Shadow payroll involves tracking an employee's income and tax obligations in a host country without officially registering them on the local payroll, often used for short-term international assignments. Formal payroll requires enrolling employees in the local tax and social security systems, ensuring full compliance with local laws and regulations. Companies must choose between shadow and formal payroll methods based on assignment duration, tax implications, and administrative complexity to maintain legal compliance and optimize payroll management.
Table of Comparison
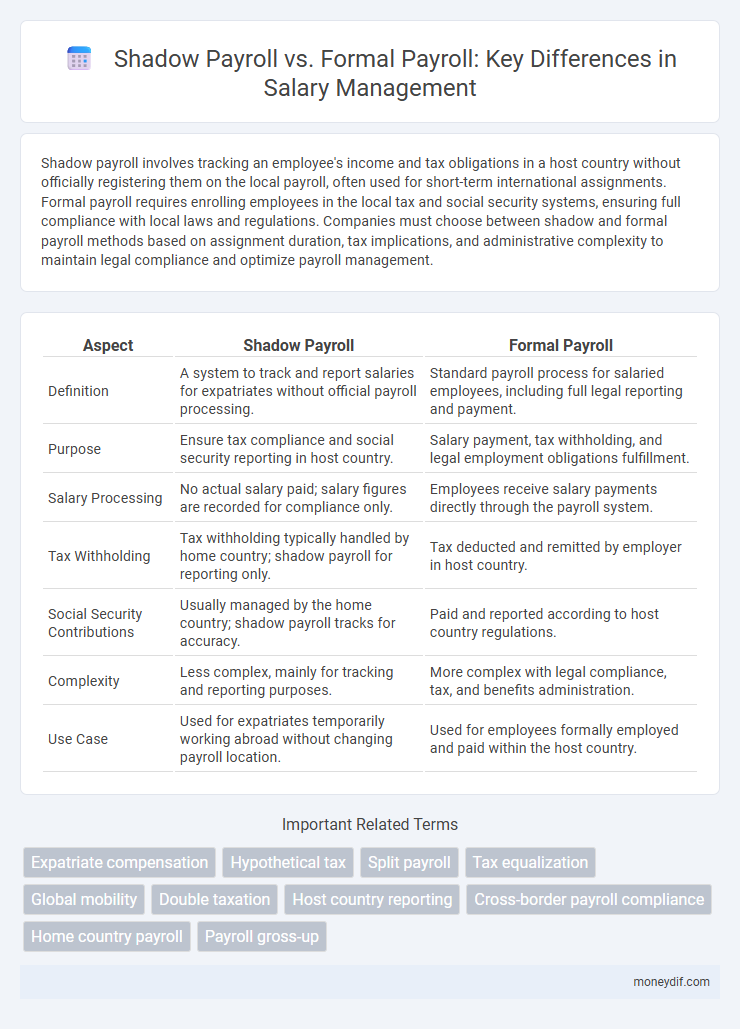
| Aspect | Shadow Payroll | Formal Payroll |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A system to track and report salaries for expatriates without official payroll processing. | Standard payroll process for salaried employees, including full legal reporting and payment. |
| Purpose | Ensure tax compliance and social security reporting in host country. | Salary payment, tax withholding, and legal employment obligations fulfillment. |
| Salary Processing | No actual salary paid; salary figures are recorded for compliance only. | Employees receive salary payments directly through the payroll system. |
| Tax Withholding | Tax withholding typically handled by home country; shadow payroll for reporting only. | Tax deducted and remitted by employer in host country. |
| Social Security Contributions | Usually managed by the home country; shadow payroll tracks for accuracy. | Paid and reported according to host country regulations. |
| Complexity | Less complex, mainly for tracking and reporting purposes. | More complex with legal compliance, tax, and benefits administration. |
| Use Case | Used for expatriates temporarily working abroad without changing payroll location. | Used for employees formally employed and paid within the host country. |
Understanding Shadow Payroll and Formal Payroll
Shadow payroll involves tracking an employee's income and taxes in a host country without actual payments being processed there, ensuring tax compliance for expatriates. Formal payroll processes employee compensation directly within the country of employment, managing tax withholdings and social security contributions according to local regulations. Understanding these distinctions helps multinational companies maintain regulatory compliance and optimize tax reporting across jurisdictions.
Key Differences Between Shadow Payroll and Formal Payroll
Shadow payroll tracks an employee's earnings and tax obligations while they work abroad without altering their official payroll records, ensuring compliance with international tax laws. Formal payroll processes an employee's salary through the host country's payroll system, including full tax reporting and local statutory deductions. Key differences include tax withholding responsibilities, reporting requirements, and the impact on local payroll obligations and social security contributions.
How Shadow Payroll Works
Shadow payroll tracks an employee's compensation and tax obligations when they work in a foreign country but remain on their home country's payroll system. It ensures compliance with local tax laws by reporting income and withholding taxes as if the employee were directly paid in the host country. This dual reporting mechanism helps multinational companies avoid double taxation and maintain accurate financial and tax records across jurisdictions.
