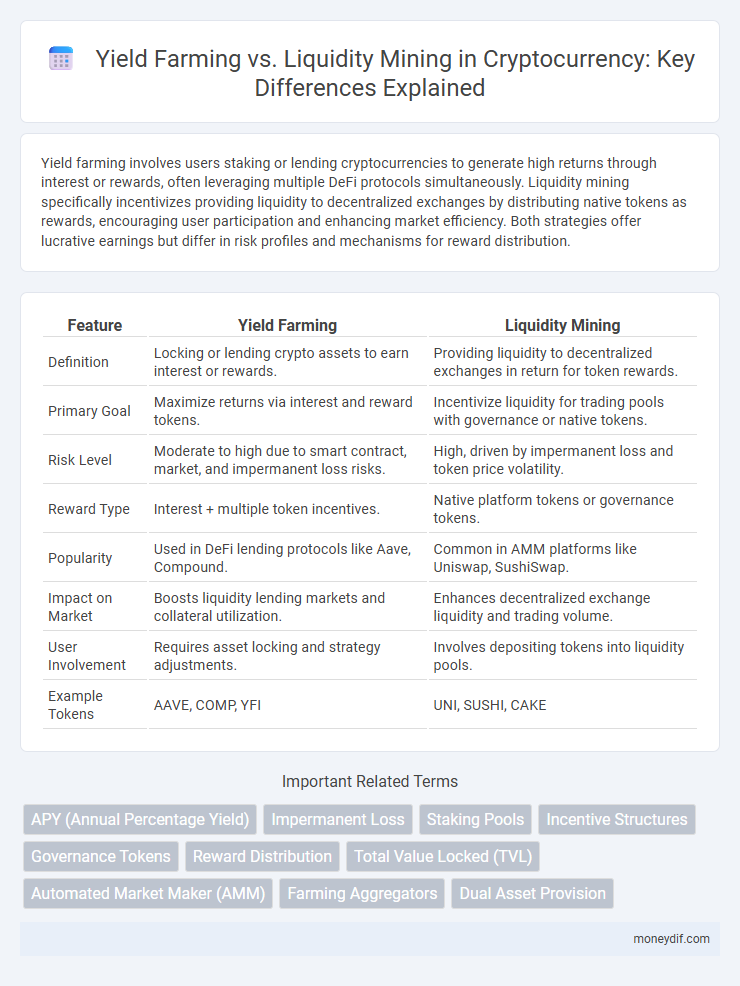
Yield farming involves users staking or lending cryptocurrencies to generate high returns through interest or rewards, often leveraging multiple DeFi protocols simultaneously. Liquidity mining specifically incentivizes providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges by distributing native tokens as rewards, encouraging user participation and enhancing market efficiency. Both strategies offer lucrative earnings but differ in risk profiles and mechanisms for reward distribution.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Yield Farming | Liquidity Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking or lending crypto assets to earn interest or rewards. | Providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges in return for token rewards. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize returns via interest and reward tokens. | Incentivize liquidity for trading pools with governance or native tokens. |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high due to smart contract, market, and impermanent loss risks. | High, driven by impermanent loss and token price volatility. |
| Reward Type | Interest + multiple token incentives. | Native platform tokens or governance tokens. |
| Popularity | Used in DeFi lending protocols like Aave, Compound. | Common in AMM platforms like Uniswap, SushiSwap. |
| Impact on Market | Boosts liquidity lending markets and collateral utilization. | Enhances decentralized exchange liquidity and trading volume. |
| User Involvement | Requires asset locking and strategy adjustments. | Involves depositing tokens into liquidity pools. |
| Example Tokens | AAVE, COMP, YFI | UNI, SUSHI, CAKE |
Yield Farming vs Liquidity Mining: Core Definitions
Yield farming involves users staking or lending cryptocurrencies to earn interest or rewards, often through complex strategies across multiple DeFi platforms. Liquidity mining specifically rewards users with native tokens for providing liquidity to a decentralized exchange or protocol, thereby enhancing market liquidity. While both methods incentivize participation in DeFi ecosystems, yield farming emphasizes maximizing returns through various yield-generating assets, whereas liquidity mining focuses on token rewards tied directly to liquidity provision.
How Yield Farming Works in Crypto
Yield farming in cryptocurrency involves lending or staking digital assets in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to earn rewards, typically paid in tokens. Users deposit their crypto into liquidity pools, enabling platforms to facilitate trading, lending, or borrowing, and in return receive yield generated by fees or additional tokens. The process incentivizes participation by maximizing returns through compound interest and token rewards, driving liquidity and growth in DeFi ecosystems.
Understanding Liquidity Mining Mechanisms
Liquidity mining involves users providing cryptocurrency assets to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols in exchange for rewards, often paid in the platform's native tokens. This mechanism incentivizes liquidity by distributing tokens based on the proportion of assets contributed, enhancing market depth and reducing slippage in trading pools. Understanding the underlying smart contracts and reward distribution models is crucial for optimizing returns and managing risks in liquidity mining strategies.
Key Differences Between Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Yield farming and liquidity mining differ primarily in their reward structures and objectives; yield farming focuses on maximizing returns through various DeFi protocols by strategically staking or lending assets, while liquidity mining specifically incentivizes users to provide liquidity in decentralized exchanges by distributing native tokens as rewards. Yield farming often involves complex strategies across multiple platforms, leveraging interest, fees, and token incentives, whereas liquidity mining typically centers on earning governance tokens for maintaining liquidity pools. Understanding these distinctions helps investors optimize their DeFi participation based on risk tolerance and desired asset exposure.
