The CAMELS rating evaluates a bank's overall health through six key components: Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk, primarily for regulatory supervision. The CRA rating assesses a bank's effectiveness in meeting the credit needs of its community, emphasizing fair lending and community development efforts. Understanding both ratings provides a comprehensive view of a bank's financial stability and commitment to social responsibility.
Table of Comparison
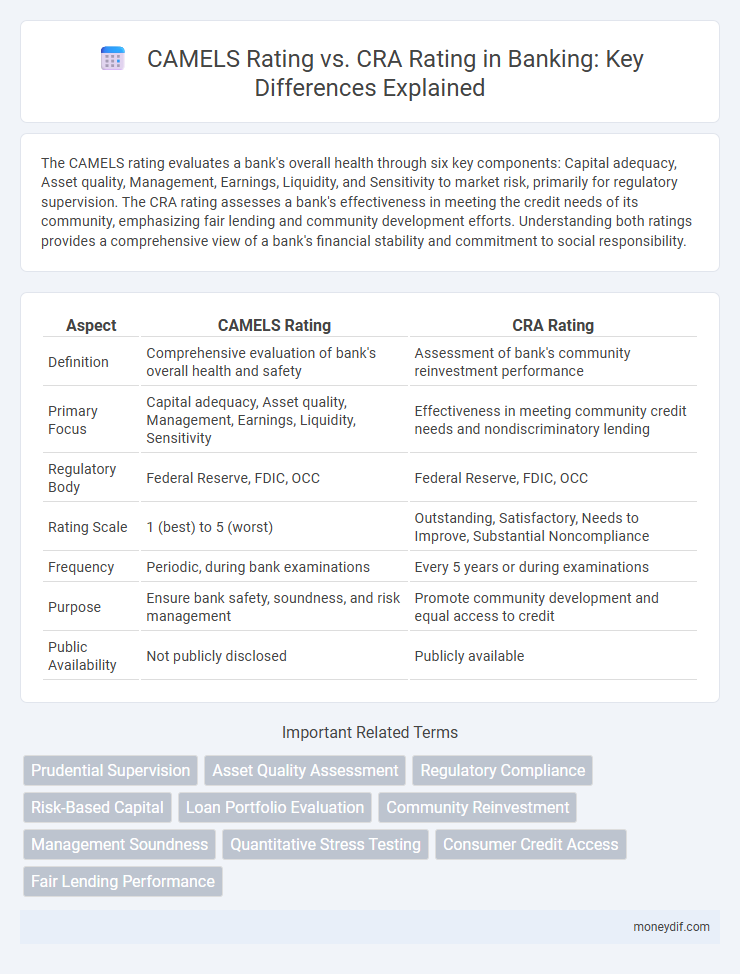
| Aspect | CAMELS Rating | CRA Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive evaluation of bank's overall health and safety | Assessment of bank's community reinvestment performance |
| Primary Focus | Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management, Earnings, Liquidity, Sensitivity | Effectiveness in meeting community credit needs and nondiscriminatory lending |
| Regulatory Body | Federal Reserve, FDIC, OCC | Federal Reserve, FDIC, OCC |
| Rating Scale | 1 (best) to 5 (worst) | Outstanding, Satisfactory, Needs to Improve, Substantial Noncompliance |
| Frequency | Periodic, during bank examinations | Every 5 years or during examinations |
| Purpose | Ensure bank safety, soundness, and risk management | Promote community development and equal access to credit |
| Public Availability | Not publicly disclosed | Publicly available |
Understanding CAMELS Rating in Banking
CAMELS Rating is a supervisory tool used by banking regulators to assess a financial institution's health based on six key components: Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management quality, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk. This composite rating helps regulators identify potential risks and vulnerabilities within banks, ensuring financial stability and protecting depositors. Unlike the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) Rating, which evaluates a bank's commitment to meeting local community credit needs, the CAMELS Rating centers on the overall safety and soundness of the institution.
