Under-the-table pay refers to cash payments made directly to employees without officially reporting the income to tax authorities, often to avoid taxes and legal obligations. Off-the-books pay similarly involves compensating workers without documentation but can extend to employer practices that omit wages from payroll records entirely. Both methods pose risks including lack of legal protections, unreported income, and potential penalties for employers and employees involved.
Table of Comparison
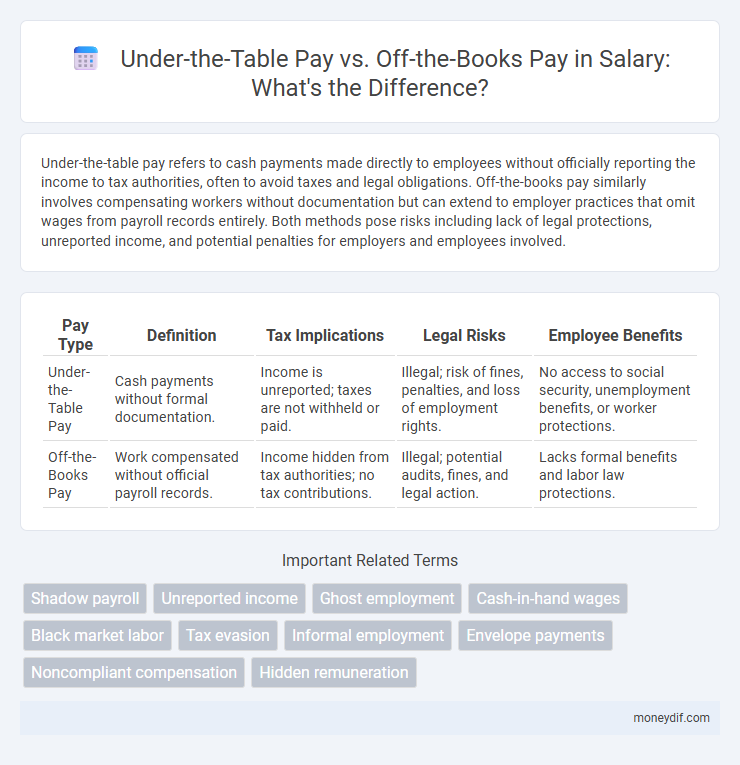
| Pay Type | Definition | Tax Implications | Legal Risks | Employee Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under-the-Table Pay | Cash payments without formal documentation. | Income is unreported; taxes are not withheld or paid. | Illegal; risk of fines, penalties, and loss of employment rights. | No access to social security, unemployment benefits, or worker protections. |
| Off-the-Books Pay | Work compensated without official payroll records. | Income hidden from tax authorities; no tax contributions. | Illegal; potential audits, fines, and legal action. | Lacks formal benefits and labor law protections. |
Understanding Under-the-Table Pay
Under-the-table pay refers to wages paid in cash without official documentation, often to avoid taxes or legal obligations. This practice can lead to lack of worker protections such as benefits, insurance, and legal recourse. Employers and employees engaging in under-the-table pay risk penalties, including fines and back taxes from government agencies.
What is Off-the-Books Pay?
Off-the-books pay refers to wages paid to employees without official record or documentation, often to avoid taxes and regulatory obligations. This method circumvents formal payroll systems, making earnings unreported to government agencies like the IRS or Social Security Administration. Employees receiving off-the-books pay may lack legal protections such as minimum wage guarantees, overtime, and workers' compensation benefits.
Key Differences Between Under-the-Table and Off-the-Books Pay
Under-the-table pay typically refers to cash transactions where wages are paid directly to employees without formal documentation or tax withholding, making it illegal and vulnerable to tax evasion. Off-the-books pay, while similar in involving unreported income, often describes wages not recorded in official business accounting but may sometimes be part of informal or unregistered work arrangements. The key differences lie in the intent and documentation: under-the-table emphasizes secret cash payments to avoid taxes, whereas off-the-books encompasses a broader range of unrecorded payment practices beyond just cash.
Legal Implications of Hidden Salary Payments
Hidden salary payments, whether under-the-table or off-the-books, expose employers and employees to significant legal risks including tax evasion charges and penalties from labor law violations. These payments circumvent wage regulations, leading to potential disputes over worker rights, benefits, and compensation claims. Regulatory agencies increasingly target such practices, emphasizing compliance to avoid costly audits, fines, and legal consequences.
