Asset Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its total assets to generate sales, reflecting overall operational performance. Inventory Turnover Ratio specifically evaluates how quickly inventory is sold and replaced within a period, indicating inventory management effectiveness. Comparing these ratios helps identify whether sales growth is driven by efficient asset utilization or inventory management strategies.
Table of Comparison
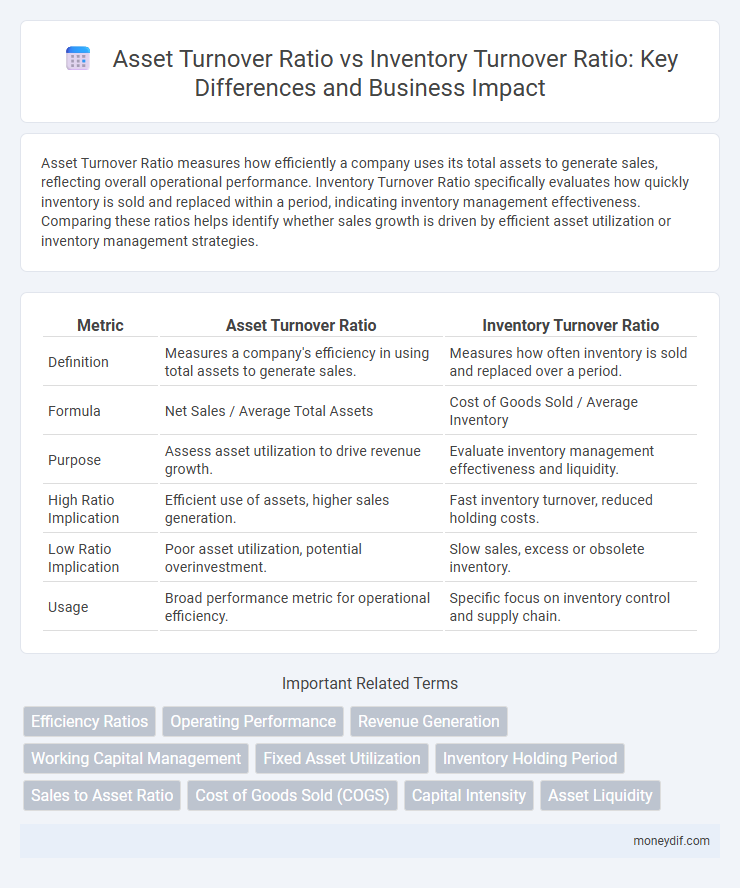
| Metric | Asset Turnover Ratio | Inventory Turnover Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures a company's efficiency in using total assets to generate sales. | Measures how often inventory is sold and replaced over a period. |
| Formula | Net Sales / Average Total Assets | Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory |
| Purpose | Assess asset utilization to drive revenue growth. | Evaluate inventory management effectiveness and liquidity. |
| High Ratio Implication | Efficient use of assets, higher sales generation. | Fast inventory turnover, reduced holding costs. |
| Low Ratio Implication | Poor asset utilization, potential overinvestment. | Slow sales, excess or obsolete inventory. |
| Usage | Broad performance metric for operational efficiency. | Specific focus on inventory control and supply chain. |
Understanding Asset Turnover Ratio
Asset Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its total assets to generate sales revenue, calculated by dividing net sales by average total assets. This ratio provides insight into asset utilization effectiveness, highlighting how well management maximizes asset investment for revenue generation. Comparing it to Inventory Turnover Ratio, which focuses solely on inventory efficiency, Asset Turnover Ratio offers a broader perspective on overall operational performance.
Defining Inventory Turnover Ratio
Inventory Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company manages its stock by calculating the number of times inventory is sold and replaced over a period. This ratio is derived by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory during the same period. A higher Inventory Turnover Ratio indicates effective inventory management and strong sales performance.
Key Differences Between Asset and Inventory Turnover Ratios
Asset Turnover Ratio measures a company's efficiency in using its total assets to generate sales, whereas Inventory Turnover Ratio specifically evaluates how effectively inventory is managed through sales. Asset Turnover Ratio is expressed as net sales divided by average total assets, reflecting overall asset utilization, while Inventory Turnover Ratio is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by average inventory, indicating inventory liquidity. The key difference lies in their scope: Asset Turnover Ratio encompasses all asset classes, providing a broad operational efficiency view, whereas Inventory Turnover Ratio focuses narrowly on inventory management and turnover speed.
Calculation Methods for Asset Turnover Ratio
Asset Turnover Ratio is calculated by dividing net sales by average total assets, measuring a company's efficiency in using assets to generate revenue. The formula is Net Sales / Average Total Assets, where average total assets equal the sum of beginning and ending total assets divided by two. This ratio provides insights into how effectively management utilizes its asset base compared to Inventory Turnover Ratio, which focuses specifically on inventory efficiency.
How to Compute Inventory Turnover Ratio
Inventory Turnover Ratio is computed by dividing the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) by the Average Inventory during a specific period, highlighting how efficiently a company manages its stock. This ratio reveals the frequency at which inventory is sold and replaced, indicating operational efficiency and liquidity. Precise calculation involves extracting accurate COGS from financial statements and calculating average inventory based on beginning and ending inventory balances.
