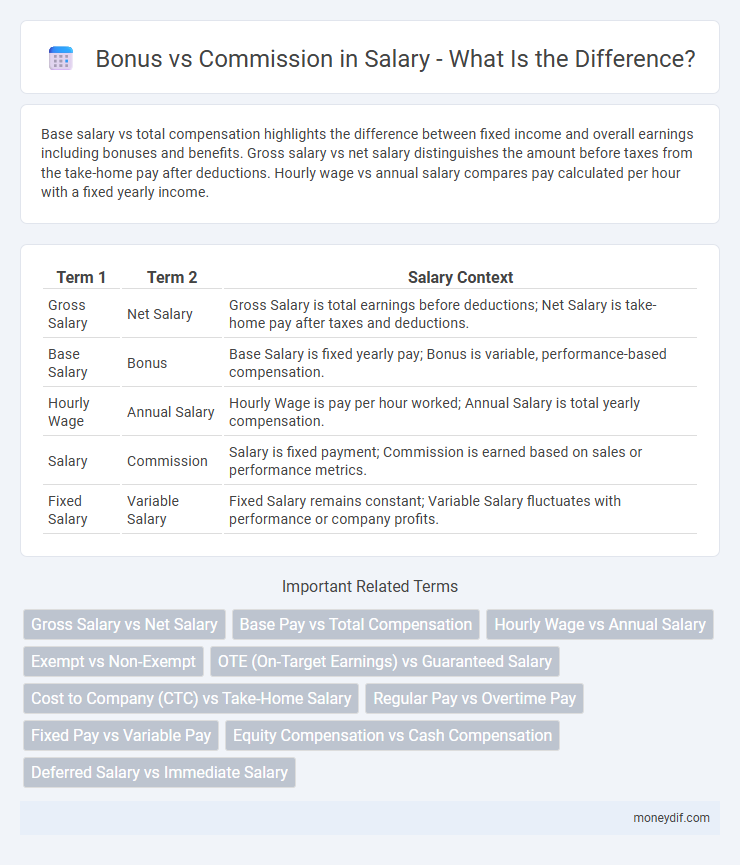
Base salary vs total compensation highlights the difference between fixed income and overall earnings including bonuses and benefits. Gross salary vs net salary distinguishes the amount before taxes from the take-home pay after deductions. Hourly wage vs annual salary compares pay calculated per hour with a fixed yearly income.
Table of Comparison
| Term 1 | Term 2 | Salary Context |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Salary | Net Salary | Gross Salary is total earnings before deductions; Net Salary is take-home pay after taxes and deductions. |
| Base Salary | Bonus | Base Salary is fixed yearly pay; Bonus is variable, performance-based compensation. |
| Hourly Wage | Annual Salary | Hourly Wage is pay per hour worked; Annual Salary is total yearly compensation. |
| Salary | Commission | Salary is fixed payment; Commission is earned based on sales or performance metrics. |
| Fixed Salary | Variable Salary | Fixed Salary remains constant; Variable Salary fluctuates with performance or company profits. |
Gross Salary vs Net Salary
Gross Salary represents the total earnings an employee receives before any deductions such as taxes, social security, and retirement contributions. Net Salary is the actual take-home pay after all mandatory deductions are subtracted from the gross amount. Understanding the difference between Gross and Net Salary is crucial for budgeting and financial planning.
Base Salary vs Total Compensation
Base salary refers to the fixed amount an employee receives before bonuses, benefits, or other incentives, forming the core of their earnings. Total compensation includes base salary plus additional financial rewards such as bonuses, stock options, health benefits, and retirement contributions, offering a complete picture of overall employee remuneration. Understanding the distinction between base salary and total compensation is crucial for accurate salary benchmarking and informed career decisions.
Salary vs Hourly Wage
Salary refers to a fixed annual amount of compensation paid to employees regardless of hours worked, typically expressed as a yearly figure. Hourly wage denotes payment based on the exact number of hours worked, with earnings calculated by multiplying hours worked by an hourly pay rate. Understanding the distinction between salary and hourly wage impacts benefits eligibility, overtime pay, and budgeting for both employers and employees.
Exempt vs Non-Exempt Salary
Exempt salary refers to employees who do not qualify for overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and typically receive a fixed annual amount regardless of hours worked. Non-exempt salary employees are eligible for overtime pay at a rate of one and a half times their regular hourly wage for hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek. Classification impacts payroll management, employee compensation, and compliance with labor laws, making clear distinctions essential for HR and finance departments.
Fixed Salary vs Variable Pay
Fixed salary represents a predetermined, consistent amount paid to employees regularly, ensuring predictable income regardless of performance or company profits. Variable pay fluctuates based on individual, team, or company performance metrics, such as bonuses, commissions, or profit-sharing, incentivizing higher productivity. Combining fixed salary with variable pay structures balances financial stability for employees with motivation through performance-based rewards.
