Custodial wallets store private keys on behalf of users, offering convenience but requiring trust in a third party to safeguard assets. Non-custodial wallets grant users full control over their private keys, enhancing security and privacy while placing responsibility for backup and recovery solely on the user. Choosing between custodial and non-custodial wallets depends on the user's preference for ease of use versus control and security in managing cryptocurrency holdings.
Table of Comparison
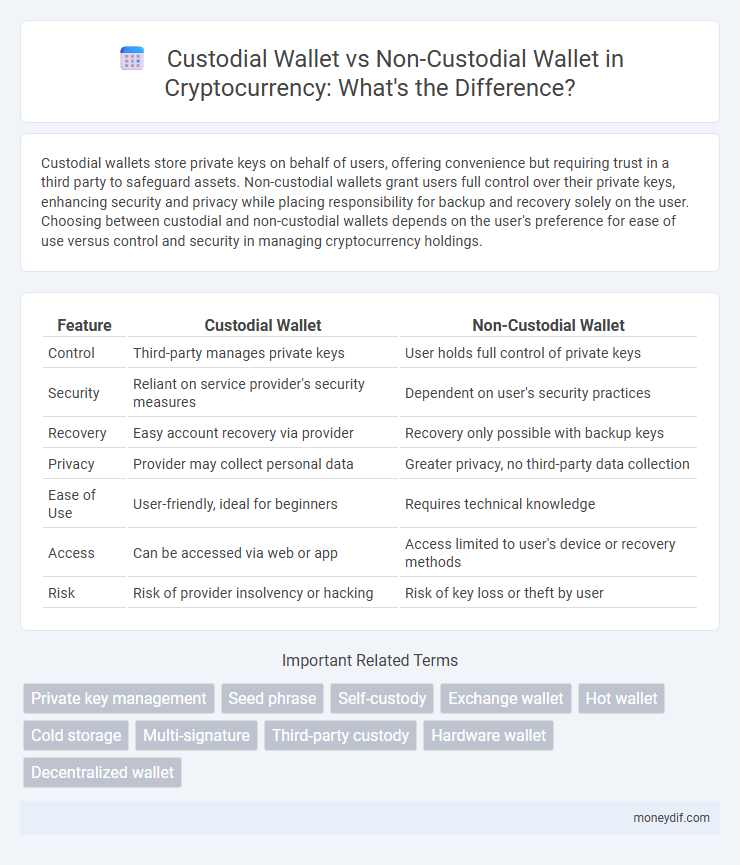
| Feature | Custodial Wallet | Non-Custodial Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Third-party manages private keys | User holds full control of private keys |
| Security | Reliant on service provider's security measures | Dependent on user's security practices |
| Recovery | Easy account recovery via provider | Recovery only possible with backup keys |
| Privacy | Provider may collect personal data | Greater privacy, no third-party data collection |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, ideal for beginners | Requires technical knowledge |
| Access | Can be accessed via web or app | Access limited to user's device or recovery methods |
| Risk | Risk of provider insolvency or hacking | Risk of key loss or theft by user |
Understanding Custodial and Non-Custodial Wallets
Custodial wallets store private keys on behalf of users, offering ease of use and recovery options while limiting full control and increasing reliance on third-party security. Non-custodial wallets grant users exclusive ownership of their private keys, enhancing security and control but requiring personal responsibility for backup and key management. Choosing between custodial and non-custodial wallets involves balancing convenience with the level of control and security desired in cryptocurrency management.
Key Differences Between Custodial and Non-Custodial Wallets
Custodial wallets store private keys on behalf of users, offering ease of access but requiring trust in a third party, while non-custodial wallets grant users full control over their private keys, enhancing security and privacy. Custodial wallets often support account recovery and customer service, whereas non-custodial wallets place responsibility for key management entirely on the user. The key difference lies in control and security trade-offs: custodial wallets prioritize convenience, and non-custodial wallets emphasize self-sovereignty and decentralization.
Security Features: Custodial vs Non-Custodial Wallets
Custodial wallets store private keys on behalf of users, offering convenience but exposing funds to risks like centralized hacking and potential withdrawal restrictions. Non-custodial wallets provide users full control over their private keys, significantly enhancing security by eliminating third-party vulnerabilities, though requiring responsible key management to prevent loss. Both wallet types incorporate encryption and multi-factor authentication, but non-custodial solutions emphasize decentralized security principles to protect cryptocurrency assets.
Control and Ownership of Crypto Assets
Custodial wallets hold private keys on behalf of users, giving third parties control over crypto assets, which may reduce user autonomy but offer ease of recovery and management. Non-custodial wallets grant users full control and ownership of their private keys, ensuring maximum security and privacy but requiring users to manage backups and recovery independently. This distinction in control and ownership directly impacts security risk, user responsibility, and accessibility in cryptocurrency management.
