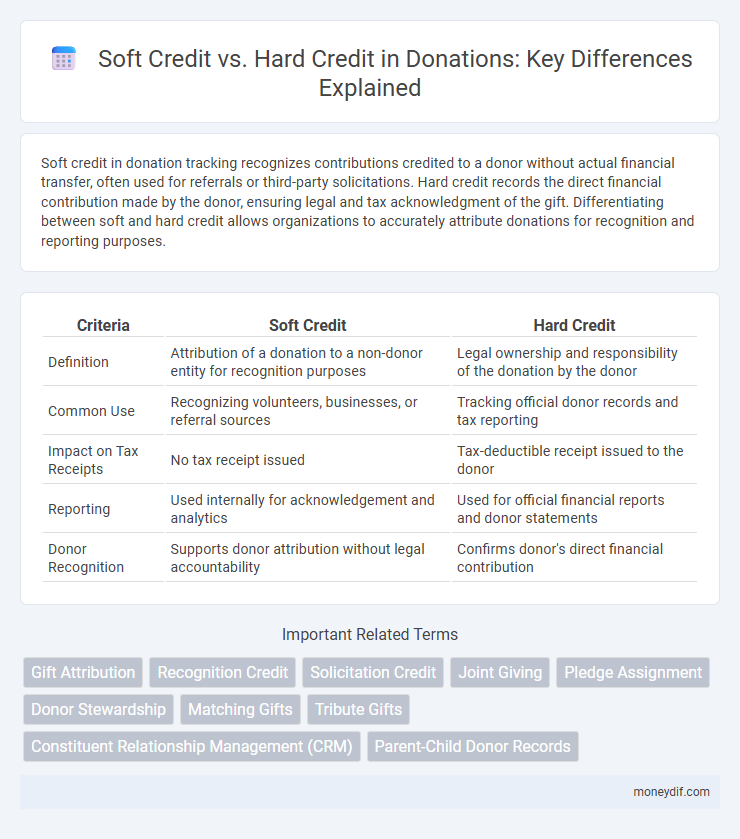
Soft credit in donation tracking recognizes contributions credited to a donor without actual financial transfer, often used for referrals or third-party solicitations. Hard credit records the direct financial contribution made by the donor, ensuring legal and tax acknowledgment of the gift. Differentiating between soft and hard credit allows organizations to accurately attribute donations for recognition and reporting purposes.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Soft Credit | Hard Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Attribution of a donation to a non-donor entity for recognition purposes | Legal ownership and responsibility of the donation by the donor |
| Common Use | Recognizing volunteers, businesses, or referral sources | Tracking official donor records and tax reporting |
| Impact on Tax Receipts | No tax receipt issued | Tax-deductible receipt issued to the donor |
| Reporting | Used internally for acknowledgement and analytics | Used for official financial reports and donor statements |
| Donor Recognition | Supports donor attribution without legal accountability | Confirms donor's direct financial contribution |
Understanding Soft Credit and Hard Credit in Donation Tracking
Soft credit in donation tracking attributes recognition to individuals or organizations who influenced a gift without providing funds directly, often used in acknowledging fundraisers or advocates. Hard credit, in contrast, records the actual donor who made the monetary contribution, ensuring accurate financial reporting and tax receipt issuance. Differentiating between soft and hard credit helps nonprofits accurately track contributions and properly recognize all parties involved in fundraising efforts.
Key Differences Between Soft Credit and Hard Credit
Soft credit acknowledges a donor's support without transferring legal ownership or tax receipt, often used to recognize intermediary fundraisers or affiliated organizations. Hard credit is the official recognition given to the individual or entity legally responsible for the donation and receives the tax deduction. The key differences lie in attribution for fundraising credit and tax reporting, where hard credit affects donor acknowledgment and IRS records, while soft credit is primarily for internal tracking and relationship management.
Why Soft Credits Matter for Fundraisers
Soft credits acknowledge a donor's indirect contribution, recognizing fundraisers, volunteers, or affiliated individuals who influenced the gift without directly providing funds. This recognition helps fundraisers build stronger relationships, track advocacy impact, and motivate ongoing support by highlighting their role in securing donations. Accurately assigning soft credits enhances donor stewardship and strategic planning for future campaigns.
How Hard Credit Impacts Donor Recognition
Hard credit directly attributes the donation to the individual or organization whose funds were used, ensuring clear and accurate donor recognition in fundraising records and reports. This precise acknowledgment enhances transparency and donor accountability, which can strengthen trust and encourage future contributions. Unlike soft credit, hard credit enables nonprofits to recognize the true financial supporter, boosting the donor's public recognition and potential eligibility for benefits or awards.
Recording Soft Credit vs Hard Credit in Your CRM
Recording soft credit versus hard credit in your CRM ensures accurate donor recognition and reporting. Hard credit reflects the actual donor responsible for the gift, while soft credit acknowledges individuals or organizations who influenced or facilitated the donation without being the legal donor. Properly distinguishing and recording both credits enhances fundraising accountability and donor relationship management.