Overview of CRA (Community Reinvestment Act) Rating
The Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) Rating evaluates a bank's commitment to meeting the credit needs of its entire community, particularly low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. This rating assesses factors such as lending, investment, and service activities by bank examiners under federal regulations. Unlike the CAMELS Rating, which focuses on overall financial health and risk management, the CRA Rating centers on community development and equitable access to financial services.
CAMELS vs CRA: Key Differences
CAMELS rating evaluates a bank's overall health based on Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management quality, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk, providing a comprehensive risk assessment used primarily by regulators. CRA rating focuses on a bank's performance in meeting community credit needs, assessing efforts to lend, invest, and provide services in low- and moderate-income neighborhoods under the Community Reinvestment Act. The key difference lies in CAMELS as a safety and soundness measure versus CRA's emphasis on community impact and fair lending practices.
Regulatory Agencies: CAMELS and CRA
CAMELS rating, developed by federal regulatory agencies such as the Federal Reserve, FDIC, and OCC, evaluates banks' capital adequacy, asset quality, management, earnings, liquidity, and sensitivity to market risk, providing a comprehensive assessment of financial health. The CRA rating, issued by the same regulatory bodies, focuses on a bank's record in meeting community credit needs, emphasizing lending, investment, and service performance in low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. Regulators use CAMELS primarily for safety and soundness supervision, while CRA ensures banks contribute to community development and equitable access to financial services.
Components of the CAMELS Rating System
The CAMELS rating system evaluates banks based on six key components: Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management quality, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk. These factors provide a comprehensive assessment of a bank's financial health and operational soundness. In contrast, the CRA rating primarily focuses on a bank's performance in serving community credit needs, making CAMELS more centered on risk and stability.
Core Elements of the CRA Rating System
The Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) Rating evaluates a bank's effectiveness in meeting the credit needs of its entire community, emphasizing three core elements: Lending, Investment, and Service. Unlike the CAMELS Rating, which focuses on a bank's overall safety and soundness, the CRA rating assesses the bank's commitment to equitable community development through lending patterns, community development investments, and responsiveness to local needs. Regulators analyze detailed data on loan distribution, qualified investments, and community services to determine a bank's CRA performance grade.
Purpose and Objectives: CAMELS vs CRA
CAMELS rating evaluates a bank's overall health by assessing Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management quality, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk to ensure safety and soundness. CRA rating focuses on a bank's performance in meeting the credit needs of its community, particularly low- and moderate-income neighborhoods, to promote fair lending and community development. The CAMELS system aims at regulatory oversight and risk management, while the CRA targets social responsibility and equitable access to financial services.
Impact on Financial Institutions: CAMELS vs CRA
CAMELS rating assesses the overall health of financial institutions by evaluating Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk, directly influencing regulatory actions and supervisory intensity. In contrast, CRA rating measures a bank's performance in meeting community credit needs, impacting its ability to expand through mergers, acquisitions, and new branches. Both ratings significantly affect financial institutions' strategic decisions, compliance costs, and public reputation but target different aspects of banking operations.
Reporting and Disclosure Requirements
CAMELS Rating, used by regulatory agencies, emphasizes comprehensive reporting on Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management quality, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk, with strict confidentiality and limited public disclosure. CRA Rating, mandated by the Community Reinvestment Act, requires banks to publicly disclose their performance in meeting community credit needs, ensuring transparency and stakeholder accountability in underserved areas. The reporting framework for CAMELS is primarily regulatory and internal, while CRA mandates detailed public disclosure to promote community investment awareness.
Recent Trends in CAMELS and CRA Evaluations
Recent trends in CAMELS ratings reveal increased regulatory emphasis on capital adequacy, asset quality, and risk management frameworks, reflecting tighter scrutiny after economic uncertainties. CRA evaluations have evolved to prioritize community development and equitable lending practices, with a growing focus on the impact of financial institutions' services on underserved populations. Both CAMELS and CRA assessments now incorporate advanced data analytics and stress testing to better predict institution resilience and community responsiveness.
