A self-billing invoice is generated by the buyer on behalf of the supplier and requires prior agreement between both parties, streamlining the billing process and reducing administrative workload. In contrast, a recipient-created invoice is prepared by the buyer but specifically for services received, often used in industries where the customer calculates the charges based on agreed terms. Understanding the differences between self-billing and recipient-created invoices helps ensure compliance with tax regulations and accurate financial record-keeping.
Table of Comparison
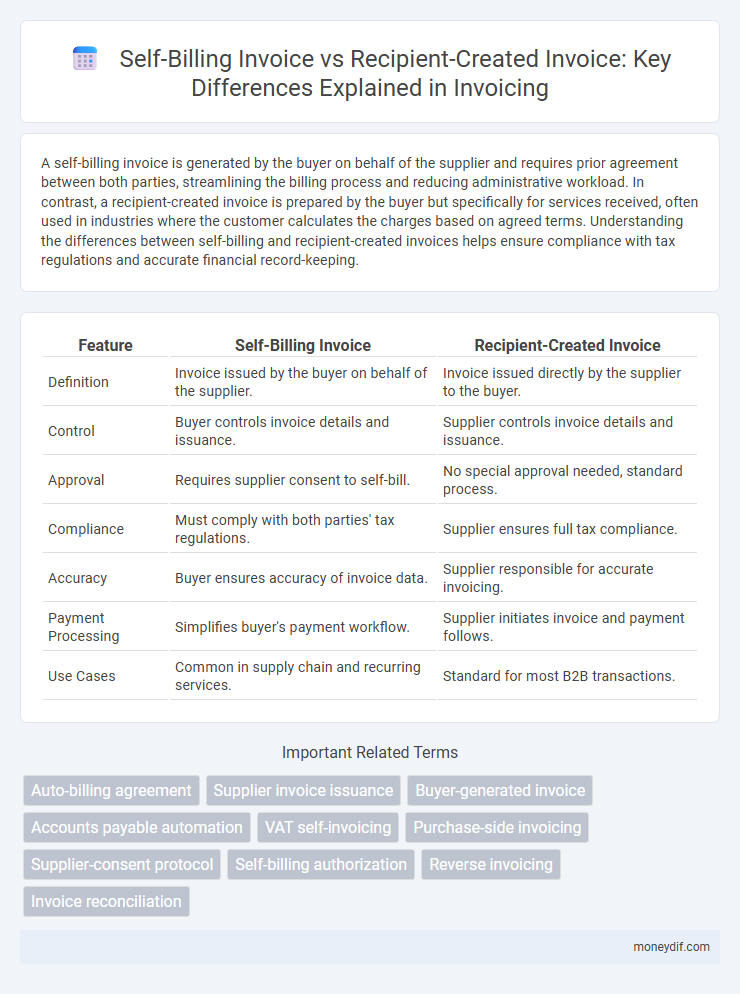
| Feature | Self-Billing Invoice | Recipient-Created Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invoice issued by the buyer on behalf of the supplier. | Invoice issued directly by the supplier to the buyer. |
| Control | Buyer controls invoice details and issuance. | Supplier controls invoice details and issuance. |
| Approval | Requires supplier consent to self-bill. | No special approval needed, standard process. |
| Compliance | Must comply with both parties' tax regulations. | Supplier ensures full tax compliance. |
| Accuracy | Buyer ensures accuracy of invoice data. | Supplier responsible for accurate invoicing. |
| Payment Processing | Simplifies buyer's payment workflow. | Supplier initiates invoice and payment follows. |
| Use Cases | Common in supply chain and recurring services. | Standard for most B2B transactions. |
Introduction to Self-Billing Invoices and Recipient-Created Invoices
Self-billing invoices are generated by the buyer on behalf of the supplier, streamlining the billing process and ensuring accurate reflection of goods or services received. Recipient-created invoices empower the recipient to produce the invoice, reducing errors and administrative workload for suppliers. Both models facilitate efficient transaction documentation but differ primarily in invoice origin and control mechanisms.
Key Definitions: Self-Billing vs Recipient-Created Invoices
Self-billing invoices are generated by the buyer on behalf of the supplier, streamlining the payment process and ensuring accuracy in transaction records. Recipient-created invoices are issued by the buyer but authorized by the supplier, shifting invoicing control to the buyer while maintaining supplier consent. Both methods enhance efficiency and compliance in accounts payable workflows, with self-billing focusing on buyer-led invoice creation and recipient-created invoices emphasizing mutual agreement.
Comparison of Self-Billing and Recipient-Created Invoice Processes
Self-billing invoices are generated by the buyer, who issues the invoice on behalf of the supplier, streamlining payment approval and reducing administrative errors. Recipient-created invoices, conversely, allow the recipient to create an invoice based on agreed terms but require explicit supplier authorization to ensure compliance and accuracy. Both processes aim to enhance invoice accuracy and operational efficiency but differ primarily in invoice origin and control mechanisms.
