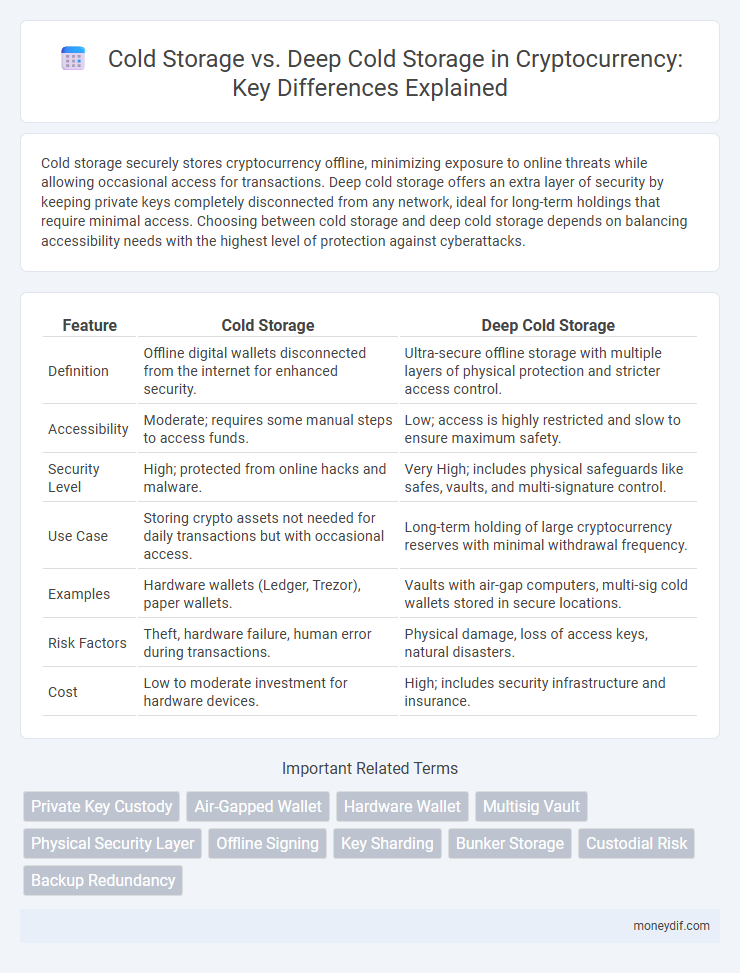
Cold storage securely stores cryptocurrency offline, minimizing exposure to online threats while allowing occasional access for transactions. Deep cold storage offers an extra layer of security by keeping private keys completely disconnected from any network, ideal for long-term holdings that require minimal access. Choosing between cold storage and deep cold storage depends on balancing accessibility needs with the highest level of protection against cyberattacks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cold Storage | Deep Cold Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Offline digital wallets disconnected from the internet for enhanced security. | Ultra-secure offline storage with multiple layers of physical protection and stricter access control. |
| Accessibility | Moderate; requires some manual steps to access funds. | Low; access is highly restricted and slow to ensure maximum safety. |
| Security Level | High; protected from online hacks and malware. | Very High; includes physical safeguards like safes, vaults, and multi-signature control. |
| Use Case | Storing crypto assets not needed for daily transactions but with occasional access. | Long-term holding of large cryptocurrency reserves with minimal withdrawal frequency. |
| Examples | Hardware wallets (Ledger, Trezor), paper wallets. | Vaults with air-gap computers, multi-sig cold wallets stored in secure locations. |
| Risk Factors | Theft, hardware failure, human error during transactions. | Physical damage, loss of access keys, natural disasters. |
| Cost | Low to moderate investment for hardware devices. | High; includes security infrastructure and insurance. |
Understanding Cold Storage in Cryptocurrency
Cold storage in cryptocurrency refers to keeping private keys offline to protect digital assets from online hacks and cyber threats. Deep cold storage enhances security by storing private keys on devices that are never connected to the internet, often using hardware wallets or even paper wallets kept in secure, physical locations. This method significantly reduces exposure to phishing attacks, malware, and unauthorized access, ensuring long-term asset safety.
