A sign-on bonus is a one-time payment offered to attract new employees, often used to secure talent quickly in competitive markets. In contrast, a retention bonus incentivizes current employees to stay with the company for a specified period, helping reduce turnover and maintain workforce stability. Both bonuses serve strategic roles in compensation plans but target different stages of the employee journey.
Table of Comparison
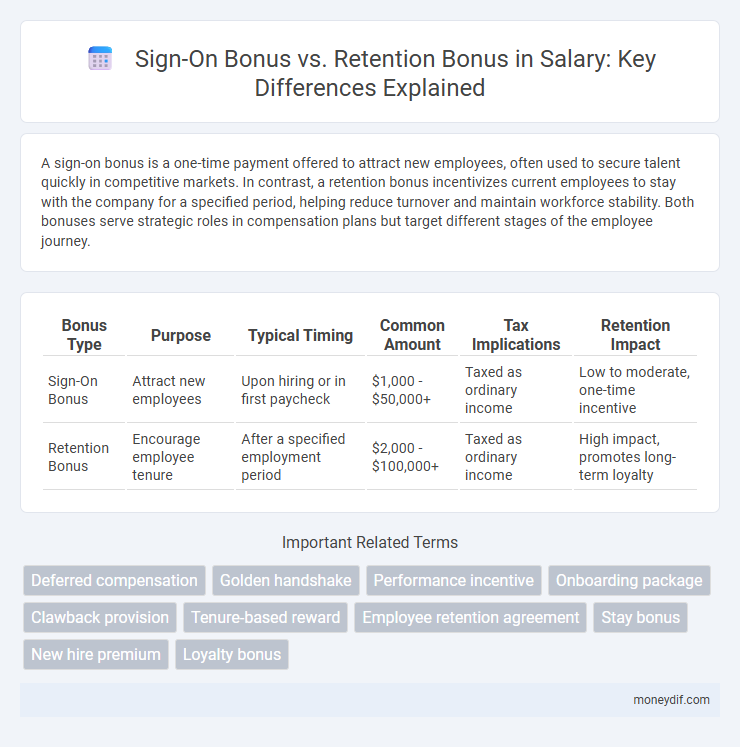
| Bonus Type | Purpose | Typical Timing | Common Amount | Tax Implications | Retention Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sign-On Bonus | Attract new employees | Upon hiring or in first paycheck | $1,000 - $50,000+ | Taxed as ordinary income | Low to moderate, one-time incentive |
| Retention Bonus | Encourage employee tenure | After a specified employment period | $2,000 - $100,000+ | Taxed as ordinary income | High impact, promotes long-term loyalty |
Understanding Sign-On Bonuses
Sign-on bonuses are one-time payments offered upfront to attract new employees, often used to make a job offer more competitive or to compensate for lost benefits at a previous employer. These bonuses differ from retention bonuses, which companies award after a set period to encourage employees to stay. Understanding sign-on bonuses helps candidates evaluate total compensation packages and negotiate more effectively during the hiring process.
What Is a Retention Bonus?
A retention bonus is a financial incentive offered by employers to encourage employees to remain with the company during critical periods, such as mergers, acquisitions, or major projects. Unlike sign-on bonuses, which reward new hires, retention bonuses are paid to existing staff to reduce turnover and maintain organizational stability. These bonuses often come with specific time commitments or terms, ensuring the employee stays for a predetermined duration.
Key Differences: Sign-On vs Retention Bonuses
Sign-on bonuses are one-time payments offered to new employees as an incentive to join a company, typically paid upon signing the employment contract. Retention bonuses are financial incentives provided to existing employees to encourage them to remain with the company for a specified period, often during critical projects or corporate restructuring. The key difference lies in timing and purpose: sign-on bonuses attract new talent, while retention bonuses aim to reduce turnover among current staff.
Advantages of Offering a Sign-On Bonus
Offering a sign-on bonus immediately attracts top talent by providing a lucrative financial incentive during the recruitment phase, enhancing employer competitiveness. This upfront payment helps offset candidate relocation expenses or forgone bonuses from previous employers, increasing acceptance rates. By delivering instant financial rewards, sign-on bonuses create positive initial employee impressions, accelerating onboarding and engagement.
Benefits of Retention Bonuses for Employers
Retention bonuses help employers maintain a stable workforce by reducing turnover costs and preserving institutional knowledge. These bonuses incentivize key employees to stay during critical periods, improving continuity and productivity within the organization. Offering retention bonuses enhances employee loyalty and can be strategically aligned with long-term business goals.
