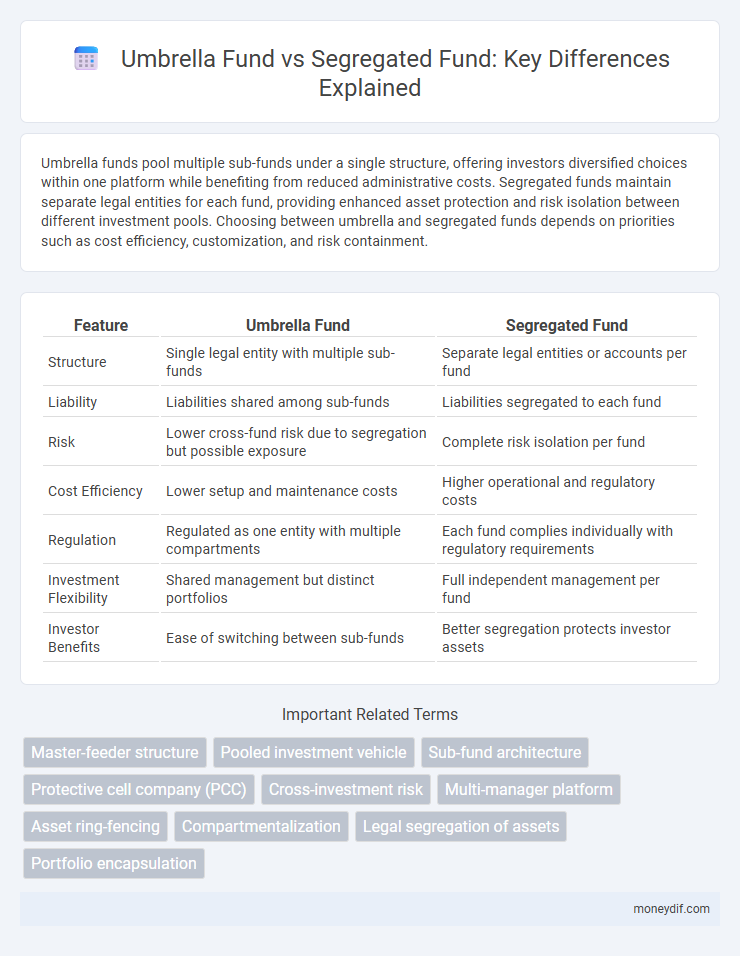
Umbrella funds pool multiple sub-funds under a single structure, offering investors diversified choices within one platform while benefiting from reduced administrative costs. Segregated funds maintain separate legal entities for each fund, providing enhanced asset protection and risk isolation between different investment pools. Choosing between umbrella and segregated funds depends on priorities such as cost efficiency, customization, and risk containment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Umbrella Fund | Segregated Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single legal entity with multiple sub-funds | Separate legal entities or accounts per fund |
| Liability | Liabilities shared among sub-funds | Liabilities segregated to each fund |
| Risk | Lower cross-fund risk due to segregation but possible exposure | Complete risk isolation per fund |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower setup and maintenance costs | Higher operational and regulatory costs |
| Regulation | Regulated as one entity with multiple compartments | Each fund complies individually with regulatory requirements |
| Investment Flexibility | Shared management but distinct portfolios | Full independent management per fund |
| Investor Benefits | Ease of switching between sub-funds | Better segregation protects investor assets |
Introduction to Umbrella Funds and Segregated Funds
Umbrella funds consolidate multiple sub-funds under a single legal structure, offering investors diversified options while sharing administrative costs and regulatory compliance. Segregated funds provide individual accounts with assets legally separated to protect investors from the liabilities of other sub-funds, enhancing risk management and asset protection. Both fund structures cater to investor needs for flexibility and security within collective investment schemes.
Key Definitions: Umbrella Fund vs Segregated Fund
An umbrella fund is a single investment vehicle comprising multiple sub-funds, each with its own investment strategy, allowing investors to switch between sub-funds without changing the overall structure. Segregated funds are separate accounts within an insurance contract that combine investment options with insurance benefits, offering creditor protection and death benefit guarantees. The key distinction lies in umbrella funds facilitating diversified portfolio management under one fund structure, while segregated funds blend investment growth with insurance features and personalized asset segregation.
Structure and Composition of Umbrella Funds
Umbrella funds feature a single legal entity housing multiple sub-funds, each with distinct investment objectives and asset pools but sharing overarching management and operational infrastructure. This structure allows investors to switch between sub-funds without triggering tax events or requiring new account setups, enhancing flexibility and cost-efficiency. The composition of umbrella funds includes separate portfolios with independent liabilities, protecting each sub-fund from financial risks associated with others under the umbrella.
Structure and Composition of Segregated Funds
Segregated funds are insurance products that combine investment growth potential with protection features, holding assets separately for each policyholder to safeguard against creditor claims and estate complications. Their structure involves individual accounts managed distinctly within the overarching fund, unlike umbrella funds which pool assets collectively for multiple sub-funds under one management. This composition allows segregated funds to offer guarantees such as principal protection and death benefits, making them a hybrid between traditional mutual funds and insurance policies.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Umbrella funds operate under a single regulatory framework with multiple sub-funds sharing the same compliance oversight, streamlining reporting and adherence to regulations such as UCITS or AIFMD. Segregated funds maintain independent regulatory status for each fund, requiring separate compliance filings and risk management protocols tailored to specific jurisdictions or investor classes. Regulatory authorities emphasize segregation to protect investor assets, ensuring clear accountability and reducing cross-liability risks within fund structures.