What is Deep Cold Storage?
Deep cold storage is an advanced form of cryptocurrency cold storage that offers enhanced security by keeping private keys completely offline for extended periods. Unlike regular cold storage, which may involve hardware wallets connected occasionally to online devices, deep cold storage involves isolating keys in environments with no digital footprint or network access, often using air-gapped computers or physical media stored in secure locations like vaults. This method significantly reduces the risk of hacking, malware, and unauthorized access, making it ideal for long-term asset preservation.
Key Differences Between Cold Storage and Deep Cold Storage
Cold Storage involves keeping cryptocurrency private keys offline on devices such as hardware wallets or USB drives, providing strong protection against online hacks. Deep Cold Storage escalates security by storing keys in more isolated environments like air-gapped computers or physical vaults, often with multi-signature requirements, minimizing risks from physical theft or network exposure. The key differences lie in the level of isolation and accessibility, where Deep Cold Storage sacrifices convenience for enhanced long-term security and tamper resistance.
Security Benefits of Cold Storage
Cold Storage significantly enhances cryptocurrency security by isolating private keys from internet access, thereby reducing exposure to hacking and malware threats. Deep Cold Storage takes this protection further by storing keys on devices kept completely offline and often in physically secure locations, making unauthorized access nearly impossible. Both methods prioritize safeguarding digital assets, but Deep Cold Storage offers an elevated level of risk mitigation against cyber-attacks and physical theft.
Enhanced Protection with Deep Cold Storage
Deep Cold Storage offers enhanced protection by storing cryptocurrency private keys in completely offline environments, eliminating exposure to internet-based threats. Unlike standard cold storage, it uses multi-layered security measures such as air-gapped hardware, encrypted physical media, and geographically dispersed vaults. This approach significantly reduces the risk of hacking, theft, and unauthorized access, making it ideal for long-term, high-value crypto asset preservation.
Accessibility: Cold Storage vs Deep Cold Storage
Cold storage offers relatively easier accessibility for cryptocurrency assets through offline wallets kept in secure physical locations, allowing users to access funds with minimal delay when necessary. Deep cold storage, however, prioritizes maximum security by storing private keys in highly isolated environments such as hardware wallets disconnected from all networks, resulting in significantly limited and slower accessibility to prevent unauthorized access. Choosing between cold storage and deep cold storage depends on balancing the need for rapid access versus enhanced protection against cyber threats.
Use Cases for Cold Storage Solutions
Cold storage solutions in cryptocurrency primarily safeguard large holdings by storing private keys offline, minimizing exposure to hacking risks during routine transactions. Deep cold storage extends this protection by isolating keys even further, often using hardware devices stored in secure geographic locations, ideal for long-term asset preservation with infrequent access requirements. Institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals favor cold storage for balancing security with accessibility, while deep cold storage serves as a vault for assets not needed for active trading or liquidity.
Ideal Scenarios for Deep Cold Storage
Deep cold storage is ideal for institutional investors and long-term holders who require the highest level of security for large cryptocurrency assets with minimal access frequency. It is best suited for assets that do not need regular transactions, such as treasury reserves or endowment funds, where protection against cyber threats and physical theft is paramount. This approach ensures that private keys remain completely offline, significantly reducing the risk of hacking or unauthorized access.
Risks and Limitations of Each Storage Method
Cold storage offers enhanced security by keeping cryptocurrency assets offline, significantly reducing exposure to online hacking threats, but remains vulnerable to physical theft or loss of access due to hardware failure or misplacement of wallets. Deep cold storage provides an even higher security level by storing assets in completely air-gapped environments, minimizing all digital attack vectors, yet it faces increased risks of permanent asset loss due to human error, forgotten keys, or natural disasters without backup solutions. Both methods require stringent risk management practices to balance accessibility and protection, emphasizing the critical importance of secure key management and disaster recovery planning in cryptocurrency asset preservation.
