Balancing market rate with internal equity ensures competitive compensation while maintaining fairness among employees within the organization. Companies analyze salary benchmarks to attract talent without disrupting internal pay structures. This approach helps prevent dissatisfaction and turnover by aligning external competitiveness with internal consistency.
Table of Comparison
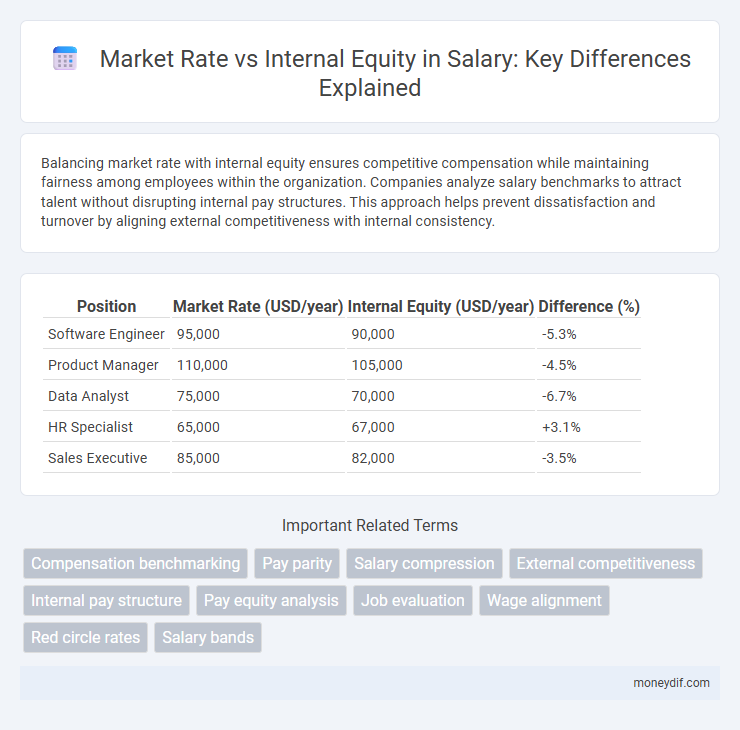
| Position | Market Rate (USD/year) | Internal Equity (USD/year) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Engineer | 95,000 | 90,000 | -5.3% |
| Product Manager | 110,000 | 105,000 | -4.5% |
| Data Analyst | 75,000 | 70,000 | -6.7% |
| HR Specialist | 65,000 | 67,000 | +3.1% |
| Sales Executive | 85,000 | 82,000 | -3.5% |
Understanding Market Rate: Definition and Importance
Market rate refers to the typical compensation for a specific role within a geographic area and industry, reflecting current supply and demand dynamics. Understanding market rate is crucial for organizations to remain competitive in attracting talent while ensuring fairness in employee remuneration. Aligning salaries with market benchmarks also supports internal equity by balancing external competitiveness with consistent pay structures internally.
What Is Internal Equity in Compensation?
Internal equity in compensation ensures employees within the same organization are paid fairly relative to each other based on their skills, experience, and job responsibilities, preventing pay disparities and promoting workplace fairness. Market rate refers to the competitive salary range for similar roles in the external job market, while internal equity compares pay within the company to maintain consistency and equity. Balancing market rate and internal equity helps organizations attract talent without causing internal pay conflicts or dissatisfaction among employees.
Why Market Rate Matters for Competitive Salaries
Market rate reflects current compensation trends for specific roles within an industry and region, ensuring salaries remain attractive to top talent. Aligning pay with market benchmarks prevents employee turnover by recognizing the external value of skills and experience. Maintaining competitive salaries based on market data supports recruitment efforts and promotes a fair, performance-driven workplace culture.
The Role of Internal Equity in Employee Retention
Internal equity plays a critical role in employee retention by ensuring fair and consistent compensation across similar roles within an organization, which helps prevent dissatisfaction and turnover. When employees perceive salary disparities as unjust compared to peers, even if market rates are competitive, retention rates decline significantly. Maintaining internal equity complements market rate benchmarking to create a balanced compensation strategy that reinforces loyalty and reduces voluntary departures.
