Assets under management (AUM) refer to the total market value of investments that a financial institution actively manages on behalf of clients, involving decision-making and portfolio strategy. Assets under custody (AUC) represent the total value of assets held and safeguarded by a custodian, ensuring security and record-keeping without direct management responsibilities. Understanding the distinction between AUM and AUC is crucial for evaluating the scope of services offered by financial firms and their risk exposure.
Table of Comparison
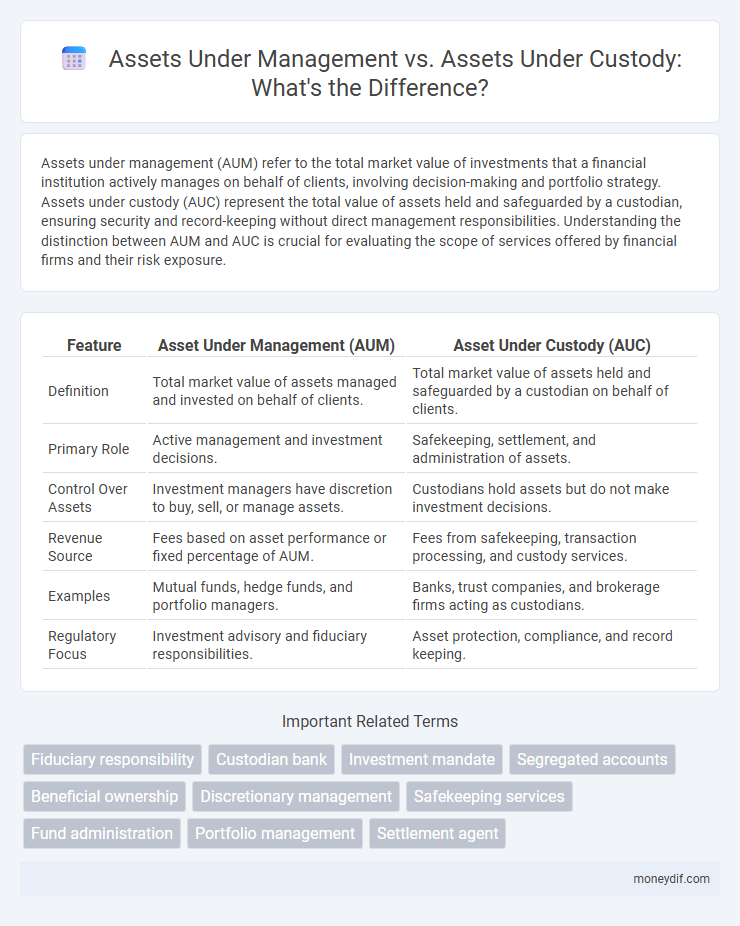
| Feature | Asset Under Management (AUM) | Asset Under Custody (AUC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total market value of assets managed and invested on behalf of clients. | Total market value of assets held and safeguarded by a custodian on behalf of clients. |
| Primary Role | Active management and investment decisions. | Safekeeping, settlement, and administration of assets. |
| Control Over Assets | Investment managers have discretion to buy, sell, or manage assets. | Custodians hold assets but do not make investment decisions. |
| Revenue Source | Fees based on asset performance or fixed percentage of AUM. | Fees from safekeeping, transaction processing, and custody services. |
| Examples | Mutual funds, hedge funds, and portfolio managers. | Banks, trust companies, and brokerage firms acting as custodians. |
| Regulatory Focus | Investment advisory and fiduciary responsibilities. | Asset protection, compliance, and record keeping. |
Introduction to Asset Under Management (AUM) and Asset Under Custody (AUC)
Asset Under Management (AUM) refers to the total market value of investments that a financial institution or fund manager actively manages for clients, influencing investment decisions and portfolio allocation. Asset Under Custody (AUC) denotes the total value of assets held and safeguarded by a custodian on behalf of clients, without direct management involvement. Understanding the distinction between AUM and AUC is vital for assessing the level of control and responsibility an institution holds over client assets.
Key Definitions: AUM vs AUC
Assets under management (AUM) refer to the total market value of investments that a financial institution actively manages on behalf of clients, including discretionary and non-discretionary portfolios. Assets under custody (AUC) represent the total value of assets held in custody by a financial institution, providing safekeeping and administrative services without active management. Understanding the distinction between AUM and AUC is crucial for evaluating a firm's service offerings and revenue models in wealth and asset management sectors.
Core Differences Between AUM and AUC
Assets under management (AUM) represent the total market value of investments actively managed and overseen by a financial institution on behalf of clients, emphasizing investment decisions and portfolio management. Assets under custody (AUC) refer to the safekeeping and administration of financial assets, where the custodian holds securities but does not make active investment decisions. The core differences lie in the roles: AUM focuses on investment management and value growth, while AUC centers on asset protection, record-keeping, and transaction settlements.
Calculation Methods for AUM and AUC
Asset under management (AUM) is calculated by aggregating the total market value of all financial assets actively managed by a firm on behalf of clients, including equities, bonds, and alternative investments, updated daily to reflect market fluctuations. Asset under custody (AUC) is determined by summing the total value of assets held and safeguarded by a custodian, encompassing securities and cash, with a focus on safekeeping rather than active management, typically reported at the end of the day or month. Precise AUM calculation requires adjusting for inflows, outflows, and investment performance, whereas AUC calculation emphasizes accurate record-keeping of holdings without investment valuation changes.