User Experience and Accessibility Comparison
Custodial wallets offer enhanced accessibility by managing private keys on behalf of users, simplifying account recovery and reducing the risk of losing access due to misplaced credentials. Non-custodial wallets provide greater control and security, requiring users to manage their private keys, which can complicate the user experience for those less familiar with cryptocurrency. The trade-off between ease of use and security makes custodial wallets more appealing to beginners, while experienced users often prefer non-custodial options for full ownership of their assets.
Privacy and Data Protection Considerations
Custodial wallets store private keys on behalf of users, increasing vulnerability to data breaches and limiting control over personal information, whereas non-custodial wallets grant users full ownership and responsibility of their private keys, enhancing privacy and reducing third-party risks. Data protection is stronger in non-custodial wallets since private keys are not stored on centralized servers, preventing unauthorized access and mitigating potential mass hacks. Users prioritizing confidentiality and control typically prefer non-custodial wallets for safeguarding sensitive cryptocurrency information.
Risks Associated with Custodial Wallets
Custodial wallets expose users to risks including potential hacks on the service provider, loss of access due to account suspension, and lack of control over private keys, which compromises ownership security. Users depend entirely on the custodian's security measures, creating a single point of failure that can result in asset theft or loss. Regulatory actions or technical malfunctions within the custodial platform can also lead to restricted access or irreversible asset loss.
Benefits of Using Non-Custodial Wallets
Non-custodial wallets provide users with full control over their private keys, enhancing security by eliminating reliance on third-party custodians susceptible to hacks or insolvency. These wallets enable peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, preserving user privacy and reducing transaction fees. Ownership of private keys also ensures users retain access to their funds regardless of external account suspensions or platform outages.
Choosing the Right Wallet for Your Crypto Needs
Choosing the right wallet for your crypto needs depends on security preferences and control over private keys. Custodial wallets offer ease of use and recovery options by entrusting third parties with private keys, while non-custodial wallets provide full user control and enhanced security by keeping private keys exclusively in the user's possession. Assessing factors like transaction frequency, asset value, and trust in service providers can guide users to select between custodial and non-custodial solutions tailored to their specific cryptocurrency management goals.
Future Trends in Cryptocurrency Wallet Technology
Custodial wallets are evolving with enhanced security protocols and integration of AI-driven risk assessment, enabling seamless user experience while maintaining regulatory compliance. Non-custodial wallets are advancing with multi-party computation (MPC) and decentralized key management to offer superior control and privacy without compromising usability. Future trends highlight hybrid solutions combining these technologies to balance security, user autonomy, and accessibility in cryptocurrency wallet technology.
Important Terms
Private key management
Private key management in custodial wallets is handled by a third party, ensuring ease of use but reduced control, whereas non-custodial wallets require users to securely store their private keys for full ownership and responsibility.
Seed phrase
A seed phrase is a crucial security feature in non-custodial wallets that enables users to fully control and recover their cryptocurrency holdings, unlike custodial wallets where the service provider manages the private keys.
Self-custody
Self-custody involves managing your own private keys securely, contrasting custodial wallets where third parties control keys, while non-custodial wallets empower users with full ownership and control over their cryptocurrency assets.
Exchange wallet
Exchange wallets typically function as custodial wallets, where the platform holds private keys on behalf of users, unlike non-custodial wallets that provide users full control and responsibility over their private keys.
Hot wallet
Hot wallets, as online cryptocurrency storage solutions, can be either custodial, where a third party controls private keys, or non-custodial, allowing users full control over their private keys for enhanced security.
Cold storage
Cold storage secures cryptocurrency by keeping private keys offline, with custodial wallets entrusting key management to third parties while non-custodial wallets grant users full control over their private keys.
Multi-signature
Multi-signature wallets enhance security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, offering a robust safeguard against unauthorized access in both custodial and non-custodial wallets. Custodial multi-signature wallets rely on third-party management for key storage and transaction approval, while non-custodial multi-signature wallets empower users with full control over private keys, reducing dependency on intermediaries and enhancing decentralized asset protection.
Third-party custody
Third-party custody involves a trusted provider managing private keys, distinguishing custodial wallets from non-custodial wallets where users retain exclusive control over their crypto assets.
Hardware wallet
Hardware wallets provide enhanced security by storing private keys offline, contrasting custodial wallets where third parties control assets and non-custodial wallets offering user-managed key ownership.
Decentralized wallet
Decentralized wallets offer users full control of private keys and funds, contrasting with custodial wallets where third parties manage assets, impacting security and ownership.
Custodial wallet vs non-custodial wallet Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com