Balancing Market Rate and Internal Equity: Key Challenges
Balancing market rate and internal equity requires organizations to align external salary benchmarks with internal pay structures to maintain fairness and competitiveness. Key challenges include addressing disparities between market-driven salary adjustments and existing employee compensation, which can impact morale and retention. Effective strategies involve continuous market analysis combined with transparent communication to ensure pay equity and organizational consistency.
Impact of Market Rate vs Internal Equity on Employee Motivation
Market rate alignment ensures competitive compensation that attracts top talent and reduces turnover, directly boosting employee motivation through perceived external validation. Internal equity fosters a sense of fairness and belonging by maintaining consistent pay among employees with similar roles and performance, which enhances job satisfaction and loyalty. Imbalanced focus on market rate over internal equity can lead to frustration and decreased motivation, as employees may feel undervalued despite competitive salaries.
Strategies for Achieving Internal Pay Equity
Aligning salaries with both market rates and internal equity requires conducting comprehensive pay audits that identify disparities across roles and departments. Implementing structured pay frameworks and transparent compensation policies promotes fairness and mitigates bias in salary decisions. Regularly updating salary data and engaging leadership in equity goals ensure sustainable internal pay equity and enhance employee satisfaction.
When to Prioritize Market Rate Over Internal Equity
Prioritizing market rate over internal equity is essential during talent acquisition to remain competitive and attract top candidates, especially in high-demand industries like technology or finance. When external market data indicates significant salary inflation, aligning pay with market rates helps prevent turnover and ensures organizational relevance. Companies experiencing rapid growth or entering new markets may also emphasize market rates to secure specialized skills before addressing internal pay structures.
Common Mistakes in Managing Market Rate and Internal Equity
Common mistakes in managing market rate and internal equity include overemphasizing external salary benchmarks while neglecting internal role value, leading to pay disparities and decreased employee morale. Failure to regularly update compensation data results in outdated salary structures that neither attract talent nor retain current employees, disrupting workforce stability. Ignoring transparent communication about pay decisions often fuels mistrust and disengagement, undermining organizational equity and competitiveness.
Best Practices for Aligning Market Rate with Internal Equity
Best practices for aligning market rate with internal equity involve conducting regular salary benchmarking using reliable industry data to ensure competitive pay while maintaining fairness within the organization. Implementing transparent pay structures and clear job leveling frameworks supports consistency and equity in compensation decisions. Incorporating employee feedback and periodic compensation audits helps identify discrepancies and fosters trust in the organization's pay philosophy.
Important Terms
Compensation benchmarking
Compensation benchmarking ensures alignment between market rate competitiveness and internal equity to attract and retain top talent while maintaining fair pay structures.
Pay parity
Pay parity ensures employee compensation aligns with both competitive market rates and internal equity to maintain fairness and retain talent.
Salary compression
Salary compression occurs when internal equity among employees is undermined because market rates for similar roles rise faster than existing salaries, narrowing pay differentials and impacting retention.
External competitiveness
External competitiveness ensures that employee compensation aligns with market rates, attracting and retaining top talent by offering salaries comparable to industry standards. Balancing this with internal equity maintains fairness within the organization, preventing pay disparities that could harm employee morale and productivity.
Internal pay structure
Internal pay structures balance market rate competitiveness with internal equity to ensure fair compensation and retain talent.
Pay equity analysis
Pay equity analysis compares market rate compensation with internal equity to ensure fair and competitive employee salaries.
Job evaluation
Job evaluation aligns internal equity by assessing roles based on responsibilities and skills, while market rate analysis ensures compensation competitiveness against external industry standards.
Wage alignment
Wage alignment ensures competitive market rate compensation while maintaining internal equity to promote fairness and employee satisfaction.
Red circle rates
Red circle rates occur when employee salaries exceed market rates yet are maintained to preserve internal equity and avoid pay compression.
Salary bands
Salary bands ensure competitive market rates while maintaining internal equity by aligning compensation structures with industry benchmarks and organizational pay fairness.
market rate vs internal equity Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com