Investment Flexibility and Diversification
Umbrella funds offer greater investment flexibility by allowing investors to switch between sub-funds with different asset allocations while maintaining a single account structure, enhancing portfolio diversification. Segregated funds, however, keep assets and liabilities separate for each investment option, limiting liquidity but providing tailored risk management. This structure benefits investors seeking specific protection guarantees alongside diversified investment exposure.
Cost Structure and Fees Comparison
Umbrella funds typically have lower overall management fees due to shared administrative costs across multiple sub-funds, whereas segregated funds often involve higher fees as each fund operates independently with separate administrative expenses. Cost structures in umbrella funds benefit from economies of scale, reducing transaction and operational fees, while segregated funds may charge higher individual expenses for fund management and custodial services. Investors should closely compare expense ratios and fee transparency when choosing between umbrella and segregated funds to optimize portfolio costs.
Risk Management Strategies
Umbrella funds offer diversified risk management by pooling assets across multiple sub-funds, allowing investors to benefit from broader portfolio diversification and operational efficiencies. Segregated funds isolate each investor's assets, minimizing cross-liability risk and providing tailored protection against creditor claims or financial insolvency. Both structures employ dynamic asset allocation and hedging techniques, but segregated funds emphasize strict legal separation to enhance investor protection in volatile markets.
Suitability for Investors and Use Cases
Umbrella funds offer investors diversified exposure across multiple sub-funds under one administration, ideal for those seeking cost efficiency and ease of switching investments within a single fund structure. Segregated funds provide legally separate accounts for each investor or investment, offering enhanced asset protection and customization, making them suitable for high-net-worth individuals or clients with specific risk tolerance and estate planning needs. Typically, umbrella funds suit retail investors looking for flexibility and lower fees, while segregated funds cater to institutional investors or those requiring asset segregation for regulatory or strategic purposes.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Umbrella and Segregated Funds
Selecting between umbrella funds and segregated funds depends on an investor's need for flexibility and asset protection. Umbrella funds offer cost efficiency and ease of switching between sub-funds within a single structure, making them ideal for diversified portfolios. Segregated funds provide enhanced creditor protection and estate planning benefits, making them suitable for investors prioritizing asset security and legacy considerations.
Important Terms
Master-feeder structure
The master-feeder structure pools investments from multiple feeder funds into a single master fund, maximizing operational efficiency and centralized management, commonly associated with umbrella funds that offer multiple sub-funds under one legal entity. In contrast, segregated funds maintain independent assets and liabilities for each fund within the umbrella, providing enhanced investor protection by isolating risks at the sub-fund level.
Pooled investment vehicle
Pooled investment vehicles structured as umbrella funds offer multiple sub-funds under one legal entity with shared administration, whereas segregated funds maintain separate legal entities to isolate assets and liabilities individually.
Sub-fund architecture
Sub-fund architecture in umbrella funds enables multiple distinct investment portfolios under a single legal entity, offering operational efficiencies and regulatory advantages, while segregated funds provide complete legal separation between portfolios, enhancing asset protection and reducing risk of cross-liabilities. This structural distinction significantly influences investor protection, fund administration, and compliance requirements within various jurisdictions.
Protective cell company (PCC)
Protective Cell Company (PCC) is a specialized corporate structure allowing multiple investors to pool assets in segregated cells, providing risk isolation akin to segregated funds while benefiting from the collective management features of umbrella funds. This structure enables each cell within a PCC to operate independently, safeguarding assets and liabilities from other cells, thereby combining the operational efficiency of umbrella funds with the risk protection characteristic of segregated funds.
Cross-investment risk
Cross-investment risk in umbrella funds arises when assets from different sub-funds are invested in overlapping securities, potentially leading to correlated losses, whereas segregated funds maintain distinct asset pools for each fund, minimizing the risk of contagion between investments. Investors in umbrella funds should assess the degree of asset overlap and internal risk controls compared to segregated funds, where legal separation and dedicated portfolios reduce cross-investment exposures.
Multi-manager platform
A Multi-manager platform aggregates diverse investment strategies, offering access to various fund managers within a single structure to optimize risk-adjusted returns. Umbrella funds pool assets across sub-funds under one regulatory umbrella, benefiting from cost efficiencies, while segregated funds maintain separate legal entities for each strategy, providing enhanced asset protection and customization options.
Asset ring-fencing
Asset ring-fencing in umbrella funds involves safeguarding each sub-fund's assets from liabilities of other sub-funds, whereas segregated funds inherently provide asset protection by maintaining legally separate entities for each fund. This structural distinction ensures that segregated funds offer a higher degree of risk isolation compared to umbrella funds, which rely on internal segregation mechanisms.
Compartmentalization
Compartmentalization in umbrella funds allows multiple sub-funds to share legal structure while segregated funds maintain individual legal entities to protect assets separately.
Legal segregation of assets
Legal segregation of assets in umbrella funds pools multiple sub-funds under one entity with asset segregation at the sub-fund level, while segregated funds maintain individual legal entities for each fund, providing stronger protection against cross-creditor claims.
Portfolio encapsulation
Portfolio encapsulation in umbrella funds allows multiple sub-funds to operate under a single legal entity, providing cost efficiency and shared administrative services while maintaining distinct asset pools. Segregated funds, however, offer legal separation of assets per portfolio, enhancing investor protection by isolating risks and liabilities within each fund.
Umbrella fund vs Segregated fund Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com