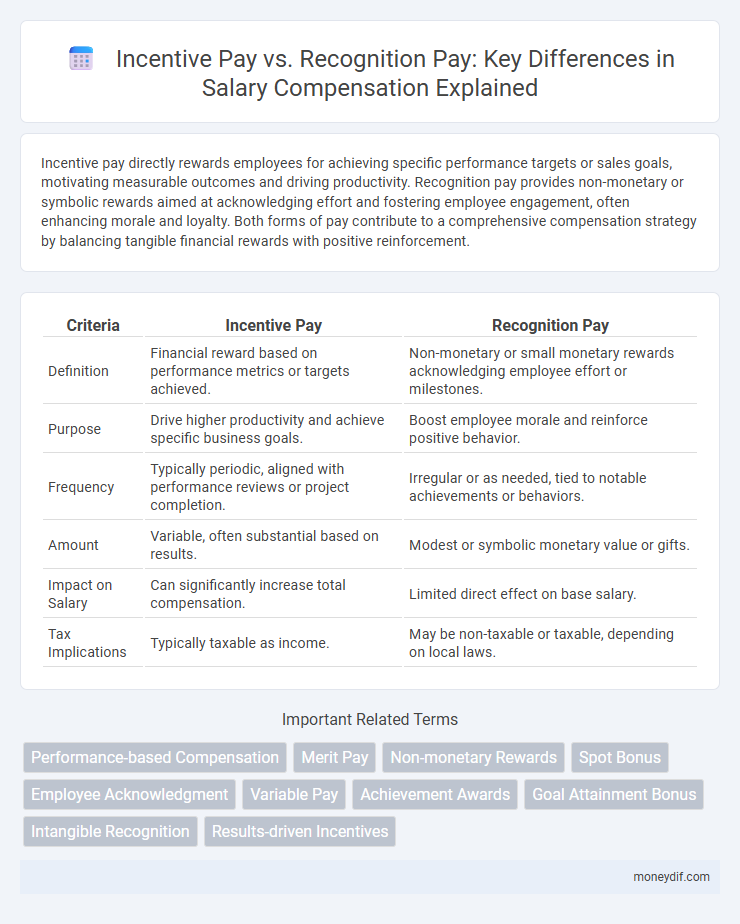
Incentive pay directly rewards employees for achieving specific performance targets or sales goals, motivating measurable outcomes and driving productivity. Recognition pay provides non-monetary or symbolic rewards aimed at acknowledging effort and fostering employee engagement, often enhancing morale and loyalty. Both forms of pay contribute to a comprehensive compensation strategy by balancing tangible financial rewards with positive reinforcement.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Incentive Pay | Recognition Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial reward based on performance metrics or targets achieved. | Non-monetary or small monetary rewards acknowledging employee effort or milestones. |
| Purpose | Drive higher productivity and achieve specific business goals. | Boost employee morale and reinforce positive behavior. |
| Frequency | Typically periodic, aligned with performance reviews or project completion. | Irregular or as needed, tied to notable achievements or behaviors. |
| Amount | Variable, often substantial based on results. | Modest or symbolic monetary value or gifts. |
| Impact on Salary | Can significantly increase total compensation. | Limited direct effect on base salary. |
| Tax Implications | Typically taxable as income. | May be non-taxable or taxable, depending on local laws. |
Understanding Incentive Pay and Recognition Pay
Incentive pay is performance-based compensation designed to motivate employees to achieve specific targets or goals, often tied to measurable outcomes such as sales figures or productivity metrics. Recognition pay, on the other hand, rewards employees for their contributions or achievements that may not be directly linked to quantitative performance, emphasizing appreciation and morale boosting. Both forms of pay enhance employee engagement but differ in structure, with incentive pay focused on results and recognition pay centered on acknowledgment.
Key Differences Between Incentive Pay and Recognition Pay
Incentive pay directly ties financial rewards to specific performance targets or productivity goals, motivating employees to achieve measurable outcomes. Recognition pay, by contrast, offers monetary bonuses as a form of appreciation for exemplary behavior or contributions, often without predetermined metrics. The key difference lies in incentive pay being goal-oriented and performance-driven, while recognition pay centers on acknowledging effort and commitment.
How Incentive Pay Motivates Performance
Incentive pay directly links employee compensation to measurable performance outcomes, driving higher productivity and goal achievement. By rewarding specific results such as sales targets or project milestones, it encourages employees to exceed standards and enhance overall business performance. This performance-contingent approach contrasts with recognition pay, which provides non-monetary acknowledgment without the same motivating power tied to tangible financial rewards.
The Role of Recognition Pay in Employee Engagement
Recognition pay plays a crucial role in boosting employee engagement by rewarding achievements beyond standard performance metrics, fostering a positive workplace culture. Unlike incentive pay, which targets specific goals or sales quotas, recognition pay motivates employees through acknowledgment of consistent effort and dedication. Studies show that organizations implementing recognition pay systems experience higher retention rates and increased overall productivity.