Interpreting Asset Turnover Ratio Results
The Asset Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its total assets to generate sales, indicating operational efficiency. A higher ratio suggests better utilization of assets in producing revenue, while a lower ratio may signal underutilized resources or inefficiencies. Comparing Asset Turnover with Inventory Turnover helps identify whether issues in asset use stem from inventory management or broader operational factors.
Analyzing Inventory Turnover Ratio Performance
Analyzing Inventory Turnover Ratio performance provides critical insights into how efficiently a company manages its stock relative to sales. A higher inventory turnover ratio indicates effective inventory management, reducing holding costs and minimizing obsolescence risks. Comparing this with the Asset Turnover Ratio helps identify whether overall asset utilization is driven by inventory efficiency or other asset components.
Impact on Business Efficiency: Asset vs Inventory Turnover
Asset Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its total assets to generate sales, indicating overall operational efficiency, while Inventory Turnover Ratio focuses specifically on how quickly inventory is sold and replaced, reflecting inventory management effectiveness. Higher Asset Turnover Ratios suggest better utilization of all assets, including machinery and receivables, whereas higher Inventory Turnover Ratios indicate efficient stock control and reduced holding costs. Both ratios impact business efficiency by highlighting different aspects of resource management essential for optimizing profitability and cash flow.
Industry Benchmarks for Turnover Ratios
Asset Turnover Ratio measures a company's efficiency in using its assets to generate sales, with industry benchmarks ranging from 0.5 in capital-intensive sectors to over 2.0 in retail and fast-moving consumer goods industries. Inventory Turnover Ratio evaluates how effectively inventory is managed, with benchmarks often exceeding 8 in grocery retail but typically lower, around 4-6, in manufacturing and automotive industries. Comparing these ratios against industry standards provides critical insight into operational efficiency and asset utilization specific to sector dynamics.
Improving Asset and Inventory Turnover Ratios
Improving the Asset Turnover Ratio involves enhancing overall asset efficiency by increasing sales revenue without proportionally increasing assets. Boosting the Inventory Turnover Ratio requires optimizing inventory management through faster stock movement and minimizing holding periods, which reduces carrying costs. Monitoring both ratios together provides a comprehensive view of operational efficiency and helps identify areas for strategic asset and inventory management improvements.
Important Terms
Efficiency Ratios
The Asset Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its total assets to generate sales, while the Inventory Turnover Ratio specifically assesses how effectively inventory is managed by indicating how many times inventory is sold and replaced within a period.
Operating Performance
Asset Turnover Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its total assets to generate sales, while Inventory Turnover Ratio specifically evaluates how quickly inventory is sold and replaced within a period, reflecting inventory management effectiveness. Comparing these ratios provides insights into operational performance by highlighting the balance between asset utilization and inventory efficiency, crucial for optimizing working capital and overall profitability.
Revenue Generation
Asset Turnover Ratio measures revenue generated per dollar of assets, while Inventory Turnover Ratio indicates how efficiently inventory is sold, both directly impacting overall revenue generation efficiency.
Working Capital Management
Effective working capital management relies on balancing the asset turnover ratio, which measures a company's efficiency in using assets to generate sales, with the inventory turnover ratio, indicating how quickly inventory is sold and replaced. High asset turnover combined with an optimal inventory turnover ratio enhances liquidity and operational efficiency, reducing holding costs and improving cash flow.
Fixed Asset Utilization
Fixed Asset Utilization is measured by the Asset Turnover Ratio, which evaluates how efficiently a company uses its fixed assets to generate sales revenue, unlike the Inventory Turnover Ratio that focuses on how quickly inventory is sold and replaced. A higher Asset Turnover Ratio indicates effective use of property, plant, and equipment, essential for capital-intensive businesses, whereas a high Inventory Turnover Ratio reflects efficient inventory management in retail or manufacturing sectors.
Inventory Holding Period
Inventory Holding Period measures the average number of days inventory is held before sale, directly impacting the Asset Turnover Ratio by influencing the efficiency of asset use in generating sales. A higher Inventory Turnover Ratio typically shortens the Inventory Holding Period, enhancing asset utilization and improving the Asset Turnover Ratio, reflecting more effective inventory and asset management.
Sales to Asset Ratio
The Sales to Asset Ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales, closely related to Asset Turnover Ratio, which focuses on total asset utilization. In contrast, Inventory Turnover Ratio zeroes in on how effectively inventory is managed to support sales, highlighting operational efficiency at the inventory level rather than overall asset productivity.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) directly affects both Asset Turnover Ratio and Inventory Turnover Ratio, where higher COGS typically increases Inventory Turnover by indicating faster inventory movement and improves Asset Turnover by generating more sales per asset dollar. Efficient management of COGS enhances operational performance metrics, reflecting quicker asset utilization and inventory liquidation cycles critical to profitability analysis.
Capital Intensity
Capital intensity inversely affects Asset Turnover Ratio by indicating higher asset investment per sales unit, whereas Inventory Turnover Ratio reflects operational efficiency in managing stock relative to sales.
Asset Liquidity
Asset liquidity directly impacts asset turnover ratio by enhancing the efficiency of asset utilization, while inventory turnover ratio specifically measures how quickly inventory converts to sales, reflecting operational efficiency within the overall asset management.
Asset Turnover Ratio vs Inventory Turnover Ratio Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com