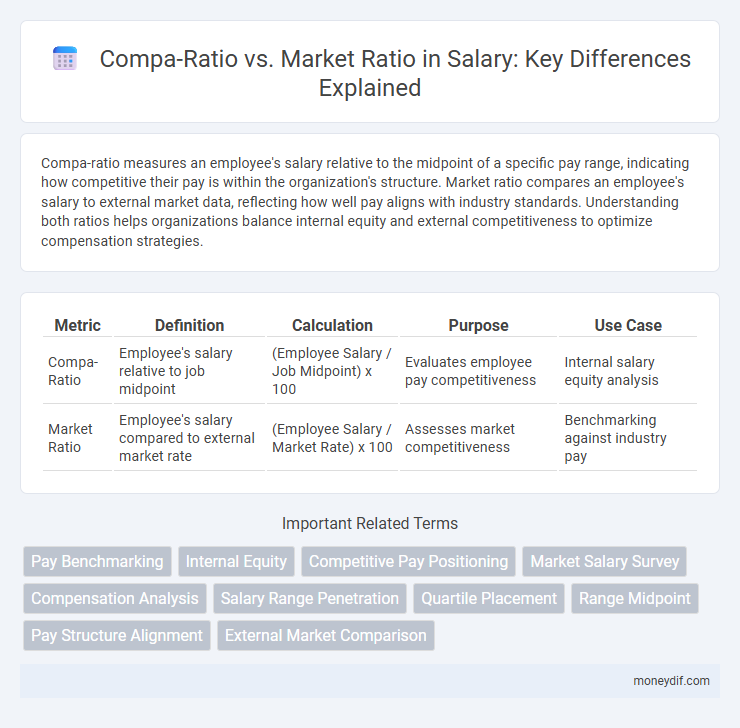
Compa-ratio measures an employee's salary relative to the midpoint of a specific pay range, indicating how competitive their pay is within the organization's structure. Market ratio compares an employee's salary to external market data, reflecting how well pay aligns with industry standards. Understanding both ratios helps organizations balance internal equity and external competitiveness to optimize compensation strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Metric | Definition | Calculation | Purpose | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compa-Ratio | Employee's salary relative to job midpoint | (Employee Salary / Job Midpoint) x 100 | Evaluates employee pay competitiveness | Internal salary equity analysis |
| Market Ratio | Employee's salary compared to external market rate | (Employee Salary / Market Rate) x 100 | Assesses market competitiveness | Benchmarking against industry pay |
Understanding Compa-Ratio: A Quick Overview
Compa-ratio is a key metric in compensation management that compares an employee's current salary to the midpoint of the market salary range, offering insight into pay competitiveness and internal equity. A compa-ratio of 1.0 indicates pay alignment with the market median, while ratios below or above 1.0 signal underpayment or premium pay, respectively. Understanding compa-ratio helps organizations make informed salary decisions, ensuring fair compensation and aiding in talent retention.
Market Ratio Explained: Key Concepts
Market Ratio measures an employee's salary relative to the market median pay for comparable roles, calculated by dividing the individual's salary by the market rate. This ratio helps organizations assess competitiveness in compensation and identify if pay is aligned with current market trends. Understanding Market Ratio enables businesses to attract and retain talent by ensuring salaries are aligned with industry standards.
How Compa-Ratio and Market Ratio Differ
Compa-Ratio measures an employee's current salary relative to the midpoint of the internal pay range, reflecting internal equity and compensation strategy effectiveness. Market Ratio compares the employee's salary to external market pay rates, indicating competitiveness in attracting and retaining talent. The key difference lies in Compa-Ratio's focus on internal salary structures versus Market Ratio's emphasis on external market benchmarking.
Calculating Compa-Ratio: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating compa-ratio involves dividing an employee's current salary by the midpoint of the salary range for their job position, expressed as a decimal or percentage. For example, if an employee earns $55,000 and the midpoint salary for their role is $50,000, the compa-ratio is 1.1 or 110%, indicating their pay is above the market midpoint. This metric helps organizations assess pay equity and make informed compensation decisions based on internal pay position relative to market benchmarks.
Determining Market Ratio: Methods and Metrics
Determining the market ratio involves comparing an employee's salary to external market data using tools like salary surveys, industry benchmarks, and compensation databases. Key metrics include median salary, percentiles (25th, 50th, 75th), and total cash compensation to assess competitiveness. Accurate market ratio calculations enable organizations to align pay structures with market trends and enhance talent retention strategies.
