Pay bands group multiple pay grades into broader ranges that allow for greater salary flexibility within an organization, accommodating a diverse set of roles and experience levels. Pay grades define specific salary levels based on job responsibilities and qualifications, establishing a clear, structured compensation framework. Understanding the difference between pay bands and pay grades helps employers design competitive salary structures and manage employee expectations effectively.
Table of Comparison
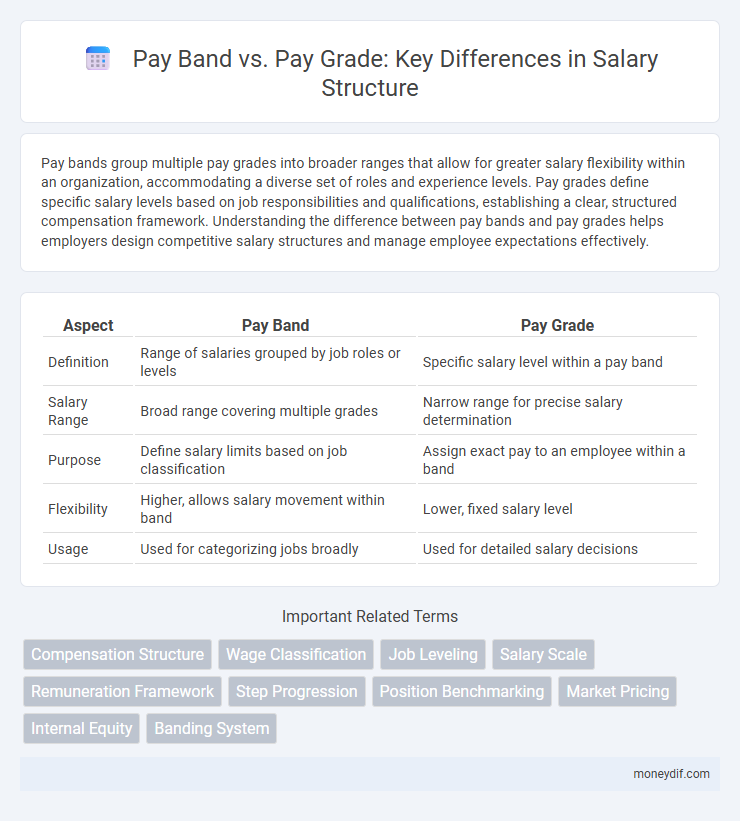
| Aspect | Pay Band | Pay Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Range of salaries grouped by job roles or levels | Specific salary level within a pay band |
| Salary Range | Broad range covering multiple grades | Narrow range for precise salary determination |
| Purpose | Define salary limits based on job classification | Assign exact pay to an employee within a band |
| Flexibility | Higher, allows salary movement within band | Lower, fixed salary level |
| Usage | Used for categorizing jobs broadly | Used for detailed salary decisions |
Understanding Pay Band and Pay Grade
Pay bands categorize salary ranges based on job roles and market rates, allowing flexibility within a broad compensation framework. Pay grades define specific salary levels tied to job responsibilities, qualifications, and organizational hierarchy, offering more structured progression. Understanding the distinction helps employees and employers align compensation strategies with career development and market competitiveness.
Key Differences Between Pay Band and Pay Grade
Pay bands group multiple salary ranges into broader categories, offering flexibility in compensation based on skill and performance, while pay grades assign fixed salary levels tied to specific job titles or responsibilities. Pay bands promote internal equity and career growth by accommodating market adjustments, whereas pay grades provide structured, transparent salary progression. Organizations choosing pay bands often benefit from adaptability in pay decisions, contrasting with the rigidity and predictability of pay grade systems.
Advantages of Pay Band Structures
Pay band structures offer increased flexibility by consolidating multiple pay grades into broader salary ranges, enabling organizations to reward employee performance and skills more dynamically. This system simplifies salary administration, reduces hierarchical rigidity, and promotes internal equity by focusing on job value rather than rigid grade levels. Employers benefit from improved workforce motivation and retention due to clear pathways for salary growth within broader bands.
Benefits of Pay Grade Systems
Pay grade systems provide clear career progression by defining specific salary ranges tied to job roles and responsibilities, enhancing transparency and fairness in compensation. They simplify budget management for organizations by standardizing pay levels across departments and facilitating consistent salary administration. Employees benefit from predictable pay increments and recognition of skills and experience within the pay grade framework, promoting motivation and retention.