Roles of Asset Managers and Custodians
Asset managers are responsible for making investment decisions and actively managing a portfolio of assets to maximize returns and meet clients' financial goals, while custodians safeguard these assets by providing secure storage, settlement, and record-keeping services. Asset under management (AUM) refers to the total market value of assets that asset managers oversee and actively manage on behalf of clients. In contrast, assets under custody (AUC) represent the total value of assets held and protected by custodians, focusing on security and operational support rather than investment decisions.
Importance of AUM in Investment Performance
Assets under management (AUM) reflect the total market value of investments an asset manager actively oversees, directly impacting investment performance through strategic allocation and risk management. In contrast, assets under custody pertain to safeguarding and administrating client assets without influence on investment decisions. A higher AUM signals robust investor confidence and provides managers with greater leverage to negotiate fees and access diversified investment opportunities, ultimately enhancing potential returns.
Importance of AUC in Safeguarding Assets
Asset under custody (AUC) plays a critical role in safeguarding assets by providing secure custody and protection against fraud, theft, or insolvency of the asset manager. Unlike assets under management (AUM), which represent the total market value of investments managed on behalf of clients, AUC emphasizes the physical or electronic custody, ensuring legal ownership and regulatory compliance. Effective asset custody enhances investor confidence and operational transparency, making AUC a fundamental component in the overall asset protection framework.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Asset under management (AUM) represents the total market value of investments a firm actively manages on behalf of clients, subject to stringent regulatory frameworks such as SEC Rule 206(4)-2 and MiFID II, which enforce transparency and fiduciary responsibilities. Asset under custody (AUC), involving the holding and safeguarding of client assets without discretionary management, must comply with regulations like the Custody Rule under the Investment Advisers Act and AML/KYC requirements to prevent fraud and money laundering. Firms handling AUM face heightened compliance risks related to investment decision-making, while those managing AUC prioritize operational controls and secure record-keeping to meet regulatory audits and client protection standards.
Implications for Investors and Institutions
Assets under management (AUM) represent the total market value of investments that an institution actively manages on behalf of clients, indicating the institution's capability to make investment decisions and generate returns. Assets under custody (AUC) refer to the financial assets held and safeguarded by a custodian, focusing on secure storage and administration rather than active investment. For investors and institutions, AUM reflects exposure to investment performance and fee structures, while AUC emphasizes risk management, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency in safeguarding assets.
Choosing Between Asset Management and Custodial Services
Asset under management (AUM) represents the total market value of investments actively managed by financial professionals to achieve growth or income objectives, whereas asset under custody (AUC) refers to the safekeeping and administration of financial assets on behalf of clients without managing investment decisions. Choosing between asset management and custodial services depends on whether the priority is portfolio growth and strategic investment guidance or secure storage and transaction processing. Investors seeking active decision-making and performance optimization typically prefer asset management, while those prioritizing security, compliance, and administrative efficiency lean towards custodial services.
Important Terms
Fiduciary responsibility
Fiduciary responsibility requires asset managers to act in clients' best interests by prudently managing Assets Under Management (AUM), whereas custodians focus on securely holding Assets Under Custody (AUC) without discretionary control over investment decisions.
Custodian bank
A custodian bank safeguards and administers assets under custody, providing secure custody services distinct from asset management, which involves making investment decisions and managing assets under management (AUM).
Investment mandate
The investment mandate outlines specific guidelines for asset allocation and risk tolerance, directly impacting both assets under management (AUM), which represent the actively managed investment portfolios, and assets under custody (AUC), which refer to the safekeeping of clients' financial assets without discretionary management.
Segregated accounts
Segregated accounts enhance asset protection by distinctly separating Asset Under Management (AUM), which represents investment control, from Asset Under Custody (AUC), which involves safekeeping and administrative management of client funds.
Beneficial ownership
Beneficial ownership defines the true owner of assets, distinguishing asset under management (AUM), where the owner's investments are actively managed, from asset under custody (AUC), where assets are held securely without direct management.
Discretionary management
Discretionary management involves professional managers making investment decisions on behalf of clients, directly impacting the assets under management (AUM), which reflect the total market value of investments actively managed. Assets under custody (AUC) represent the total assets held and safeguarded by a custodian, encompassing both discretionary and non-discretionary portfolios, highlighting the distinction between management responsibility and asset safeguarding.
Safekeeping services
Safekeeping services primarily focus on the protection and administration of assets held in custody, ensuring secure record-keeping and risk mitigation for physical and electronic assets. Assets under management (AUM) refer to the total market value of investments actively managed by an asset manager, whereas assets under custody represent the total assets held and safeguarded by a custodian without active management responsibility.
Fund administration
Fund administration involves comprehensive management of assets under management (AUM), focusing on portfolio valuation, investor reporting, and compliance to maximize investor value. Asset under custody (AUC) primarily refers to safeguarding clients' securities and facilitating transactions, ensuring secure custody and accurate record-keeping without direct investment decision-making.
Portfolio management
Portfolio management focuses on optimizing Asset Under Management (AUM) by actively investing client assets, whereas Asset Under Custody (AUC) refers to the total value of assets held and safeguarded without direct investment decisions.
Settlement agent
Settlement agents facilitate the transfer and settlement of financial transactions, playing a crucial role in managing assets under custody, which differ from assets under management as the latter involves active investment decisions while custody focuses on safekeeping and administrative services.
Asset under management vs Asset under custody Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com