Advantages of Formal Payroll Systems
Formal payroll systems ensure compliance with tax regulations and labor laws, reducing the risk of penalties for businesses and employees. They provide accurate salary tracking, enabling transparent reporting and streamlined financial audits. Implementing formal payroll enhances payroll accuracy, fosters employee trust, and supports comprehensive benefits administration.
Compliance Risks in Shadow Payroll
Shadow payroll poses significant compliance risks due to its informal nature and lack of full integration with official tax and social security reporting systems. Companies using shadow payroll may face penalties, back taxes, and legal issues arising from inconsistent tax withholding, misreported income, or failure to comply with local labor laws. Ensuring alignment with formal payroll processes and maintaining proper documentation are critical to mitigating exposure to audits and regulatory enforcement.
Salary Reporting in Shadow vs Formal Payroll
Shadow payroll involves recording and reporting salaries for expatriates on a host country's tax system without actual salary disbursement, ensuring tax compliance and social security obligations. Formal payroll processes the actual salary payments to employees, including deductions and contributions, with comprehensive reporting to tax authorities and social security institutions. Salary reporting in shadow payroll focuses on imputed earnings for tax purposes, while formal payroll reflects the real salary transaction and statutory compliance.
Tax Implications for Shadow and Formal Payroll
Shadow payroll involves reporting an employee's income in a host country without actual salary disbursement there, creating tax obligations in that jurisdiction; it ensures compliance with local tax laws while minimizing double taxation risks. Formal payroll processes salary payments directly in the host country, subjecting the employee to full local tax withholding and social security contributions. Tax implications differ significantly as shadow payroll can complicate tax credit claims and reporting accuracy, whereas formal payroll offers clearer tax treatment but may increase immediate tax liabilities.
When to Use Shadow Payroll
Shadow payroll is used when employees work temporarily abroad but remain on their home country's formal payroll to ensure tax compliance and social security benefits in both jurisdictions. It is essential for multinational companies managing short-term international assignments without fully transferring employees to the host country's formal payroll system. This approach helps in accurately reporting and withholding taxes, while maintaining employee benefits continuity during overseas assignments.
Challenges in Managing Shadow Payroll
Managing shadow payroll presents significant challenges, including complexities in ensuring compliance with multiple tax jurisdictions and accurately tracking employee income for cross-border assignments. Inaccurate data synchronization between shadow and formal payroll systems can lead to errors in tax reporting and social security contributions. Organizations must invest in advanced payroll technology and robust internal controls to mitigate risks associated with shadow payroll management.
Best Practices for Transitioning to Formal Payroll
Transitioning from shadow payroll to formal payroll requires meticulous data reconciliation to ensure accurate tax compliance and reporting. Establishing clear communication channels between global HR, finance teams, and local tax authorities helps streamline employee compensation documentation. Leveraging payroll automation software reduces errors and enhances the efficiency of integrating expatriate salaries into the formal payroll system.
Important Terms
Expatriate compensation
Expatriate compensation management differentiates shadow payroll, which tracks tax obligations without disbursing salary, from formal payroll, where actual salary payments are processed and reported by the host country employer.
Hypothetical tax
Hypothetical tax in shadow payroll allows multinational companies to calculate and withhold estimated employee taxes in a host country without formal payroll processing, contrasting with formal payroll where actual tax liabilities are reported and paid through the employer's official payroll system.
Split payroll
Split payroll divides employee compensation between shadow payroll, which handles taxation and compliance without actual fund disbursement, and formal payroll, where actual salary payments are processed and reported.
Tax equalization
Tax equalization ensures employees on shadow payroll or formal payroll experience consistent tax liabilities regardless of international assignments.
Global mobility
Global mobility management often requires navigating between shadow payroll and formal payroll systems to ensure tax compliance and accurate employee compensation across different jurisdictions. Shadow payroll tracks expatriate earnings for tax reporting while formal payroll processes actual salary disbursement, helping multinational companies avoid double taxation and maintain regulatory adherence.
Double taxation
Double taxation occurs when employees on a shadow payroll face tax liabilities in both the host and home countries, whereas formal payroll ensures compliant tax withholding in the host country to prevent duplicate taxation.
Host country reporting
Host country reporting requires accurate differentiation between shadow payroll and formal payroll to ensure compliance with local tax regulations and social security contributions.
Cross-border payroll compliance
Cross-border payroll compliance requires accurately managing shadow payroll for expatriates alongside formal payroll to ensure tax withholding, social security contributions, and reporting obligations are met in both home and host countries.
Home country payroll
Shadow payroll tracks expatriate employee earnings for tax compliance without affecting home country payroll, while formal payroll processes all salary payments and statutory deductions within the home country's official system.
Payroll gross-up
Payroll gross-up ensures employees receive full net pay by increasing gross wages to cover tax liabilities, often used in shadow payroll to mirror formal payroll tax obligations for expatriates.
Shadow payroll vs Formal payroll Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com