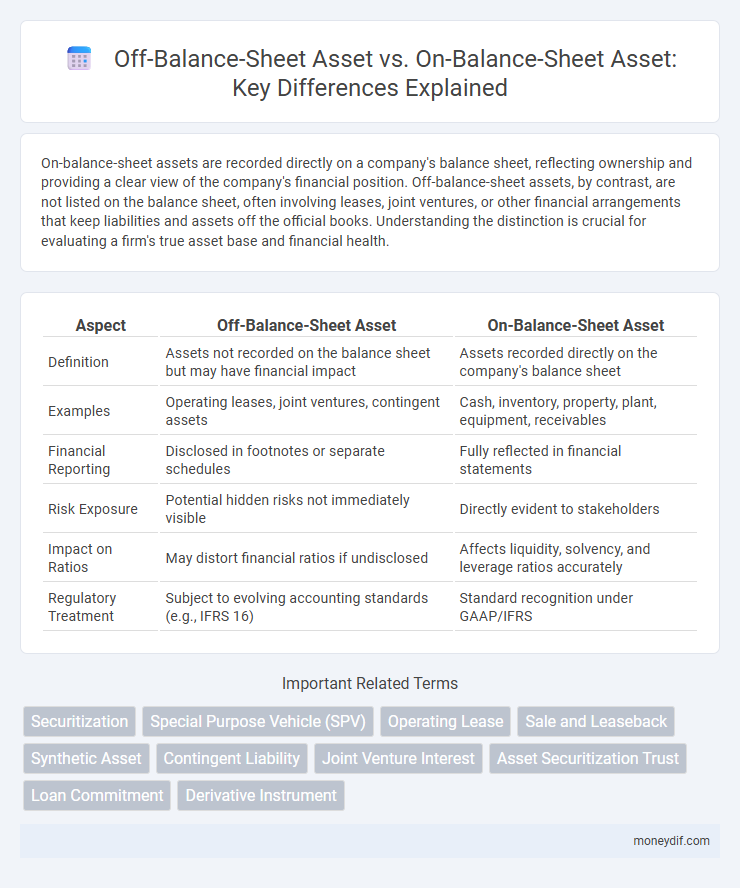
On-balance-sheet assets are recorded directly on a company's balance sheet, reflecting ownership and providing a clear view of the company's financial position. Off-balance-sheet assets, by contrast, are not listed on the balance sheet, often involving leases, joint ventures, or other financial arrangements that keep liabilities and assets off the official books. Understanding the distinction is crucial for evaluating a firm's true asset base and financial health.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Off-Balance-Sheet Asset | On-Balance-Sheet Asset |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assets not recorded on the balance sheet but may have financial impact | Assets recorded directly on the company's balance sheet |
| Examples | Operating leases, joint ventures, contingent assets | Cash, inventory, property, plant, equipment, receivables |
| Financial Reporting | Disclosed in footnotes or separate schedules | Fully reflected in financial statements |
| Risk Exposure | Potential hidden risks not immediately visible | Directly evident to stakeholders |
| Impact on Ratios | May distort financial ratios if undisclosed | Affects liquidity, solvency, and leverage ratios accurately |
| Regulatory Treatment | Subject to evolving accounting standards (e.g., IFRS 16) | Standard recognition under GAAP/IFRS |
Introduction to Asset Classification
Assets are classified based on their representation in financial statements, with on-balance-sheet assets explicitly recorded and valued within a company's balance sheet, such as cash, inventory, and property. Off-balance-sheet assets refer to resources or rights that do not appear directly on the balance sheet but still provide economic benefits, including operating leases, joint ventures, and certain intellectual property rights. Understanding the distinction between these classifications is crucial for accurate financial analysis and risk assessment.
Defining On-Balance-Sheet Assets
On-balance-sheet assets are resources owned or controlled by a company that are recorded directly on the balance sheet, including cash, accounts receivable, inventory, property, and equipment. These assets are recognized at their book value and impact the company's financial position and liquidity assessments. Unlike off-balance-sheet assets, on-balance-sheet assets are fully disclosed, providing transparency for creditors and investors in financial reporting.
Understanding Off-Balance-Sheet Assets
Off-balance-sheet assets represent resources or potential value that a company controls but does not record directly on its balance sheet, such as operating leases, joint ventures, or certain intellectual property rights. These assets can impact a firm's financial health and risk profile without appearing in traditional financial metrics, making thorough analysis essential for accurate asset valuation. Understanding off-balance-sheet assets helps investors and analysts evaluate hidden financial obligations and potential future benefits beyond on-balance-sheet disclosures.
Key Differences: On-Balance-Sheet vs Off-Balance-Sheet Assets
On-balance-sheet assets are recorded directly on a company's balance sheet, reflecting tangible and intangible resources like cash, equipment, and receivables that impact financial ratios and equity valuation. Off-balance-sheet assets, such as operating leases or joint ventures, remain unrecorded on the balance sheet but can influence a company's risk profile and future obligations. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate financial analysis and assessing a company's true economic value.