Choosing the Right Storage Method for Your Crypto
Cold storage stores cryptocurrencies offline on hardware wallets or paper wallets, providing strong protection against online hacks while maintaining relatively easy access. Deep cold storage enhances security by using additional offline layers such as air-gapped devices and multi-signature setups, ideal for long-term holdings that rarely require access. Selecting between cold storage and deep cold storage depends on the balance of security needs and frequency of asset access, with deep cold storage suited for institutional investors or large portfolios requiring maximum protection.
Important Terms
Private Key Custody
Private key custody methods differentiate primarily by security and accessibility, with cold storage involving offline wallets like hardware devices, while deep cold storage refers to ultra-secure, air-gapped environments such as physically isolated paper wallets or hardware kept in vaults. Deep cold storage significantly reduces cyberattack risks through minimized digital exposure but sacrifices quick transaction convenience compared to standard cold storage solutions.
Air-Gapped Wallet
Air-gapped wallets provide enhanced security by isolating private keys from internet-connected devices, making them a vital component in cold storage solutions. Compared to deep cold storage, which involves storing keys on hardware kept offline in ultra-secure environments, air-gapped wallets offer a balance between accessibility and protection against remote cyber threats.
Hardware Wallet
Hardware wallets provide secure private key management by isolating keys offline, forming the basis of cold storage solutions that prevent exposure to internet threats. Deep cold storage enhances security by storing hardware wallets in tamper-proof, physically isolated environments, minimizing risks from physical theft and environmental damage.
Multisig Vault
Multisig vaults enhance security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions, making them ideal for cold storage solutions that keep crypto assets offline but accessible with coordinated approvals. Deep cold storage, in contrast, involves storing keys in isolated, air-gapped environments with multi-signature setups to maximize protection against remote threats and physical theft.
Physical Security Layer
Physical security layers in cold storage facilities involve controlled access, temperature monitoring, and robust perimeter defenses to protect perishable goods. Deep cold storage requires enhanced security measures such as reinforced insulation, advanced fire suppression systems, and biometric access controls to maintain ultra-low temperatures and safeguard high-value or sensitive inventory.
Offline Signing
Offline signing involves authorizing transactions on a device completely disconnected from the internet, significantly reducing exposure to cyber threats. Cold storage refers to keeping cryptocurrency private keys offline for security, while deep cold storage extends this concept by storing keys in even more isolated environments, such as air-gapped hardware or physical safes, ensuring maximum protection against hacking and physical theft.
Key Sharding
Key sharding enhances security by splitting cryptographic keys into multiple parts stored separately, reducing single points of failure in cold storage solutions. In deep cold storage, key shards are often distributed across geographically isolated, air-gapped locations to maximize protection against physical and cyber threats.
Bunker Storage
Bunker storage in data centers offers scalable capacity for cold storage, efficiently preserving infrequently accessed data at low cost. Deep cold storage extends these capabilities by providing ultra-low temperature environments optimized for long-term archiving and enhanced data durability.
Custodial Risk
Custodial risk in cold storage involves potential loss or theft of digital assets due to security vulnerabilities in offline wallets, while deep cold storage significantly reduces this risk by using multi-layered encryption and air-gapped hardware, ensuring enhanced protection against cyberattacks. Deep cold storage solutions are typically preferred for institutional investors managing large cryptocurrency holdings due to their superior security protocols and minimized exposure to hacking threats.
Backup Redundancy
Backup redundancy enhances data durability by storing multiple copies across Cold Storage and Deep Cold Storage solutions, with Cold Storage offering quicker access for infrequent retrieval and Deep Cold Storage optimizing cost-efficiency for long-term archiving. Evaluating access frequency and retention duration ensures the strategic balance between redundancy reliability and storage expenditure.
Cold Storage vs Deep Cold Storage Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com