A salary band defines the range of compensation allocated for a specific job category, offering flexibility in pay based on experience and performance. Pay grade, on the other hand, establishes a fixed level within the organizational hierarchy, setting standard salary levels tied to job responsibilities and seniority. Understanding the distinction between salary bands and pay grades helps employers maintain equitable and competitive compensation structures.
Table of Comparison
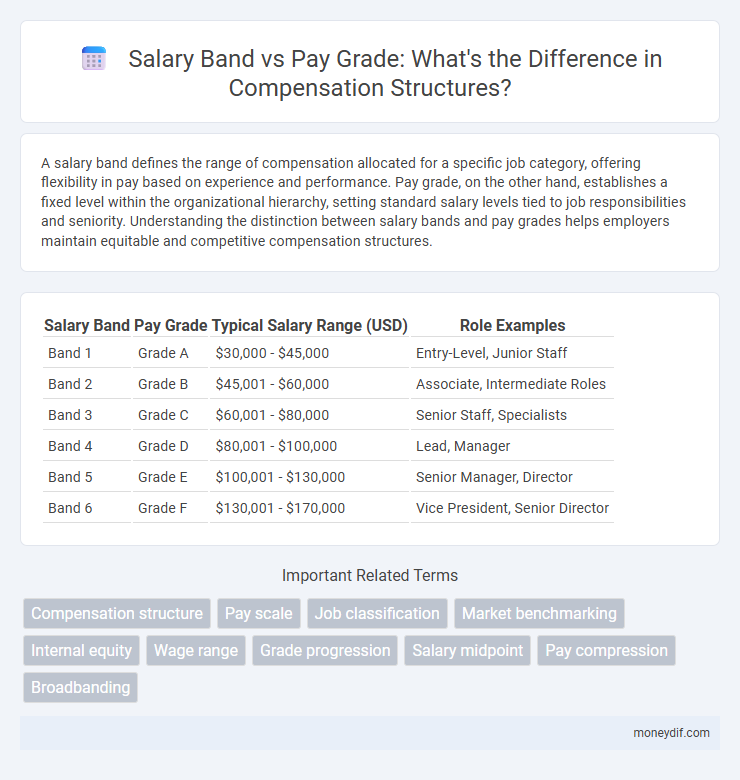
| Salary Band | Pay Grade | Typical Salary Range (USD) | Role Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band 1 | Grade A | $30,000 - $45,000 | Entry-Level, Junior Staff |
| Band 2 | Grade B | $45,001 - $60,000 | Associate, Intermediate Roles |
| Band 3 | Grade C | $60,001 - $80,000 | Senior Staff, Specialists |
| Band 4 | Grade D | $80,001 - $100,000 | Lead, Manager |
| Band 5 | Grade E | $100,001 - $130,000 | Senior Manager, Director |
| Band 6 | Grade F | $130,001 - $170,000 | Vice President, Senior Director |
Understanding Salary Bands and Pay Grades
Salary bands define a range of compensation allocated to specific job roles or levels within an organization, providing flexibility in pay based on experience and performance. Pay grades categorize jobs into hierarchical levels with set salary minimums and maximums, ensuring internal equity and consistent pay structures. Differentiating between salary bands and pay grades helps organizations design effective compensation frameworks that balance market competitiveness and internal fairness.
Key Differences Between Salary Bands and Pay Grades
Salary bands define the range of possible pay for a group of similar jobs, offering flexibility based on experience and performance, while pay grades are structured levels within an organizational hierarchy with fixed pay steps. Salary bands provide broader compensation variability, enabling customized salary offers, whereas pay grades emphasize consistency and equity across employee roles. Understanding these distinctions helps organizations balance competitive compensation with internal pay fairness.
How Salary Bands Work in Modern Organizations
Salary bands define a range of pay rates for specific job categories, providing flexibility within set minimum and maximum limits to accommodate experience and performance variations. Modern organizations use salary bands to standardize compensation, promote internal equity, and support career progression by aligning pay with skills and responsibilities. Pay grades, often linked to salary bands, categorize positions into hierarchical levels, simplifying salary administration and budget planning.
