A signing bonus is a one-time payment offered to new employees as an incentive to join a company, while a retention bonus is given to current employees to encourage them to stay with the organization for a specified period. Signing bonuses help attract top talent quickly, whereas retention bonuses aim to reduce turnover and maintain workforce stability. Both bonuses play strategic roles in talent management but target different stages of the employment lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
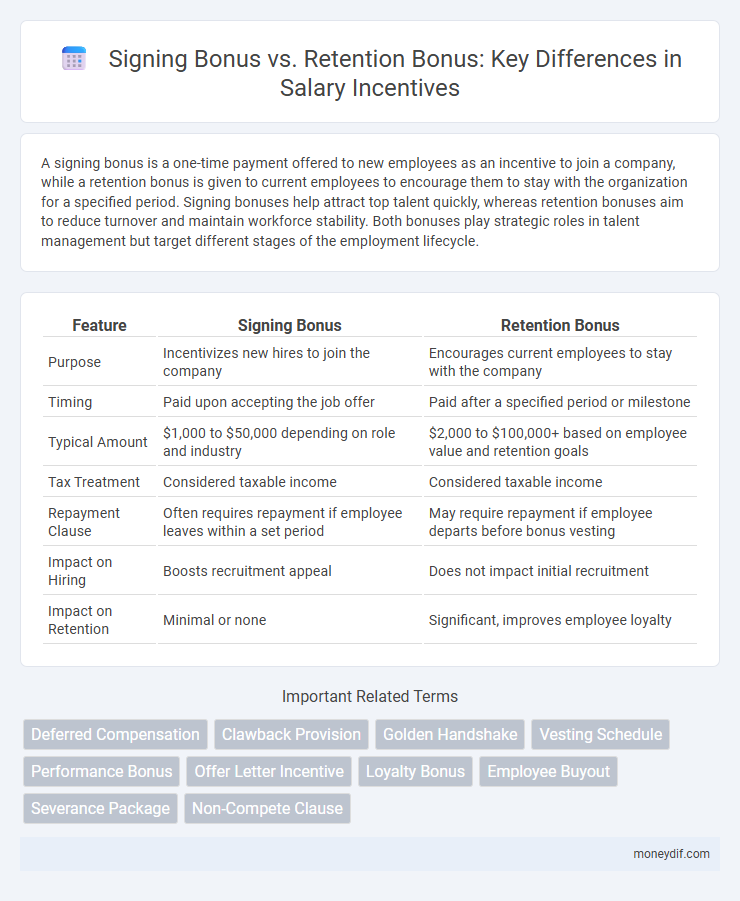
| Feature | Signing Bonus | Retention Bonus |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Incentivizes new hires to join the company | Encourages current employees to stay with the company |
| Timing | Paid upon accepting the job offer | Paid after a specified period or milestone |
| Typical Amount | $1,000 to $50,000 depending on role and industry | $2,000 to $100,000+ based on employee value and retention goals |
| Tax Treatment | Considered taxable income | Considered taxable income |
| Repayment Clause | Often requires repayment if employee leaves within a set period | May require repayment if employee departs before bonus vesting |
| Impact on Hiring | Boosts recruitment appeal | Does not impact initial recruitment |
| Impact on Retention | Minimal or none | Significant, improves employee loyalty |
Understanding Signing Bonuses
Signing bonuses are one-time payments offered to new employees as an incentive to join a company, often used to attract top talent in competitive job markets. These bonuses are typically paid shortly after accepting the job offer and can vary from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars depending on the industry and role. Understanding signing bonuses helps candidates evaluate the total compensation package and negotiate better terms during the hiring process.
What is a Retention Bonus?
A retention bonus is a financial incentive offered by employers to encourage employees to remain with the company for a specified period, especially during critical projects or organizational changes. Unlike a signing bonus, which is paid upfront to attract new hires, a retention bonus is typically disbursed after the employee has met certain tenure or performance milestones. This strategic compensation helps reduce turnover and maintain workforce stability in competitive industries.
Key Differences Between Signing and Retention Bonuses
Signing bonuses are one-time incentives offered to new employees to attract talent, typically paid upon joining the company. Retention bonuses are financial rewards given to existing employees to encourage them to stay with the organization for a specified period, often tied to achieving particular goals. Unlike signing bonuses that incentivize initial commitment, retention bonuses focus on long-term loyalty and performance continuity.
Pros and Cons of Signing Bonuses
Signing bonuses offer immediate financial incentives that attract top talent and boost initial employee satisfaction but may create expectations for future bonuses and impact salary negotiations negatively. These upfront payments can improve recruitment chances in competitive markets yet might result in higher turnover if employees leave after receiving the bonus. Employers must balance the cost of signing bonuses against long-term retention goals and potential impacts on overall compensation structures.
