Fixed salary provides employees with consistent, predictable income which enhances financial stability and budgeting ease. Variable pay, often tied to performance metrics or company profits, motivates productivity and aligns employee efforts with organizational goals. Combining both pay structures can balance security with incentives, driving engagement and rewarding achievement.
Table of Comparison
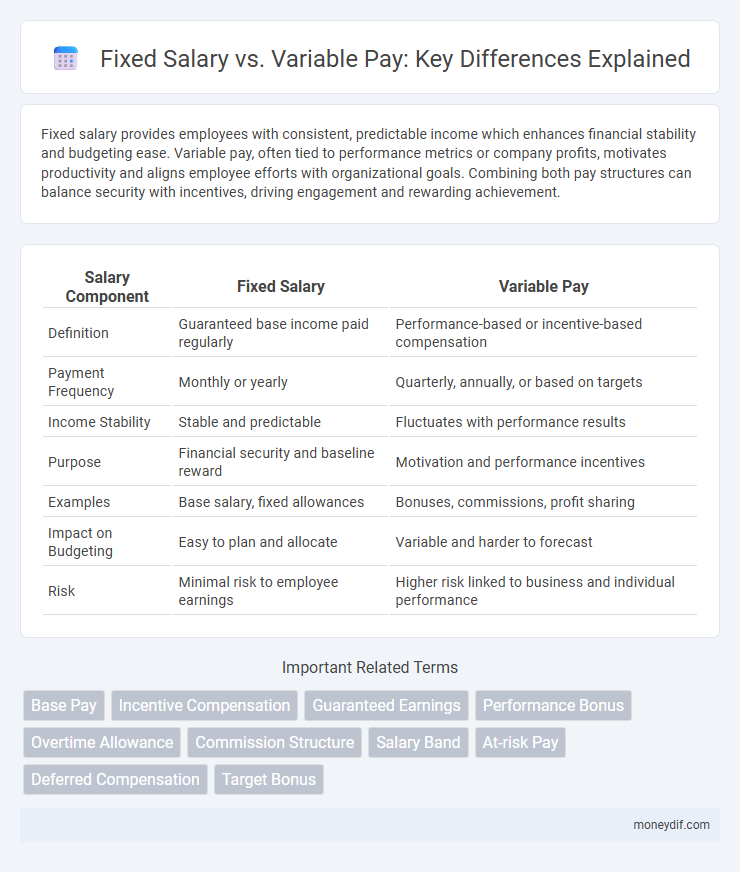
| Salary Component | Fixed Salary | Variable Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guaranteed base income paid regularly | Performance-based or incentive-based compensation |
| Payment Frequency | Monthly or yearly | Quarterly, annually, or based on targets |
| Income Stability | Stable and predictable | Fluctuates with performance results |
| Purpose | Financial security and baseline reward | Motivation and performance incentives |
| Examples | Base salary, fixed allowances | Bonuses, commissions, profit sharing |
| Impact on Budgeting | Easy to plan and allocate | Variable and harder to forecast |
| Risk | Minimal risk to employee earnings | Higher risk linked to business and individual performance |
Understanding Fixed Salary and Variable Pay
Fixed salary provides employees with a consistent, predictable income based on a set amount, ensuring financial stability and easier budgeting. Variable pay fluctuates according to individual or company performance metrics, such as bonuses, commissions, or profit-sharing, incentivizing higher productivity and goal achievement. Understanding the balance between fixed salary and variable pay is crucial for both employers and employees to align compensation strategies with organizational objectives and personal financial goals.
Key Differences Between Fixed Salary and Variable Pay
Fixed salary refers to a predetermined, consistent amount of compensation paid regularly regardless of performance, providing financial stability and predictable income. Variable pay, such as bonuses or commissions, fluctuates based on individual, team, or company performance metrics, aligning employee incentives with organizational goals. Key differences include payment consistency, motivation impact, and risk distribution, with fixed salary offering security while variable pay drives performance and rewards achievement.
Advantages of Fixed Salary Structures
Fixed salary structures provide employees with consistent and predictable income, enhancing financial stability and budgeting ease. This compensation model fosters employee loyalty and reduces turnover by minimizing income uncertainty. Employers benefit from streamlined payroll administration and clearer budgeting forecasts, improving overall financial planning.
Benefits of Variable Pay Systems
Variable pay systems enhance employee motivation by directly linking compensation to performance outcomes, leading to increased productivity and goal alignment. These systems offer organizations flexibility in managing labor costs, adjusting payouts based on business results without increasing fixed expenses. Variable pay also promotes a culture of accountability and incentivizes innovation by rewarding individual and team achievements effectively.