The Role of Compa-Ratio in Salary Benchmarking
Compa-ratio plays a critical role in salary benchmarking by quantifying an employee's pay relative to the midpoint of the market salary range, providing a clear measure of competitiveness and internal equity. This metric allows organizations to assess whether compensation levels align with market standards and make informed adjustments to retain top talent. Unlike market ratio, which compares salary to the overall market average, compa-ratio emphasizes position within the pay range, facilitating precise salary management strategies.
Market Ratio: Aligning Pay with Industry Standards
Market ratio measures an employee's salary relative to the median pay for similar roles in the industry, ensuring compensation stays competitive and aligned with market standards. This metric helps organizations benchmark salaries against industry trends, attracting and retaining top talent. Using market ratio supports strategic pay decisions by reflecting external market pressures and maintaining internal equity.
Advantages and Limitations of Compa-Ratio
Compa-ratio provides a clear measure of how an employee's salary compares to the midpoint of a pay range, facilitating internal equity and performance-based pay adjustments. It helps organizations identify underpaid or overpaid employees relative to market benchmarks, promoting fair compensation practices. However, compa-ratio may overlook external market trends and does not account for factors like skill scarcity or geographic pay differences, limiting its effectiveness as a standalone metric.
When to Use Market Ratio vs Compa-Ratio
Market ratio is ideal for benchmarking salaries against external market data to ensure competitiveness and attract talent. Compa-ratio is best used internally to assess employee pay relative to midpoint salary ranges, supporting equitable compensation decisions. Combining both metrics provides a comprehensive understanding of pay alignment within the organization and the broader labor market.
Strategic Salary Decisions: Combining Both Ratios
Strategic salary decisions benefit from integrating both Compa-Ratio and Market Ratio metrics to balance internal equity and external competitiveness. Compa-Ratio assesses an employee's pay relative to the midpoint of the internal pay range, while Market Ratio compares salary against external market benchmarks. Using both ratios enables organizations to optimize compensation strategies, ensuring fair employee rewards and attracting top talent in the industry.
Important Terms
Pay Benchmarking
Pay benchmarking evaluates employee compensation by comparing Compa-Ratio, which measures an individual's salary relative to the internal pay range midpoint, against Market Ratio, reflecting salary positioning against external market data. Analyzing these two metrics helps organizations ensure competitive pay structures, optimize talent retention, and maintain equitable compensation aligned with industry standards.
Internal Equity
Internal equity ensures fair employee compensation by comparing Compa-Ratio, which measures an individual's pay relative to the internal pay range midpoint, against Market Ratio, which benchmarks salaries against external market data to maintain competitive and equitable pay structures.
Competitive Pay Positioning
Competitive pay positioning evaluates employee salaries by comparing the Compa-Ratio, which measures an individual's pay relative to the midpoint of the internal pay range, against the Market Ratio, reflecting pay relative to external market benchmarks. Aligning Compa-Ratios with Market Ratios ensures compensation competitiveness while maintaining internal equity and budget control.
Market Salary Survey
Market Salary Surveys analyze Compa-Ratio and Market Ratio to benchmark employee compensation against industry standards, ensuring competitive and equitable pay structures.
Compensation Analysis
Compa-ratio evaluates an employee's current salary relative to the midpoint of a defined pay range, offering insight into pay competitiveness within the organization. Market ratio compares the employee's salary against external market rates, enabling companies to align compensation strategies with industry standards.
Salary Range Penetration
Salary range penetration measures an employee's position within a pay range, while compa-ratio compares individual salary to the midpoint of the salary range, and market ratio evaluates salary relative to the external market rate.
Quartile Placement
Quartile placement categorizes employee salaries based on Compa-Ratio relative to Market Ratio benchmarks, highlighting compensation competitiveness within market salary distributions.
Range Midpoint
The range midpoint represents the midpoint of a pay range and serves as a reference point for calculating Compa-Ratio, which compares an employee's salary to the market ratio, indicating competitive positioning within market pay data.
Pay Structure Alignment
Pay structure alignment ensures internal equity and external competitiveness by comparing compa-ratio, which measures an employee's current pay relative to their job's midpoint, against the market ratio that reflects prevailing industry salary benchmarks. Evaluating discrepancies between compa-ratios and market ratios helps organizations calibrate compensation strategies to attract, retain, and reward talent effectively.
External Market Comparison
External market comparison evaluates employee compensation by analyzing Compa-Ratio against Market Ratio to align pay structures with industry standards.
Compa-Ratio vs Market Ratio Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com