Examples of On-Balance-Sheet Assets
On-balance-sheet assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, property, plant, and equipment, reflecting tangible and financial resources owned by a company. These assets are recorded on the balance sheet, providing transparency for investors and creditors regarding the company's financial position. Examples also encompass intangible assets like patents and trademarks, which contribute to a company's value and are recognized under accounting standards.
Common Types of Off-Balance-Sheet Assets
Common types of off-balance-sheet assets include operating leases, joint ventures, and certain financial derivatives that do not appear on the company's balance sheet but can influence financial performance. These assets help firms manage risk and optimize balance sheet presentation by keeping liabilities or assets off the record. Understanding off-balance-sheet assets is crucial for accurate assessment of a company's financial health and potential obligations.
Impact on Financial Statements
Off-balance-sheet assets, such as operating leases or joint ventures, do not appear directly on the balance sheet, reducing reported asset value and liabilities, which can affect key financial ratios like debt-to-equity and return on assets. On-balance-sheet assets, including property, plant, equipment, and accounts receivable, are recorded within the asset section, providing a transparent view of the company's financial position. The treatment of these assets significantly impacts financial statement analysis, influencing investor perception and creditworthiness assessment.
Regulatory Framework and Disclosure Requirements
On-balance-sheet assets are recorded directly on a company's financial statements, subject to strict regulatory frameworks such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), which mandate comprehensive disclosure requirements to ensure transparency. Off-balance-sheet assets, including operating leases and joint ventures, are managed under specific regulatory guidelines like the Financial Accounting Standards Board's ASC 842 or IFRS 16, requiring partial disclosure in footnotes to address risks and obligations without reflecting them on the balance sheet. Regulatory frameworks aim to balance transparency and risk management by enforcing detailed disclosures for off-balance-sheet items while maintaining the integrity of on-balance-sheet asset reporting.
Risks and Benefits of Using Off-Balance-Sheet Assets
Off-balance-sheet assets, such as operating leases and joint ventures, help companies reduce reported liabilities and improve financial ratios, enhancing perceived creditworthiness and investor appeal. However, these assets carry risks including reduced transparency, potential regulatory scrutiny, and hidden obligations that may impact future liquidity. On-balance-sheet assets provide clearer accountability and risk assessment but can constrain balance sheet flexibility and potentially reduce borrowing capacity.
Best Practices for Asset Reporting and Transparency
Best practices for asset reporting and transparency emphasize clear differentiation between off-balance-sheet assets, such as operating leases and special purpose entities, and on-balance-sheet assets like property, equipment, and receivables. Accurate classification ensures compliance with accounting standards like IFRS 16 and ASC 842, improving stakeholder trust and regulatory adherence. Implementing robust disclosure policies and leveraging advanced financial software enhance visibility and rigorous monitoring of all asset types.
Important Terms
Securitization
Securitization transforms on-balance-sheet assets into off-balance-sheet securities, improving liquidity and reducing reported liabilities.
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) is a legal entity used to isolate financial risk by holding off-balance-sheet assets separate from the parent company's on-balance-sheet assets, thereby improving financial transparency and risk management.
Operating Lease
Operating leases are classified as off-balance-sheet assets because they do not appear as liabilities or owned assets on the lessee's balance sheet, enabling companies to keep lease obligations and asset ownership off their financial statements. Conversely, on-balance-sheet assets include capital leases or finance leases, which recognize both the leased asset and corresponding liability, impacting debt ratios and asset totals directly.
Sale and Leaseback
Sale and leaseback transactions enable companies to convert on-balance-sheet assets into off-balance-sheet leases, improving liquidity while maintaining asset use.
Synthetic Asset
Synthetic assets replicate the performance of traditional on-balance-sheet assets without being physically held, allowing firms to manage risk and gain exposure off-balance-sheet. These derivatives enhance financial flexibility by creating off-balance-sheet exposures, which do not directly impact the company's balance sheet but require careful disclosure to manage transparency and regulatory compliance.
Contingent Liability
Contingent liabilities are potential obligations recorded off-balance-sheet until they become probable and measurable, unlike on-balance-sheet liabilities which are recognized immediately.
Joint Venture Interest
Joint venture interests classified as off-balance-sheet assets do not appear directly on a company's balance sheet, whereas on-balance-sheet assets reflect the investor's proportional share of the joint venture's assets and liabilities.
Asset Securitization Trust
Asset securitization trusts enable the transfer of off-balance-sheet assets into tradable securities, improving liquidity while keeping the originating company's balance sheet clear.
Loan Commitment
Loan commitments are off-balance-sheet assets representing a bank's obligation to lend under specified terms, unlike on-balance-sheet assets, which include loans already disbursed and recorded as financial assets.
Derivative Instrument
Derivative instruments classified as off-balance-sheet assets represent contingent claims that are not recorded on the balance sheet until they meet specific recognition criteria, while on-balance-sheet assets reflect recognized financial instruments with measurable future economic benefits. Off-balance-sheet treatment allows for contingent exposure management without immediate impact on financial leverage ratios, contrasting with on-balance-sheet assets that directly influence reported financial position and capital adequacy.
off-balance-sheet asset vs on-balance-sheet asset Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com