When Should Companies Offer a Sign-On Bonus?
Companies should offer a sign-on bonus when aiming to attract top talent in competitive industries or filling critical roles that require immediate expertise. This upfront financial incentive can differentiate an offer from competitors, particularly for candidates weighing multiple opportunities. Sign-on bonuses are most effective during hiring phases with talent shortages or when rapid onboarding is essential to meet business goals.
Best Timing for Retention Bonuses
Retention bonuses are most effective when offered at critical employment milestones such as the completion of a probationary period or just before contract renewals to ensure employee commitment. Companies often time retention bonuses during business transitions like mergers or acquisitions to prevent key talent from leaving amid uncertainty. Strategically timed retention bonuses align employee incentives with long-term organizational goals, maximizing retention and reducing turnover costs.
Tax Implications: Sign-On vs Retention Bonuses
Sign-on bonuses are typically taxed as ordinary income in the year they are received, often resulting in immediate withholding at a higher tax rate due to their lump-sum nature. Retention bonuses may be subject to similar income tax treatment but can sometimes be spread over the duration of employment, potentially moderating tax impact if structured as deferred compensation. Employers and employees should carefully evaluate the timing and tax withholding strategies associated with each bonus type to optimize net income outcomes.
Employee Perspective: Which Bonus Is More Attractive?
Employees often find sign-on bonuses more attractive due to their immediate financial reward upon joining a company, providing instant liquidity and a sense of value. Retention bonuses appeal to those prioritizing long-term job stability and financial incentives tied to continued service, enhancing commitment and career progression. The choice depends on individual financial needs and career goals, with sign-on bonuses favored by those seeking upfront gains and retention bonuses preferred by employees focused on future security.
How To Structure Effective Bonuses
Structuring effective bonuses requires aligning sign-on and retention bonuses with company goals and employee motivations. Sign-on bonuses should offer immediate financial incentives to attract top talent, while retention bonuses are designed as long-term rewards to encourage employee loyalty and reduce turnover. Clear performance metrics, milestone-based payments, and transparent communication maximize the impact of these bonuses on workforce stability and productivity.
Important Terms
Deferred compensation
Deferred compensation agreements often structure sign-on bonuses as immediate incentives paid upon joining, while retention bonuses are typically distributed over time to encourage employees to remain with the company.
Golden handshake
Golden handshake refers to a substantial severance package typically offered upon departure, whereas sign-on bonuses incentivize new hires to join, and retention bonuses reward employees for staying through critical periods.
Performance incentive
Performance incentives such as sign-on bonuses attract new talent quickly, while retention bonuses are strategically designed to maintain employee loyalty and reduce turnover over time.
Onboarding package
An onboarding package often includes a sign-on bonus, which serves as an immediate financial incentive to attract new hires, whereas a retention bonus is designed to encourage long-term commitment by rewarding employees for staying with the company over a specified period. Employers strategically combine these bonuses within onboarding packages to balance initial appeal and sustained employee retention, optimizing workforce stability and reducing turnover costs.
Clawback provision
A clawback provision requires employees to repay sign-on or retention bonuses if they leave the company before a specified period, ensuring financial commitment and reducing turnover risk.
Tenure-based reward
Tenure-based rewards often favor retention bonuses over sign-on bonuses by incentivizing long-term employee loyalty rather than initial hiring attraction.
Employee retention agreement
Employee retention agreements often compare sign-on bonuses, which incentivize new hires upfront, with retention bonuses designed to reward employees for staying with the company over a specified period.
Stay bonus
A stay bonus is a financial incentive designed to encourage employees to remain with a company for a specific period, contrasting with a sign-on bonus which is awarded upfront to attract new hires, and a retention bonus that rewards current employees for staying during critical business periods or transitions. Companies use stay bonuses strategically to ensure workforce stability, often linking them to key project completions or business milestones.
New hire premium
New hire premiums typically consist of sign-on bonuses offered upfront to attract candidates, while retention bonuses are paid over time to incentivize employee tenure and reduce turnover.
Loyalty bonus
A loyalty bonus rewards employees for long-term commitment, often complementing a sign-on bonus that attracts new hires and a retention bonus designed to encourage current employees to stay during critical periods.
sign-on bonus vs retention bonus Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com