Pros and Cons of Incentive Pay Structures
Incentive pay structures motivate employees through performance-based financial rewards, driving productivity and goal alignment but risk fostering short-term thinking and unhealthy competition. These pay systems often create clear, measurable targets that can boost company profits and individual output, yet may undermine teamwork and employee morale if goals are unrealistic or overly aggressive. Companies must balance incentive pay carefully to avoid turnover and ensure sustainable performance growth.
Advantages and Limitations of Recognition Pay
Recognition pay boosts employee morale and motivation by directly rewarding individual achievements, fostering increased productivity and job satisfaction. It tends to be more flexible and immediate than incentive pay, allowing organizations to tailor rewards to specific contributions without rigid performance metrics. However, recognition pay can sometimes create perceptions of favoritism and may have limited impact if not consistently aligned with clear performance criteria.
When to Choose Incentive Pay Over Recognition Pay
Choose incentive pay over recognition pay when employee performance directly impacts measurable business outcomes, such as sales targets or production quotas. Incentive pay motivates employees to achieve specific goals by offering financial rewards tied to quantifiable achievements, enhancing productivity and accountability. Use incentive pay in roles where performance metrics are clear and results-driven to maximize employee motivation and organizational success.
Impact on Retention: Incentive Pay vs Recognition Pay
Incentive pay directly boosts retention by providing tangible financial rewards that motivate employees to meet specific performance targets and remain with the company. Recognition pay enhances retention through emotional engagement and job satisfaction, fostering loyalty and a positive workplace culture. Companies combining both approaches see higher retention rates by addressing both extrinsic and intrinsic employee motivators effectively.
Case Studies: Successful Incentive and Recognition Programs
Case studies of successful incentive pay programs reveal significant improvements in employee productivity by directly linking bonuses to performance targets, as seen at companies like Salesforce and Google. Recognition pay initiatives, exemplified by Zappos and Adobe, enhance employee satisfaction and retention through monetary rewards aligned with peer-to-peer recognition and milestone achievements. Both approaches demonstrate that combining financial incentives with meaningful acknowledgment fosters a motivated workforce and drives organizational success.
Best Practices for Implementing Pay-for-Performance Strategies
Incentive pay drives employee motivation through direct financial rewards tied to measurable outcomes, while recognition pay emphasizes non-monetary acknowledgment that boosts morale and engagement. Best practices for pay-for-performance strategies include setting clear, achievable performance metrics aligned with company goals and regularly communicating expectations to ensure transparency. Combining both incentive and recognition pay fosters a balanced approach that enhances productivity and employee satisfaction.
Important Terms
Performance-based Compensation
Performance-based compensation differentiates incentive pay, which rewards measurable achievement of specific targets, from recognition pay, which acknowledges outstanding contributions and behaviors beyond standardized performance metrics.
Merit Pay
Merit Pay directly ties salary increases to individual performance, whereas Incentive Pay offers bonuses for achieving specific targets and Recognition Pay provides non-monetary rewards to acknowledge employee contributions.
Non-monetary Rewards
Non-monetary rewards such as public recognition, career development opportunities, and personalized feedback effectively complement incentive pay by enhancing employee motivation beyond financial compensation. Recognition pay emphasizes acknowledgment of achievements and contributions, fostering a positive work culture, while incentive pay primarily drives performance through direct monetary bonuses linked to specific targets.
Spot Bonus
Spot Bonus is a form of incentive pay designed to reward employees immediately for exceptional performance or achievements, typically linked to specific goals or results. Unlike recognition pay, which focuses on acknowledging ongoing employee efforts and morale, spot bonuses are typically one-time financial rewards aimed at motivating high-impact contributions within a short timeframe.
Employee Acknowledgment
Employee acknowledgment through recognition pay enhances motivation and morale more effectively than incentive pay by rewarding ongoing contributions rather than solely performance-based results.
Variable Pay
Variable pay encompasses incentive pay, which directly rewards performance outcomes, and recognition pay, which acknowledges employee contributions through non-performance-based rewards.
Achievement Awards
Achievement awards effectively enhance employee motivation by offering tangible recognition tied to specific performance goals, differentiating from recognition pay which focuses on appreciating overall contributions without direct performance metrics. Incentive pay drives targeted productivity increases through financial rewards, whereas recognition pay fosters long-term engagement and morale by acknowledging ongoing efforts and accomplishments.
Goal Attainment Bonus
Goal Attainment Bonus serves as a targeted Incentive Pay designed to reward employees upon achieving specific performance milestones, driving measurable business outcomes. Unlike Recognition Pay, which acknowledges general contributions or behaviors, Goal Attainment Bonuses are directly tied to predefined targets, ensuring alignment with organizational objectives and motivating goal-focused performance.
Intangible Recognition
Intangible recognition enhances employee motivation through personalized acknowledgment and appreciation, which often leads to higher engagement than monetary incentive pay alone. Unlike recognition pay that provides a tangible financial reward, intangible recognition fosters a culture of value and belonging, driving long-term performance and job satisfaction.
Results-driven Incentives
Results-driven incentives prioritize incentive pay by directly linking employee compensation to measurable performance outcomes, while recognition pay emphasizes non-monetary appreciation and morale-boosting rewards.
Incentive Pay vs Recognition Pay Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com