Legal Requirements and Compliance Considerations
Self-billing invoices require mutual agreement between supplier and buyer, with legal mandates varying across jurisdictions, often demanding clear documentation and supplier consent to ensure compliance. Recipient-created invoices place responsibility on the buyer to accurately reflect transaction details, necessitating stringent adherence to tax regulations and audit trails to prevent disputes. Both invoice types must comply with local VAT laws, invoice authenticity, and retention policies to satisfy regulatory authorities.
Advantages of Self-Billing Invoices
Self-billing invoices streamline the invoicing process by reducing administrative burden for suppliers and ensuring faster payment cycles. They improve accuracy since the buyer generates the invoice based on actual received goods or services, minimizing errors or disputes. Enhanced compliance with tax regulations is achieved because self-billing invoices provide clear documentation controlled by the purchaser, facilitating easier auditing and record-keeping.
Benefits of Recipient-Created Invoices
Recipient-created invoices enhance accuracy by allowing buyers to verify and control invoice details before processing payments, reducing disputes and errors. This approach streamlines accounts payable workflows, improving visibility into transactional data and accelerating approval cycles. Enhanced compliance and audit trails are achieved since recipients directly manage invoice creation, ensuring alignment with contractual terms and internal procurement policies.
Common Use Cases for Each Invoice Type
Self-billing invoices are commonly used in industries with frequent transactions between regular suppliers and buyers, such as retail and manufacturing, where the buyer generates the invoice on behalf of the supplier to streamline payment processes. Recipient-created invoices are prevalent in services sectors like advertising and consulting, allowing the recipient to accurately document services received when the supplier cannot issue invoices promptly. Both invoice types enhance efficiency and reduce administrative burden by allocating invoicing responsibilities based on transactional dynamics and compliance requirements.
Risks and Challenges Involved
Self-billing invoices pose risks such as compliance challenges with tax regulations and potential disputes over invoice accuracy since the supplier relies on the buyer to generate the invoice. Recipient-created invoices can lead to challenges including errors in billing data, difficulties in audit trail maintenance, and increased responsibility for the buyer to ensure timely and correct payments. Both methods require clear agreements and robust reconciliation processes to mitigate financial discrepancies and legal liabilities.
Best Practices for Implementing Each Invoice Method
Self-billing invoices require clear agreements between suppliers and buyers to ensure compliance with tax regulations and prevent disputes, emphasizing accurate real-time data sharing and automated reconciliation processes. Recipient-created invoices demand stringent verification protocols and consistent documentation to maintain audit trails and mitigate risks of errors or fraud. Both methods benefit from integrating digital platforms that support transparency, secure data exchange, and timely reporting to optimize financial workflows and regulatory adherence.
Choosing the Right Invoice System for Your Business
Choosing the right invoice system depends on your business structure and control preferences. Self-billing invoices streamline the process by allowing the buyer to generate invoices on behalf of the supplier, improving accuracy and reducing administrative workload. Recipient-created invoices empower vendors to maintain control over billing, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and providing clear transaction records.
Important Terms
Auto-billing agreement
Auto-billing agreements automate invoice generation by allowing the supplier or recipient to create self-billing invoices, streamlining reconciliation and compliance in B2B transactions.
Supplier invoice issuance
Supplier invoice issuance differs as self-billing invoices are generated by the buyer on behalf of the supplier, while recipient-created invoices are produced by the customer based on agreed terms and supplier authorization.
Buyer-generated invoice
A buyer-generated invoice, also known as a self-billing invoice, is an invoice created by the recipient of goods or services rather than the supplier, streamlining accounting processes and ensuring accurate payment records.
Accounts payable automation
Accounts payable automation improves efficiency by streamlining self-billing invoices, where the supplier authorizes the buyer to generate invoices, contrasting with recipient-created invoices that require manual submission from the supplier.
VAT self-invoicing
VAT self-invoicing allows the recipient to issue a self-billing invoice on behalf of the supplier, streamlining tax compliance and reducing invoicing errors.
Purchase-side invoicing
Purchase-side invoicing involves buyer-generated self-billing invoices where the purchaser issues the invoice on behalf of the supplier, contrasting with recipient-created invoices where the buyer generates the invoice independently to streamline payment processing and improve accuracy.
Supplier-consent protocol
The Supplier-consent protocol mandates explicit approval from suppliers for self-billing invoices, ensuring compliance and accuracy compared to recipient-created invoices generated without prior supplier verification.
Self-billing authorization
Self-billing authorization enables the buyer to issue invoices on behalf of the supplier, differentiating self-billing invoices from recipient-created invoices where the recipient generates the invoice without prior authorization.
Reverse invoicing
Reverse invoicing involves the recipient creating the invoice, contrasting with self-billing where the supplier issues the invoice on behalf of the buyer.
Invoice reconciliation
Invoice reconciliation ensures accuracy by matching self-billing invoices issued by the buyer with recipient-created invoices submitted by the supplier to prevent discrepancies and payment errors.
self-billing invoice vs recipient-created invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com