquidity pools, often resulting in less valuable holdings compared to simply holding the tokens outside the pool. Understanding impermanent loss is crucial for DeFi users to evaluate the risks of providing liquidity versus potential trading fees earned.
Key Differences Between Slippage and Impermanent Loss
Slippage refers to the difference between the expected price of a cryptocurrency trade and the actual executed price, often occurring during high volatility or low liquidity. Impermanent loss happens when a liquidity provider's staked assets in an automated market maker experience a reduction compared to simply holding the assets due to price divergence between the paired tokens. The key difference lies in slippage being a short-term trading issue affecting individual trades, while impermanent loss affects liquidity providers over time as asset prices fluctuate.
Factors Influencing Slippage in Crypto Markets
Slippage in crypto markets is primarily influenced by factors such as trade size relative to market liquidity, volatility, and order execution speed on decentralized exchanges. Large orders in low-liquidity pools often experience higher slippage due to insufficient depth to fulfill the trade at a desired price. Rapid price fluctuations exacerbate slippage risk by causing the execution price to deviate from the quoted price between transaction initiation and confirmation.
Causes of Impermanent Loss for Liquidity Providers
Impermanent loss for liquidity providers occurs when the price of deposited assets changes relative to their initial value, creating a divergence between the pool's token ratios and external market prices. This loss is primarily caused by volatile price fluctuations in paired assets within automated market makers (AMMs), leading to reduced portfolio value compared to simply holding the tokens. Impermanent loss differs from slippage, which results from trade execution price differences, whereas impermanent loss directly impacts liquidity providers due to market dynamics.
How to Mitigate Slippage on Exchanges
Slippage on cryptocurrency exchanges can be mitigated by using limit orders instead of market orders to control the execution price, thereby avoiding significant price deviations during trade execution. Utilizing exchanges with deeper liquidity pools and lower spread cryptocurrencies reduces the risk of slippage by ensuring more stable pricing and quicker order fulfillment. Employing tools such as slippage tolerance settings on decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and Sushiswap helps traders set acceptable price deviation limits, minimizing unexpected losses during volatile market conditions.
Strategies to Minimize Impermanent Loss
Minimizing impermanent loss in cryptocurrency liquidity pools relies heavily on strategies such as diversifying assets across multiple pools, selecting stablecoin pairs with lower volatility, and implementing dynamic rebalancing protocols that adjust holdings in response to market fluctuations. Utilizing automated market makers (AMMs) with impermanent loss protection features and participating in pools offering rewards that offset potential losses can further reduce exposure. Careful evaluation of pool composition and leveraging hedging tools like options also contribute to mitigating impermanent loss risks effectively.
Real-World Examples: Slippage vs. Impermanent Loss
Slippage occurs when executing large cryptocurrency trades on decentralized exchanges, such as swapping 100 ETH for USDC on Uniswap, where price impact causes a worse-than-expected rate. Impermanent loss happens when liquidity providers on automated market makers like Balancer face losses compared to simply holding assets, exemplified by depositing ETH and DAI during volatile market conditions and experiencing divergence in asset prices. Understanding these differences is critical for DeFi participants to optimize strategies for yield farming and trading efficiency.
Tools and Calculators for Risk Assessment
Tools and calculators for risk assessment in cryptocurrency trading help quantify slippage and impermanent loss by analyzing historical price volatility and liquidity pool metrics. Slippage calculators estimate price impact during high-volume trades, while impermanent loss calculators assess the risk of holding assets in automated market maker (AMM) pools over time. Utilizing these tools enables traders to optimize entry points and liquidity provision strategies by evaluating potential losses and price fluctuations accurately.
Choosing the Right Approach: Trading vs. Liquidity Provision
Slippage occurs when the execution price of a trade differs from the expected price, often impacting short-term traders seeking immediate market entry. Impermanent loss affects liquidity providers who experience a temporary reduction in asset value due to price divergence within automated market maker platforms. Choosing between trading to minimize slippage or providing liquidity to endure impermanent loss depends on risk tolerance and investment goals within decentralized finance ecosystems.
Important Terms
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools enable decentralized trading by allowing users to provide assets that facilitate swaps, where slippage refers to the difference between expected and executed trade prices due to market fluctuations. Impermanent loss occurs when liquidity providers experience a temporary reduction in asset value compared to holding the assets outside the pool, often influenced by price volatility and pool composition.
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) facilitate decentralized trading by using liquidity pools, where slippage occurs when large trades alter the pool's price, and impermanent loss represents the temporary loss faced by liquidity providers due to price divergence between deposited assets. Minimizing slippage involves optimizing trade sizes and pool liquidity, while impermanent loss risk can be mitigated through careful asset selection and hedging strategies.
Price Impact
Price impact measures the change in an asset's price caused by a trade, directly influencing slippage, which is the difference between expected and executed trade prices during order fulfillment. Impermanent loss occurs in liquidity pools when the asset price diverges from the initial deposit ratio, but unlike slippage, it represents a potential loss for liquidity providers rather than traders.
Arbitrage
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across markets but faces challenges from slippage, which reduces profit margins by causing trade execution at less favorable prices. Compared to impermanent loss in liquidity provision, slippage directly impacts immediate trade outcomes, while impermanent loss reflects unrealized value shifts affecting long-term liquidity positions.
Volatility
Volatility significantly impacts slippage as rapid price fluctuations cause larger spreads between expected and executed trade prices, while impermanent loss arises from divergence in asset prices within liquidity pools during volatile market conditions. Understanding their interplay helps liquidity providers optimize strategies to minimize losses and maximize returns in decentralized finance environments.
Pool Rebalancing
Pool rebalancing aims to minimize slippage by adjusting asset ratios to maintain liquidity equilibrium, thereby reducing the price impact during trades. Unlike impermanent loss, which arises from price divergence between pooled tokens, effective rebalancing strategies help preserve portfolio value by mitigating transient imbalance effects.
Order Execution
Order execution speed significantly influences slippage, which occurs when trade prices differ from expected levels during volatile market conditions. Impermanent loss, primarily relevant in liquidity provision, differs as it reflects temporary value divergence caused by price fluctuations rather than trade execution delays.
Yield Farming
Yield farming involves earning returns by providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, where slippage can reduce profitability during token swaps and impermanent loss affects liquidity providers when asset prices diverge. Managing slippage through optimized transaction settings and minimizing impermanent loss by choosing stable asset pairs or employing hedging strategies are crucial for maximizing yield farming returns.
Flash Loans
Flash loans enable users to borrow assets instantly without collateral, but high slippage during rapid trades can erode potential gains, especially when paired with the risk of impermanent loss in liquidity pools. Managing slippage is critical to mitigate the impact of impermanent loss on borrowed assets within decentralized finance platforms.
Token Pair Correlation
Token pair correlation directly influences slippage and impermanent loss in decentralized finance (DeFi) liquidity pools, where highly correlated token pairs typically experience lower slippage and reduced impermanent loss. Understanding the price movement relationship between tokens helps liquidity providers optimize portfolio risk and minimize losses during market volatility.
Slippage vs Impermanent Loss Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com