Pros and Cons of Yield Farming
Yield farming offers high potential returns by allowing users to earn interest or rewards from lending or staking cryptocurrencies, but it often carries risks like smart contract vulnerabilities and price volatility. While liquidity mining incentivizes users to provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges with additional token rewards, yield farming's complexity and varying protocols can lead to unpredictable yields and impermanent loss. Despite its challenges, yield farming remains popular for maximizing passive income in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
Benefits and Risks of Liquidity Mining
Liquidity mining offers the benefit of earning rewards by providing assets to a decentralized exchange's liquidity pool, enhancing market efficiency and generating passive income. Participants face risks such as impermanent loss, where asset price fluctuations reduce returns, and smart contract vulnerabilities that may lead to loss of funds. Proper risk assessment and choosing reputable platforms are essential to maximize the benefits of liquidity mining in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Popular Platforms for Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Popular platforms for yield farming include Aave, Compound, and Yearn Finance, which offer diverse pools with competitive annual percentage yields (APYs). Liquidity mining predominantly thrives on decentralized exchanges like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap, rewarding users with native tokens such as UNI, SUSHI, and CAKE. Both methods leverage smart contracts on Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain networks, driving high-volume decentralized finance (DeFi) activity.
Profitability Comparison: Yield Farming vs Liquidity Mining
Yield farming often offers higher profitability through diverse token rewards and compounding strategies, whereas liquidity mining provides steady returns primarily from trading fees and incentive tokens. Yield farmers can capitalize on volatile market conditions by shifting assets between protocols for optimal yields, while liquidity miners benefit from consistent, lower-risk income streams. Portfolio risk management and market volatility significantly impact the overall returns in both yield farming and liquidity mining.
Security Considerations and Smart Contract Risks
Yield farming and liquidity mining expose participants to significant smart contract risks, including vulnerabilities like coding errors and exploits that can lead to loss of funds. Security considerations emphasize the importance of auditing protocols, using well-established platforms, and diversifying investments to mitigate risk. Understanding the difference in incentive structures and the potential for impermanent loss is crucial for managing security in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Future Trends: Evolution of Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Yield farming and liquidity mining are evolving with increasing integration of cross-chain protocols and automated yield optimization tools to maximize returns. The future will see enhanced DeFi governance mechanisms and AI-driven strategies reshaping how users participate in liquidity provision. Innovations like dynamic reward allocations and multi-asset staking platforms are set to redefine user engagement and profitability in decentralized finance.
Important Terms
APY (Annual Percentage Yield)
APY (Annual Percentage Yield) quantifies the real rate of return on yield farming by accounting for compound interest, whereas liquidity mining typically offers token rewards without automatically compounding returns. Yield farming often results in higher APY due to reinvestment strategies, while liquidity mining provides direct incentives that may enhance overall profitability depending on market token appreciation.
Impermanent Loss
Impermanent loss occurs when the value of tokens provided as liquidity in yield farming changes relative to holding them, causing potential losses compared to simply holding the assets; this risk is crucial in yield farming strategies where liquidity providers earn fees but face price divergence. Liquidity mining enhances yield farming by distributing additional rewards or governance tokens, incentivizing participation despite impermanent loss, thereby balancing risk and reward for liquidity providers.
Staking Pools
Staking pools aggregate cryptocurrency holdings to increase earning potential through yield farming by locking assets in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols for interest or rewards, whereas liquidity mining incentivizes users to provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges in return for native tokens and trading fees. Both methods enhance passive income but differ in risk exposure and reward structures within DeFi ecosystems.
Incentive Structures
Yield farming and liquidity mining both reward participants with cryptocurrency tokens for providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, but yield farming typically involves optimizing returns across multiple platforms and strategies, while liquidity mining focuses on earning native project tokens as direct incentives. Effective incentive structures balance token emission rates and user engagement to ensure sustainable liquidity without causing excessive inflation or market volatility.
Governance Tokens
Governance tokens empower holders with voting rights on protocol decisions, directly influencing decentralized finance (DeFi) project development and incentive structures. Yield farming rewards users for providing liquidity or staking assets, while liquidity mining specifically distributes governance tokens as incentives, aligning user participation with governance engagement in DeFi ecosystems.
Reward Distribution
Reward distribution in yield farming typically involves earning interest or project tokens proportionate to the amount of cryptocurrency staked, incentivizing long-term liquidity provision. In liquidity mining, rewards are often distributed more aggressively and frequently, targeting users who supply liquidity to decentralized exchanges, thus promoting platform growth and token adoption.
Total Value Locked (TVL)
Total Value Locked (TVL) represents the aggregate amount of assets staked or locked in DeFi protocols, serving as a key metric to evaluate the scale and security of yield farming and liquidity mining activities. Yield farming typically involves locking assets to earn rewards based on protocol token incentives, while liquidity mining specifically rewards users for providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges, both contributing significantly to TVL fluctuations.
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) utilize liquidity pools to enable decentralized trading without order books, which are integral to both yield farming and liquidity mining strategies. Yield farming involves users staking or lending crypto assets within AMMs to earn interest and rewards, while liquidity mining specifically incentivizes provision of liquidity by distributing governance tokens proportionally to the amount and duration of capital supplied.
Farming Aggregators
Farming aggregators streamline DeFi yield strategies by automating asset allocation between yield farming and liquidity mining protocols, maximizing annual percentage yields (APYs) while minimizing gas fees and impermanent loss. These platforms harness smart contract algorithms to optimize rewards from staking tokens in liquidity pools and yield farming farms across decentralized exchanges like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap.
Dual Asset Provision
Dual Asset Provision integrates capital into two distinct digital assets simultaneously, enhancing yield farming strategies by providing diversified liquidity exposure. Yield farmers leverage this approach to maximize returns through compounded rewards, whereas liquidity mining focuses more on incentivizing pool participation with token bonuses linked directly to specific asset pairs.
Yield Farming vs Liquidity Mining Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com