Factors Influencing Pay Band and Pay Grade Decisions
Factors influencing pay band and pay grade decisions include market salary data, job responsibilities, and organizational hierarchy, which ensure competitive compensation and internal equity. Employee qualifications, performance levels, and cost-of-living adjustments also play critical roles in defining pay structures. Legal regulations and industry standards further shape pay band and grade classifications to maintain compliance and attract talent.
How Pay Bands Affect Career Progression
Pay bands offer flexible salary ranges that enable employees to progress within a broad compensation spectrum based on performance and skill development. Unlike rigid pay grades, pay bands encourage career growth by allowing faster salary increases and promoting lateral moves without immediate job title changes. This flexibility fosters continuous development and motivation, aligning compensation with evolving roles and responsibilities.
Pay Grades and Fair Compensation Practices
Pay grades establish structured salary ranges based on job responsibilities, experience, and qualifications, ensuring consistency and fairness in compensation. Implementing fair compensation practices within pay grades promotes equity by aligning employee pay with market standards and internal role value. Organizations use pay grades to facilitate transparent salary decisions and support employee retention through equitable pay frameworks.
Pay Band vs Pay Grade: Which Is More Flexible?
Pay bands offer greater flexibility than pay grades by encompassing a wider range of salaries within a single category, allowing employers to adjust compensation based on skills, experience, and market conditions without the need for formal reclassification. Pay grades typically have fixed salary ranges tied to specific job levels, limiting adaptability but ensuring consistency in compensation structures. Organizations seeking dynamic wage management often prefer pay bands for their ability to accommodate diverse employee competencies and evolving business needs.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Retention
Pay bands offer broader salary ranges that encourage employee motivation by providing flexibility for skill growth and performance-based pay increases within a category. Pay grades establish fixed salary levels that enhance retention through clear, structured compensation paths and predictable pay progression. Organizations using pay bands often see improved engagement, while those with pay grades benefit from stability and transparency in employee compensation.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Organization
Selecting the optimal salary structure involves understanding the distinctions between pay bands and pay grades to align with organizational goals and workforce dynamics. Pay bands offer flexibility by encompassing a broad range of salaries within a category, supporting lateral career movement and merit-based increases, while pay grades provide a more rigid, hierarchical framework with defined salary ranges for each position level. Organizations prioritizing scalability and adaptability often favor pay bands, whereas those emphasizing clear job classifications and control may opt for pay grades to maintain equity and transparency in compensation.
Important Terms
Compensation Structure
Compensation structures differentiate pay bands, which set salary ranges for groups of jobs based on market data, from pay grades, which classify positions by internal value and job evaluation criteria. Pay bands offer flexibility in salary progression, while pay grades ensure hierarchical consistency and equity across organizational roles.
Wage Classification
Wage classification distinguishes employee compensation by organizing pay structures into pay bands, which cover a range of salaries, and pay grades, which define specific salary steps within those bands for consistent and equitable pay management.
Job Leveling
Job leveling defines the hierarchy of roles within an organization by categorizing positions into pay grades based on skill and responsibility, while pay bands group multiple pay grades to provide salary ranges that accommodate market competitiveness and employee progression.
Salary Scale
Salary scale varies significantly between pay bands, which define broad salary ranges based on job categories, and pay grades, which specify precise salary levels within those bands reflecting employee experience and performance.
Remuneration Framework
A remuneration framework organizes employee compensation using pay bands and pay grades to reflect job levels and salary ranges. Pay bands encompass a broader range of salaries for multiple roles, promoting flexibility, while pay grades define precise salary steps within a narrower scope based on job complexity and hierarchy.
Step Progression
Step progression refers to the incremental salary increases employees receive within a specific pay grade, reflecting tenure, performance, or skill development. Pay bands encompass multiple pay grades and offer a broader salary range with more flexibility, while pay grades provide structured levels with fixed step increments tied to job responsibilities and experience.
Position Benchmarking
Position benchmarking compares pay bands and pay grades to align compensation structures with industry standards and ensure equitable employee remuneration.
Market Pricing
Market pricing aligns pay bands with external salary data to ensure competitive compensation, while pay grades establish internal hierarchies based on job value and organizational structure.
Internal Equity
Internal equity ensures fair compensation by aligning pay bands with corresponding pay grades based on job responsibilities and market benchmarks.
Banding System
The Banding System consolidates multiple pay grades into broader pay bands to streamline salary structures and enhance career progression clarity within organizations.
Pay Band vs Pay Grade Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com