Important Terms
Prudential Supervision
Prudential supervision employs the CAMELS rating system--focusing on Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management quality, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk--to comprehensively assess a bank's overall health and stability. The CRA rating, by contrast, specifically evaluates a financial institution's performance in meeting community credit needs, emphasizing lending, investment, and service activities in underserved markets.
Asset Quality Assessment
Asset Quality Assessment in CAMELS Rating focuses on evaluating the risk and performance of a bank's loan and investment portfolios to determine potential credit losses, while CRA Rating emphasizes compliance with the Community Reinvestment Act by assessing how effectively a financial institution meets the credit needs of its entire community, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. CAMELS provides a comprehensive risk-based supervisory framework covering capital adequacy, asset quality, management, earnings, liquidity, and sensitivity to market risk, whereas CRA specifically measures social responsibility and community impact without directly addressing asset risk.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance in banking rigorously evaluates CAMELS ratings--assessing Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management capability, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk--to ensure institutional stability, while CRA ratings focus specifically on compliance with the Community Reinvestment Act, measuring a bank's responsiveness to community credit needs and impact on local economic development. Effective regulatory frameworks mandate adherence to both CAMELS and CRA standards to balance financial soundness with equitable community engagement.
Risk-Based Capital
Risk-Based Capital (RBC) frameworks quantify a bank's capital adequacy relative to its risk exposure, serving as a critical measure within the CAMELS rating system that evaluates Capital, Asset quality, Management, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk. In contrast, the CRA (Community Reinvestment Act) rating assesses a bank's commitment to meeting community credit needs, focusing on lending, investment, and service performance rather than capital adequacy or risk management.
Loan Portfolio Evaluation
Loan portfolio evaluation assesses credit risk, asset quality, and diversification by analyzing loan performance metrics, which directly influence the CAMELS rating components of asset quality and management. While the CAMELS rating focuses on overall bank safety and soundness, including capital adequacy and liquidity, the CRA rating emphasizes fair lending practices and community reinvestment, making both evaluations essential for comprehensive financial institution assessment.
Community Reinvestment
Community Reinvestment performance evaluates a bank's commitment to meeting local credit needs, reflecting its CRA Rating, which focuses on community development efforts and fair lending practices. CAMELS Rating assesses overall bank health through Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to market risk, providing a broader risk profile unrelated to specific community reinvestment activities.
Management Soundness
Management Soundness in CAMELS rating assesses the effectiveness of a bank's board and management in identifying, measuring, and controlling risk, directly influencing stability and operational efficiency. CRA (Community Reinvestment Act) rating evaluates a financial institution's responsiveness to community credit needs, focusing on lending, investment, and services; while both ratings reflect management quality, CAMELS emphasizes internal risk management, and CRA prioritizes community engagement and compliance.
Quantitative Stress Testing
Quantitative Stress Testing evaluates the resilience of financial institutions by simulating adverse economic scenarios, integral to CAMELS Rating components like Capital adequacy and Liquidity risk. While CAMELS focuses on safety and soundness metrics, CRA Rating emphasizes community reinvestment performance, making stress testing less central to CRA but critical for regulatory assessments under CAMELS.
Consumer Credit Access
Consumer credit access is influenced by CAMELS ratings, which assess a bank's capital adequacy, asset quality, management, earnings, liquidity, and sensitivity to risk, providing a comprehensive evaluation of financial stability. CRA ratings, focused on a bank's commitment to meeting community credit needs, directly impact consumer lending availability by encouraging institutions to offer equitable credit products and services.
Fair Lending Performance
Fair Lending Performance significantly influences both CAMELS and CRA ratings, with CAMELS focusing on overall financial health and risk management, while CRA emphasizes community reinvestment and equitable lending practices. Strong fair lending practices enhance CAMELS credit and management components, and directly improve CRA scores through demonstrated commitment to serving diverse communities.
CAMELS Rating vs CRA Rating Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com