Challenges of Fixed Salary Arrangements
Fixed salary arrangements pose challenges such as limited motivation for employees to exceed performance expectations, leading to potential stagnation in productivity. These rigid structures can also hinder financial flexibility for employers during economic downturns or fluctuating business demands. Furthermore, fixed salaries often fail to account for individual contributions, reducing incentives for skill development and innovation.
Drawbacks of Variable Pay Models
Variable pay models introduce financial uncertainty for employees due to fluctuating monthly earnings tied to performance metrics. This inconsistency can lead to stress and reduced job satisfaction, as income unpredictability hampers effective financial planning. Moreover, variable pay systems may foster unhealthy competition, diminishing teamwork and collaboration within organizations.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Performance
Fixed salary provides employees with financial stability and predictability, which can enhance job satisfaction and reduce stress, promoting consistent performance. Variable pay, tied to individual or team achievements, directly incentivizes higher productivity and goal attainment by aligning rewards with performance outcomes. Combining both approaches often maximizes motivation by balancing security with performance-driven rewards.
Industry Trends in Compensation Strategies
Industry trends reveal a growing shift towards variable pay structures to drive performance and align employee incentives with company goals, particularly in technology and sales sectors. Fixed salary remains essential for financial stability, but organizations increasingly blend it with bonuses, commission, and profit-sharing to boost motivation and retain top talent. Data from Mercer's 2024 Global Talent Trends shows that 67% of companies now integrate variable compensation elements to foster agility in competitive markets.
Choosing the Right Pay Structure for Your Business
Selecting the optimal pay structure requires balancing fixed salary stability with variable pay incentives to motivate performance and manage costs. A fixed salary ensures predictable expenses and attracts talent seeking financial security, while variable pay aligns compensation with individual or company achievements, driving productivity and goal attainment. Businesses must assess industry standards, employee roles, and financial goals to design a compensation model that optimally supports retention and growth.
Future Outlook: Evolving Pay Models in the Workplace
Fixed salary structures provide stability and predictable income, while variable pay offers performance-based incentives that align with company goals. Future pay models increasingly integrate hybrid compensation, combining base salary with bonuses, stock options, and profit-sharing to enhance employee motivation and retention. Advanced analytics and AI-driven performance metrics are shaping personalized pay strategies, making compensation more adaptive to individual and market dynamics.
Important Terms
Base Pay
Base pay refers to the fixed salary component of total compensation, excluding variable pay such as bonuses or commissions.
Incentive Compensation
Incentive compensation balances fixed salary and variable pay to motivate performance while ensuring financial stability; fixed salary provides consistent income, whereas variable pay such as bonuses or commissions aligns employee rewards with individual or company achievements. Optimizing this mix enhances employee engagement, drives productivity, and supports business goals by linking compensation directly to measurable results.
Guaranteed Earnings
Guaranteed earnings consist of a fixed salary that provides financial stability, while variable pay offers performance-based incentives to enhance overall compensation.
Performance Bonus
Performance bonuses directly increase variable pay, providing employees with financial incentives beyond their fixed salary to reward achievements and drive productivity.
Overtime Allowance
Overtime allowance is typically calculated based on fixed salary components and does not usually apply to variable pay, which varies according to performance or output.
Commission Structure
Commission structure often balances a fixed salary with variable pay to incentivize employee performance while ensuring financial stability. Variable pay, usually a percentage of sales or profits, motivates higher productivity, whereas a fixed salary offers consistent income regardless of fluctuating sales outcomes.
Salary Band
Salary bands define the structured range of fixed salary an employee can earn, providing clear benchmarks for base compensation within a role. Variable pay supplements the fixed salary, offering performance-based incentives such as bonuses or commissions that fluctuate according to individual or company performance metrics.
At-risk Pay
At-risk pay combines fixed salary with variable pay components tied to performance metrics to incentivize employee productivity and align compensation with company goals.
Deferred Compensation
Deferred compensation plans allow employees to postpone a portion of their fixed salary or variable pay to a future date, often for tax advantages or retirement savings. Comparing fixed salary and variable pay, deferred compensation provides a strategic mechanism for managing income stability and long-term financial planning, balancing guaranteed earnings with performance-based incentives.
Target Bonus
Target bonus is a variable pay component designed to complement fixed salary by incentivizing performance-based compensation.
Fixed salary vs Variable pay Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com