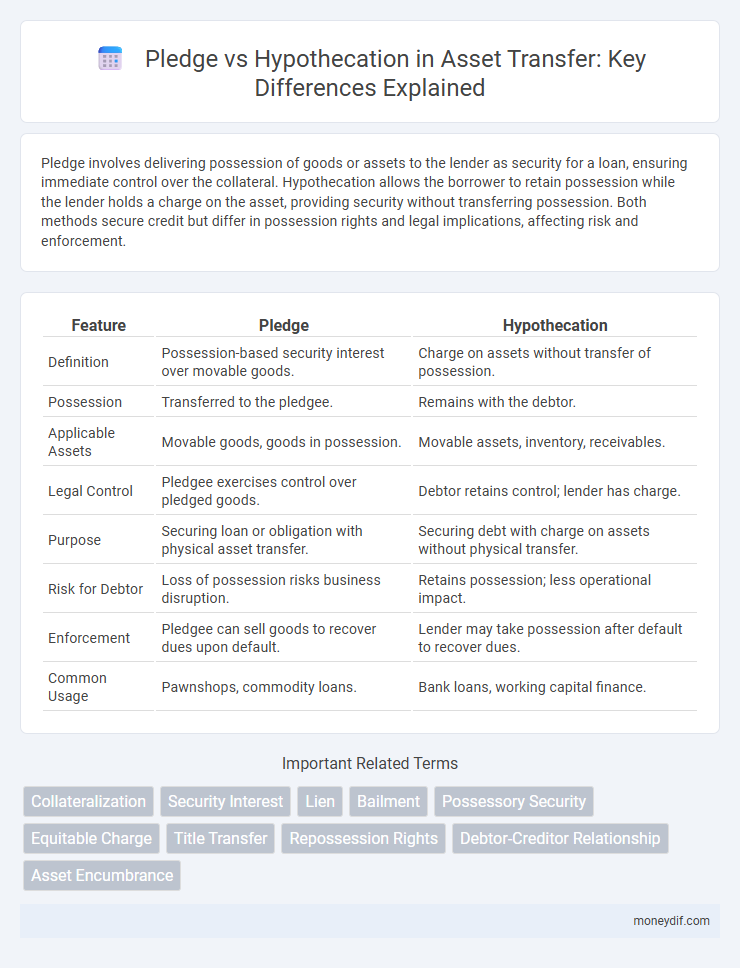
Pledge involves delivering possession of goods or assets to the lender as security for a loan, ensuring immediate control over the collateral. Hypothecation allows the borrower to retain possession while the lender holds a charge on the asset, providing security without transferring possession. Both methods secure credit but differ in possession rights and legal implications, affecting risk and enforcement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pledge | Hypothecation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Possession-based security interest over movable goods. | Charge on assets without transfer of possession. |
| Possession | Transferred to the pledgee. | Remains with the debtor. |
| Applicable Assets | Movable goods, goods in possession. | Movable assets, inventory, receivables. |
| Legal Control | Pledgee exercises control over pledged goods. | Debtor retains control; lender has charge. |
| Purpose | Securing loan or obligation with physical asset transfer. | Securing debt with charge on assets without physical transfer. |
| Risk for Debtor | Loss of possession risks business disruption. | Retains possession; less operational impact. |
| Enforcement | Pledgee can sell goods to recover dues upon default. | Lender may take possession after default to recover dues. |
| Common Usage | Pawnshops, commodity loans. | Bank loans, working capital finance. |
Understanding Pledge and Hypothecation: Key Definitions
Pledge involves the transfer of possession of goods or securities from the borrower to the lender as security for a loan, ensuring the lender's right to sell the asset in case of default. Hypothecation allows the borrower to retain possession of the asset while providing the lender a charge over the asset, commonly used for movable property like vehicles or inventories. Both serve as collateral mechanisms but differ primarily in possession rights and enforcement procedures.
Legal Framework: Pledge vs Hypothecation
Pledge and hypothecation differ fundamentally in their legal frameworks, with pledge involving the transfer of possession of goods to the lender as security, thereby creating a possessory lien under common law principles. Hypothecation, governed primarily by contract law, allows the borrower to retain possession while providing the lender a non-possessory security interest that can be enforced in case of default. Jurisdictions often regulate pledges through specific property laws, whereas hypothecation is typically governed by commercial and banking regulations, impacting enforcement procedures and creditor rights.
Core Differences Between Pledge and Hypothecation
Pledge involves the physical delivery of goods or assets as security for a loan, giving the lender possession rights until the debt is repaid, whereas hypothecation allows the borrower to retain possession of the assets while providing them as collateral. In pledge, the lender has the right to sell the pledged goods in case of default, contrasting with hypothecation where the lender must typically go through legal procedures to claim the asset. The core difference lies in possession and control: pledge transfers possession but not ownership, while hypothecation maintains borrower possession with a charge on the asset.
Asset Ownership and Control in Pledge vs Hypothecation
In a pledge, the ownership of the asset is transferred to the pledgee, who gains physical possession and control as security for the debt. Hypothecation allows the borrower to retain ownership and possession of the asset while granting the lender a charge over it, maintaining control under the borrower's use. The distinction impacts risk management, as pledge offers greater control and protection to the lender compared to hypothecation where ownership and possession remain with the debtor.