Tax Risks of Unreported Income
Under-the-table pay and off-the-books pay both involve unreported income, creating significant tax risks for employees and employers alike. Failure to report such income can lead to audits, penalties, and back taxes imposed by the IRS, along with potential legal consequences. Proper documentation and compliance with tax laws are essential to avoid financial liabilities and maintain transparent financial records.
Employer Motivations for Alternative Pay Methods
Employers often choose under-the-table pay or off-the-books methods to reduce tax liabilities, avoid payroll taxes, and minimize regulatory compliance costs. These alternative payment practices can also facilitate flexible wage negotiations and quick cash transactions, helping businesses manage cash flow discreetly. However, such methods increase legal risks and limit employee benefits, posing long-term challenges for both parties.
Employee Consequences of Unofficial Pay
Receiving under-the-table pay or off-the-books pay exposes employees to significant risks including lack of legal protections, absence of benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, and potential difficulties in proving income for loans or unemployment claims. These unofficial payments often result in tax evasion, which can lead to penalties or loss of future social security benefits. Employees also forfeit workers' compensation and unemployment insurance, leaving them vulnerable in cases of workplace injury or job loss.
Detecting and Preventing Under-the-Table Payments
Detecting and preventing under-the-table payments involves thorough auditing and monitoring of payroll records alongside verifying reported income with tax filings to identify discrepancies. Implementing secure digital payment systems and employee reporting mechanisms helps ensure transparency and compliance with labor laws. Strong regulatory enforcement combined with education on the legal implications of off-the-books pay reduces the risk of salary fraud and supports fair wage practices.
Reporting Unlawful Salary Practices
Under-the-table pay and off-the-books pay both involve compensating employees without proper documentation, making tax evasion and labor law violations common risks. Reporting unlawful salary practices safeguards workers' rights by ensuring compliance with minimum wage laws, tax regulations, and social security contributions. Legal mechanisms for reporting include whistleblower protections and labor department hotlines, which help enforce transparency and accountability in salary payments.
Safe Alternatives to Cash or Unreported Pay
Safe alternatives to under-the-table or off-the-books pay include prepaid debit cards and electronic payment platforms like PayPal or Venmo, which provide traceable transactions while maintaining privacy. Employers and employees should consider mobile banking apps that offer secure, official records to mitigate risks of unreported income. Utilizing formal payroll services ensures compliance with tax regulations and reduces legal liabilities associated with cash payments.
Important Terms
Shadow payroll
Shadow payroll refers to a legal payroll system used by multinational companies to track employee compensation abroad, contrasting with under-the-table pay and off-the-books pay, which involve undisclosed, illegal wage payments.
Unreported income
Unreported income refers to earnings from under-the-table pay or off-the-books pay that are intentionally concealed from tax authorities to avoid legal reporting and taxation.
Ghost employment
Ghost employment involves listing non-existent employees on payroll, enabling companies to divert salaries as under-the-table pay, which is informal cash compensation avoided in official records. Off-the-books pay represents income not reported to tax authorities, often linked to ghost employment schemes, undermining labor regulations and fiscal transparency.
Cash-in-hand wages
Cash-in-hand wages refer to under-the-table pay, where employees receive unreported cash compensation not documented in official payroll records, often distinguishing it from off-the-books pay that may still involve partial reporting or informal arrangements.
Black market labor
Black market labor involves under-the-table pay and off-the-books pay, both referring to unreported wages that evade taxes and labor regulations.
Tax evasion
Tax evasion involves illegal practices such as under-the-table pay, where employees receive wages secretly without reporting them to tax authorities, and off-the-books pay, which refers to compensating workers without any official documentation or payroll records. Both forms of hidden income result in significant revenue losses for governments and undermine labor protections and social security systems.
Informal employment
Informal employment often involves under-the-table pay, which refers to cash wages paid directly without official records, while off-the-books pay encompasses all unreported earnings excluded from formal accounting and taxation.
Envelope payments
Envelope payments refer to cash wages handed directly to employees, often as under-the-table pay that avoids official payroll records, whereas off-the-books pay includes all forms of undeclared compensation not reported to tax authorities.
Noncompliant compensation
Noncompliant compensation often involves under-the-table pay, which is unreported cash given directly to employees, whereas off-the-books pay refers to wages paid without official documentation or payroll records.
Hidden remuneration
Hidden remuneration often refers to under-the-table pay, which involves unreported cash payments, whereas off-the-books pay includes all forms of income deliberately excluded from official accounting records to evade taxes or regulations.
under-the-table pay vs off-the-books pay Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com