Pros and Cons of Retention Bonuses
Retention bonuses provide financial incentives that encourage employees to stay with a company during critical periods, enhancing workforce stability and reducing turnover costs. However, these bonuses may lead to employee dependency on incentives, potentially lowering intrinsic motivation and causing dissatisfaction once the bonus period ends. The effectiveness of retention bonuses varies by industry and role, often requiring careful structuring to balance short-term retention benefits with long-term organizational commitment.
When Employers Offer Signing Bonuses
Employers typically offer signing bonuses to attract top talent during competitive hiring markets or for hard-to-fill positions, providing immediate financial incentives to secure candidates quickly. These bonuses are common in industries like technology, finance, and healthcare, where skilled professionals are in high demand. Signing bonuses help offset potential income loss from leaving a current job and can make an offer more appealing compared to competing offers.
Situations Favoring Retention Bonuses
Retention bonuses are favored in situations where a company faces critical projects or transitions, aiming to keep key employees engaged and prevent turnover during high-stress periods. These bonuses are common in mergers, acquisitions, or restructuring phases where maintaining workforce stability is essential. Unlike signing bonuses, retention bonuses are contingent on employees remaining with the company for a specified duration, aligning incentives with long-term organizational goals.
Impact on Total Compensation Package
A signing bonus provides an immediate financial incentive that boosts the initial total compensation package, attracting candidates to accept a job offer quickly. Retention bonuses, paid after a specified period, enhance long-term total compensation by encouraging employees to remain with the company and contribute to sustained organizational performance. Both bonuses strategically impact overall compensation but target different stages of the employment lifecycle to maximize talent acquisition and retention.
Negotiating Signing vs Retention Bonuses
Negotiating signing bonuses requires emphasizing immediate value and upfront compensation, often leveraging competitive offers to maximize initial payout. Retention bonuses hinge on long-term commitment and performance benchmarks, making it essential to clearly define timelines and measurable goals during negotiations. Understanding the company's priorities and aligning bonus terms with career objectives strengthens your position in securing favorable signing or retention bonuses.
Which Bonus is Right for You?
Signing bonuses provide immediate financial incentives to attract new talent, ideal for candidates seeking upfront rewards when starting a new job. Retention bonuses are designed to encourage employees to stay with a company long-term, offering periodic payments tied to tenure or project completion. Choosing the right bonus depends on your career goals: prioritize a signing bonus if you need instant financial gain, or opt for a retention bonus if job stability and long-term earnings are more important.
Important Terms
Deferred Compensation
Deferred compensation plans often impact the timing and tax treatment of signing bonuses and retention bonuses, with signing bonuses typically paid upfront and retention bonuses structured to incentivize long-term employment through delayed payouts.
Clawback Provision
A clawback provision in signing bonuses requires repayment if an employee leaves before a specified period, ensuring commitment and protecting companies from upfront costs. In contrast, retention bonuses are typically paid incrementally and subject to clawbacks if the employee departs prematurely, incentivizing long-term tenure.
Golden Handshake
A Golden Handshake typically involves a large severance package offered upon departure, whereas a Signing Bonus incentivizes initial employment and a Retention Bonus rewards continued service.
Vesting Schedule
A vesting schedule determines the timeline over which a signing bonus or retention bonus becomes fully earned, ensuring employees meet specific tenure or performance milestones before receiving the full payout. Signing bonuses typically vest quickly or upfront to attract new hires, while retention bonuses vest over a longer period to encourage employees to remain with the company.
Performance Bonus
Performance bonuses directly reward employee achievements, while signing bonuses incentivize new hires and retention bonuses encourage long-term commitment.
Offer Letter Incentive
Offer letter incentives typically include a signing bonus as an upfront reward to attract new hires, while retention bonuses are performance-based incentives given later to encourage employee loyalty and reduce turnover.
Loyalty Bonus
A Loyalty Bonus rewards employees for their continuous service over a specific period, differentiating it from a Signing Bonus, which is given upfront to attract talent, and a Retention Bonus, designed to keep employees during critical company phases or projects. Loyalty Bonuses emphasize long-term commitment and company allegiance, often increasing with tenure to encourage sustained productivity and reduce turnover.
Employee Buyout
Employee buyouts often involve choosing between a signing bonus, which incentivizes new hires upfront, and a retention bonus, designed to retain existing employees during transitional periods.
Severance Package
A severance package typically includes a signing bonus as an upfront incentive for joining, whereas a retention bonus is awarded to encourage employees to remain with the company during specific periods, both impacting the overall compensation strategy.
Non-Compete Clause
A Non-Compete Clause restricts employees from joining competitors after receiving a Signing Bonus, ensuring the company protects its investment in new hires by preventing immediate moves to rival firms. In contrast, a Retention Bonus is tied to continued employment, making the Non-Compete Clause enforceable during and sometimes after the retention period to safeguard company interests.
Signing Bonus vs Retention Bonus Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com