Types of Assets Involved: Pledge vs Hypothecation
Pledge involves the transfer of tangible movable assets such as goods, stocks, or valuables to the lender as security, granting possession but not ownership. Hypothecation pertains to movable assets like vehicles or inventory where possession remains with the borrower, while the lender holds a charge on the asset until the debt is repaid. The distinction lies in possession rights: pledge transfers possession; hypothecation only creates a security interest without possession transfer.
Lender’s Rights and Remedies Explained
In a pledge, the lender obtains possession of the collateral, granting immediate control and the right to sell the asset if the borrower defaults, ensuring stronger recovery options. In hypothecation, the borrower retains possession, limiting the lender's recourse to legal action without direct asset control, thus often requiring court intervention for asset seizure. Lenders prefer pledge over hypothecation for enhanced enforcement of security interests and quicker remedies in default scenarios.
Documentation and Process Differences
Pledge requires the delivery of goods or documents as security to the lender, establishing possession as a key factor, whereas hypothecation allows the borrower to retain possession while granting security interest. Documentation for pledge involves a formal pledge deed and transfer of possession, while hypothecation demands a hypothecation agreement without changing possession, often supported by invoices or stock statements. The process of pledge is typically straightforward due to physical transfer, while hypothecation involves detailed monitoring and periodic verification of the charged assets.
Risk Assessment: Borrower and Lender Perspectives
Pledge involves the borrower physically handing over assets to the lender as security, reducing lender risk through direct control but increasing borrower risk due to asset surrender. Hypothecation allows the borrower to retain possession of assets while granting security interest, posing higher risk for lenders who rely on the borrower's integrity and asset maintenance. Risk assessment prioritizes collateral valuation, asset liquidity, and borrower creditworthiness to balance protection for both parties.
Common Use Cases in Banking and Finance
Pledge and hypothecation are distinct security interests used in banking and finance for securing loans. Pledge involves the physical delivery of goods or assets to the lender as collateral, commonly used in commodity financing and pawn transactions. Hypothecation allows the borrower to retain possession of the assets, such as stock portfolios or receivables, while the lender holds a lien, frequently applied in working capital loans and vehicle financing.
Choosing Between Pledge and Hypothecation: Factors to Consider
Choosing between pledge and hypothecation depends on the nature of the asset and control requirements; pledge involves transferring possession of goods as security, while hypothecation allows the debtor to retain possession. The type of asset, risk tolerance, and legal implications significantly influence the decision, as pledge offers stronger creditor protection through physical control, whereas hypothecation provides operational flexibility. Credit terms, duration, and enforcement mechanisms must be carefully evaluated to align the security arrangement with business objectives and financial strategies.
Important Terms
Collateralization
Collateralization involves securing a loan by pledging tangible assets where possession transfers to the lender, whereas hypothecation allows borrowers to retain possession while offering assets as security.
Security Interest
Security interest in pledge involves the actual delivery of goods or assets to the lender as collateral, ensuring possession and control by the secured party, whereas hypothecation allows the borrower to retain possession of the assets while granting a charge to the lender, typically used in movable property financing. Pledge offers stronger protection for the creditor due to physical possession, while hypothecation provides flexibility to the borrower but requires additional legal processes to enforce the security interest.
Lien
A lien legally authorizes a creditor to retain possession of a debtor's property until a debt is satisfied, differing from a pledge which involves transfer of possession with consent, while hypothecation allows debtors to retain possession of the property used as collateral.
Bailment
Bailment involves the transfer of possession without ownership, where pledge creates a possession-based security interest with delivery of goods, while hypothecation allows a charge over movable property without transferring possession.
Possessory Security
Possessory security involves the creditor taking possession of the debtor's movable property as collateral, where pledge requires physical delivery to secure the debt, whereas hypothecation allows the debtor to retain possession while granting the creditor rights over the asset.
Equitable Charge
Equitable charge grants a lender a non-possessory security interest over specific assets without transferring ownership, differing from pledge which requires possession and hypothecation which allows asset retention with the borrower.
Title Transfer
Title transfer under pledge involves the transfer of ownership of the pledged asset to the pledgee until the debt is repaid, ensuring greater security and control. In contrast, hypothecation involves the borrower retaining ownership while the lender holds a lien over the asset, allowing the borrower to use the asset but restricting transfer or sale until the debt is cleared.
Repossession Rights
Repossession rights under pledge allow the pledgee to take physical possession of the pledged asset upon default, reinforcing security through actual custody. In contrast, hypothecation grants the creditor a charge over the asset without transferring possession, relying on legal remedies to enforce repossession only after default.
Debtor-Creditor Relationship
In debtor-creditor relationships, a pledge involves transferring possession of goods as security for a debt, while hypothecation allows the debtor to retain possession while providing the creditor a charge over the goods.
Asset Encumbrance
Asset encumbrance occurs when assets are pledged or hypothecated to secure liabilities, affecting a firm's borrowing capacity and balance sheet transparency. Pledge involves transfer of possession of the collateral to the lender, while hypothecation allows the borrower to retain possession but grants the lender a charge over the asset until debt repayment.
Pledge vs Hypothecation Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com