Best Practices for Assigning Soft and Hard Credit
Best practices for assigning soft and hard credit in donation tracking emphasize clear documentation of the donor's role and recognition preferences to ensure accurate attribution and reporting. Soft credit should be used to acknowledge individuals or entities who influenced the donation without being the actual giver, while hard credit must be assigned to the primary donor who legally owns the gift. Implementing a consistent policy with donor management software improves transparency and donor engagement by distinguishing between financial responsibility and acknowledgment.
Common Scenarios for Using Soft Credit in Donations
Soft credit in donations is commonly used when recognizing individuals or organizations who influenced a gift but are not the primary donor, such as employers matching employee donations or family members encouraging contributions. It allows nonprofits to acknowledge the broader network supporting fundraising efforts without recording those donors as the official source of funds. This practice enhances donor relationships and provides detailed insights into giving patterns and stewardship opportunities.
Reporting and Analyzing Soft vs Hard Credit Data
Soft credit in donation reporting acknowledges a donor's indirect contribution, typically linked to fundraising events or donor referrals, without assigning them financial responsibility. Hard credit directly attributes the donation to the individual who legally made the gift, ensuring precise tracking for tax receipts and financial auditing. Analyzing soft versus hard credit data allows nonprofits to accurately assess donor influence, optimize fundraising strategies, and enhance relationship management by distinguishing between actual financial contributions and supportive referrals.
Mistakes to Avoid with Soft and Hard Credit Attribution
Confusing soft credit with hard credit attribution often leads to inaccurate donor recognition and flawed fundraising reports. Avoid attributing soft credit as hard credit, as this can misrepresent actual financial contributions and affect incentive allocations. Ensuring clear differentiation between referral acknowledgment (soft credit) and direct donations (hard credit) prevents errors in donor databases and maintains transparency in fundraising metrics.
Enhancing Donor Relationships Through Credit Recognition
Soft credit attribution acknowledges a donor's indirect involvement in a contribution, fostering recognition among affiliates and enhancing transparency in donor relationships. Hard credit is assigned to the actual contributor, ensuring precise acknowledgment for tax and reporting purposes. Balancing both types of credit deepens engagement by highlighting the collective impact of supporters while maintaining clear attribution for gift processing and donor appreciation.
Important Terms
Gift Attribution
Gift attribution distinguishes between soft credit, acknowledging a donor's indirect influence without being the primary giver, and hard credit, which assigns official recognition to the individual who directly made the donation. This differentiation is crucial for accurate donor recognition, fundraising analytics, and ensuring effective stewardship in nonprofit organizations.
Recognition Credit
Recognition Credit categorizes contributions as Soft Credit--acknowledging indirect donor influence--and Hard Credit--recording direct financial contributions for accurate fundraising metrics.
Solicitation Credit
Solicitation credit, often recorded as soft credit, recognizes a donor's influence in securing a donation without assigning financial responsibility or legal obligation, unlike hard credit which directly attributes the donation to the individual or entity legally responsible. Soft credit is essential for tracking referral impact, donor stewardship, and relationship management, while hard credit is critical for accurate financial reporting and revenue recognition.
Joint Giving
Soft credit in Joint Giving recognizes donor influence without legal responsibility, while hard credit assigns formal donation acknowledgment and tax benefits to the contributing donor.
Pledge Assignment
Pledge assignment involves transferring donation responsibilities where soft credit recognizes donor acknowledgment without financial responsibility, while hard credit assigns official financial credit to an individual or entity.
Donor Stewardship
Donor stewardship involves personalized communication and recognition strategies to maintain donor relationships, emphasizing the accurate allocation of contributions through soft credit and hard credit distinctions. Hard credit directly credits the individual or entity making the donation, whereas soft credit acknowledges those who facilitated or influenced the gift without receiving formal recognition as the donor.
Matching Gifts
Matching gifts often use soft credit to recognize donor involvement without affecting fundraising totals, while hard credit directly attributes the donation to the original donor for reporting and incentive purposes.
Tribute Gifts
Tribute gifts credited as soft credits recognize donor acknowledgments without affecting tax receipts, whereas hard credits assign official donation records impacting tax documentation.
Constituent Relationship Management (CRM)
Constituent Relationship Management (CRM) systems in nonprofits differentiate between soft credit and hard credit to accurately track donor contributions; hard credit records the primary donor responsible for the gift, while soft credit acknowledges associated individuals or organizations who referred or influenced the donation. This distinction enhances donor recognition strategies and reporting accuracy, optimizing fundraising efforts and maintaining transparent donor relationships.
Parent-Child Donor Records
Parent-Child Donor Records establish a hierarchical relationship between donor accounts, enabling the tracking of contributions from multiple related sources under a single umbrella. Soft credit attributes recognition to the parent donor without financial liability, while hard credit assigns actual monetary acknowledgment and tax receipting to the child donor's transaction.
Soft Credit vs Hard Credit Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com