Annual Salary vs Monthly Salary
Annual salary represents the total gross income earned over a full year, typically including bonuses and other compensation, while monthly salary is the portion of that income distributed each month. Understanding the distinction aids in budgeting and tax planning, as annual salary impacts yearly tax brackets and benefits calculations whereas monthly salary reflects regular cash flow. Employers often use annual salary for job offers and negotiations, whereas employees track monthly salary for everyday expenses.
Commission vs Bonus
Commission is a variable salary component based on a percentage of sales generated, directly incentivizing performance, while a bonus is typically a discretionary, fixed or variable payment awarded for achieving specific targets or company profitability. Commissions are commonly used in sales roles to align employee earnings with revenue generation, whereas bonuses can apply to broader employee groups as recognition or reward. Understanding the difference between commission and bonus structures is crucial for designing effective compensation plans that motivate employees and control payroll costs.
Overtime Pay vs Standard Salary
Overtime pay refers to the additional compensation employees receive for hours worked beyond their standard work schedule, typically calculated at a higher hourly rate, often one-and-a-half times the regular wage. Standard salary is a fixed annual or monthly amount paid regardless of hours worked, covering regular job responsibilities within agreed working hours. Understanding the distinction between overtime pay and standard salary is essential for ensuring fair compensation practices and compliance with labor laws.
In-House Salary vs Remote Salary
In-house salary typically includes fixed compensation with added benefits like office amenities, commuting reimbursements, and on-site bonuses, reflecting higher cost-of-living adjustments in urban locations. Remote salary often factors in geographic location variances, offering flexible pay scales based on employee residence, reduced commuting expenses, and sometimes lower base salaries balanced by self-managed work environments. Employers may optimize total compensation packages differently, emphasizing either standardized base pay for in-house roles or location-based differential salaries for remote positions.
Contract Salary vs Full-Time Employee Salary
Contract salary typically reflects a higher hourly rate compared to full-time employee salary due to the lack of benefits and job security. Full-time employee salary often includes additional compensation such as bonuses, health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, which enhance overall earnings beyond the base pay. Employers balance these cost factors when determining pay structures for contract versus full-time positions.
Important Terms
Gross Salary vs Net Salary
Gross salary represents the total earnings before deductions, while net salary is the actual take-home pay after taxes, benefits, and other withholdings.
Base Pay vs Total Compensation
Base pay refers to the fixed salary an employee receives before any bonuses, benefits, or incentives are included, representing the core earnings agreed upon in the employment contract. Total compensation encompasses base pay plus additional financial benefits such as bonuses, health insurance, stock options, retirement contributions, and other perks, providing a complete view of an employee's overall earning package.
Hourly Wage vs Annual Salary
Hourly wage represents compensation paid for each hour worked, offering flexibility and the potential for overtime earnings, whereas annual salary is a fixed amount paid over the year, providing financial stability regardless of hours worked. Hourly wage calculations typically include overtime rates, impacting total income, while annual salary often incorporates benefits like paid leave and bonuses not reflected in hourly pay.
Exempt vs Non-Exempt
Exempt employees are salaried workers not eligible for overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act, while non-exempt employees are paid hourly and entitled to overtime compensation for hours worked beyond 40 per week.
OTE (On-Target Earnings) vs Guaranteed Salary
OTE (On-Target Earnings) combines guaranteed salary with performance-based incentives to reflect total potential earnings, whereas guaranteed salary is a fixed amount paid regardless of performance.
Cost to Company (CTC) vs Take-Home Salary
Cost to Company (CTC) represents the total expense an employer incurs for an employee, including salary, benefits, taxes, bonuses, and other perks, whereas Take-Home Salary is the actual amount an employee receives after deductions like income tax, provident fund contributions, and professional tax. Understanding the distinction between CTC and Take-Home Salary is crucial for employees to accurately assess their net earnings and for employers to budget compensation packages effectively.
Regular Pay vs Overtime Pay
Regular pay refers to the standard hourly wage for scheduled working hours, while overtime pay is the higher rate compensated for hours worked beyond the regular schedule, typically 1.5 times the regular pay rate according to labor laws.
Fixed Pay vs Variable Pay
Fixed pay guarantees a consistent salary regardless of performance, while variable pay fluctuates based on individual or company performance metrics.
Equity Compensation vs Cash Compensation
Equity compensation, such as stock options or restricted shares, provides employees with ownership stakes that can appreciate over time, aligning their interests with company performance, whereas cash compensation offers immediate and guaranteed monetary rewards in the form of salary or bonuses. Equity's long-term value potential contrasts with cash's liquidity and stability, influencing employee motivation, tax implications, and retention strategies.
Deferred Salary vs Immediate Salary
Deferred salary offers long-term financial security through postponed payments, while immediate salary provides instant cash flow for daily expenses.
sure, here’s a list of niche “term1 vs term2” distinctions in the context of salary: Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com