The Structure of Pay Grades Explained
Pay grades are hierarchical levels within an organization's compensation system that define specific salary ranges based on job responsibilities and qualifications. Each pay grade corresponds to a salary band, which outlines the minimum and maximum pay limits for positions within that grade, enabling consistent and equitable compensation management. The structure of pay grades ensures clear progression paths, aligning employee roles with appropriate salary expectations while maintaining internal equity and market competitiveness.
Advantages of Implementing Salary Bands
Implementing salary bands offers companies enhanced flexibility in compensation management by accommodating varying skill levels and experience within the same pay range. This approach improves employee motivation and retention by providing clear pathways for salary growth without necessitating immediate job reclassification. Organizations benefit from streamlined budgeting and increased pay equity, reducing disparities and promoting fairness across similar roles.
Benefits of Pay Grade Systems
Pay grade systems streamline compensation management by grouping jobs with similar responsibilities and qualifications into defined salary ranges, ensuring internal equity and transparency. This structure simplifies salary adjustments, promotes fairness, and supports career progression planning. Organizations benefit from improved budget control and consistent pay practices that align compensation with performance and market standards.
Salary Bands vs Pay Grades: Which Is Right for Your Company?
Salary bands provide a flexible range of compensation tied to job families, allowing companies to adjust pay based on experience and market conditions, while pay grades offer fixed salary steps that ensure consistency and simplify administration. Organizations seeking adaptability in compensation strategies often prefer salary bands to attract and retain diverse talent, whereas those prioritizing structured progression and internal equity may lean toward pay grades. Evaluating company size, industry standards, and workforce complexity helps determine whether salary bands or pay grades best align with organizational goals.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Retention
Salary bands offer broader ranges that accommodate skill development and market adjustments, enhancing employee motivation by providing clear pathways for growth. Pay grades establish structured compensation levels that ensure internal equity, reducing turnover through consistent salary frameworks. Combining both systems effectively aligns employee expectations with organizational goals, boosting retention and satisfaction.
Best Practices for Managing Compensation Structures
Salary bands provide flexible ranges that accommodate market variability and employee growth, while pay grades establish fixed levels for roles based on hierarchy and responsibility. Effective compensation management combines clear pay grade frameworks with adaptable salary bands to maintain internal equity and competitiveness. Regular market benchmarking and transparent communication ensure alignment with organizational goals and employee satisfaction.
Future Trends in Salary Bands and Pay Grades
Future trends in salary bands and pay grades emphasize increased flexibility and personalization, leveraging AI-driven compensation analytics to align pay structures with market demands and individual performance. Companies are adopting dynamic salary bands that adjust in real time to inflation and skill scarcity, replacing rigid pay grades to enhance talent retention and acquisition. Embracing transparent pay frameworks supported by data analytics fosters equitable compensation practices and boosts employee engagement in evolving workforce landscapes.
Important Terms
Compensation structure
Compensation structure aligns salary bands with pay grades to ensure equitable salary ranges based on job roles and experience levels.
Pay scale
Salary bands define broad compensation ranges for job categories, while pay grades specify exact pay levels within those bands to ensure structured salary progression.
Job classification
Job classification organizes roles into pay grades that correspond to specific salary bands, ensuring structured and equitable compensation across an organization.
Market benchmarking
Market benchmarking analyzes salary bands by comparing internal pay grades with external market compensation data to ensure competitive and equitable employee remuneration. This process helps organizations align pay structures with industry standards, optimize talent retention, and maintain fair salary distribution.
Internal equity
Internal equity ensures fair compensation by aligning salary bands with corresponding pay grades based on job responsibilities and market benchmarks.
Wage range
Wage range defines the minimum and maximum pay within a salary band, which groups positions by pay grade to ensure consistent compensation structures.
Grade progression
Grade progression aligns pay grades with corresponding salary bands to ensure structured employee compensation growth.
Salary midpoint
Salary midpoint represents the central value within a salary band, indicating the typical pay level for a specific pay grade.
Pay compression
Pay compression occurs when the salary differences between employees in different pay grades narrow due to overlapping salary bands, undermining the hierarchical value of experience or role. Analyzing pay bands and pay grades reveals structural misalignments that can lead to retention challenges and perceived inequities within workforce compensation.
Broadbanding
Broadbanding consolidates multiple traditional salary bands into fewer, wider salary bands to provide greater pay flexibility compared to the rigid structure of pay grades.
salary band vs pay grade Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com