A recurring invoice automates billing at regular intervals, streamlining cash flow and reducing administrative tasks, while a single invoice is issued once for a one-time payment. Businesses benefit from recurring invoices when providing subscription services or ongoing products, ensuring consistent revenue without manual intervention. Single invoices are ideal for one-off transactions, offering flexibility for occasional or non-repetitive sales.
Table of Comparison
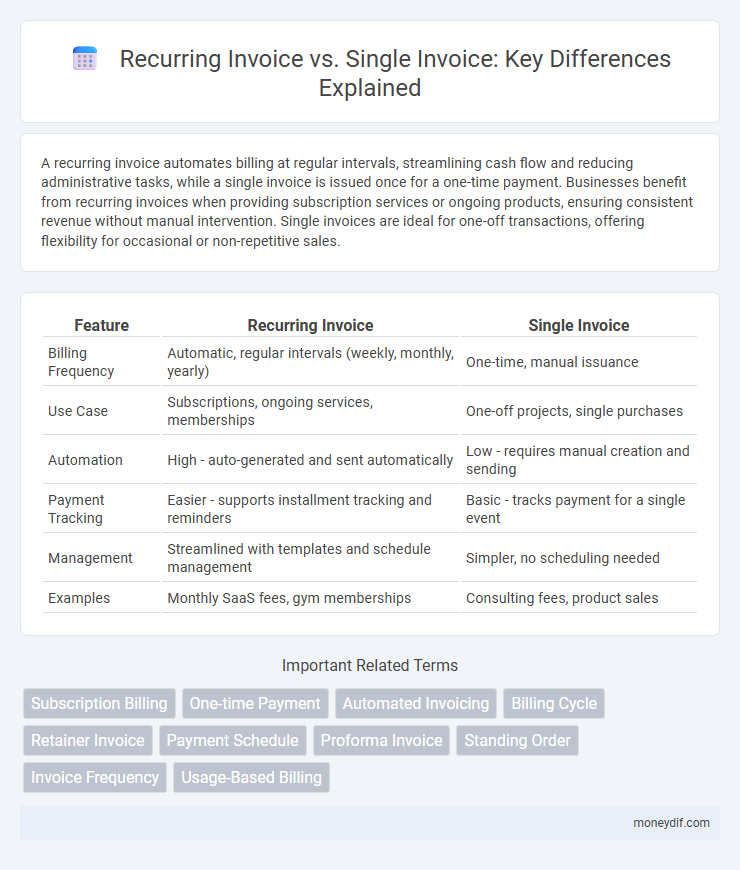
| Feature | Recurring Invoice | Single Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Billing Frequency | Automatic, regular intervals (weekly, monthly, yearly) | One-time, manual issuance |
| Use Case | Subscriptions, ongoing services, memberships | One-off projects, single purchases |
| Automation | High - auto-generated and sent automatically | Low - requires manual creation and sending |
| Payment Tracking | Easier - supports installment tracking and reminders | Basic - tracks payment for a single event |
| Management | Streamlined with templates and schedule management | Simpler, no scheduling needed |
| Examples | Monthly SaaS fees, gym memberships | Consulting fees, product sales |
Understanding Recurring Invoices
Recurring invoices automate billing by generating regular, scheduled charges for ongoing services or subscriptions, ensuring consistent cash flow and reducing administrative workload. Unlike single invoices, which are issued once for one-time transactions, recurring invoices streamline payment collection through predefined intervals such as monthly or annually. Businesses benefit from improved financial forecasting and enhanced customer retention with recurring invoices due to predictable billing cycles.
What is a Single Invoice?
A single invoice is a one-time billing document issued to request payment for specific goods or services provided on a particular date. It includes detailed information such as item descriptions, quantities, prices, taxes, and total amount due, enabling clear and precise financial transactions between buyer and seller. Unlike recurring invoices, a single invoice is generated and paid once, without automatic renewal or repetition.
Key Differences Between Recurring and Single Invoices
Recurring invoices automate regular billing by generating and sending invoices at preset intervals, ideal for subscription-based services or ongoing contracts. Single invoices are issued once for a unique transaction, suitable for one-time purchases or projects with fixed scope. Key differences include billing frequency, automation level, and applicability to customer payment cycles, with recurring invoices enhancing cash flow consistency and single invoices providing transaction-specific documentation.
Benefits of Recurring Invoices
Recurring invoices streamline billing processes by automating payment schedules, reducing manual errors and saving time for businesses. They improve cash flow predictability and customer retention by ensuring timely, consistent payments for subscription services or ongoing contracts. Businesses benefit from increased efficiency and enhanced financial management through the regular, automated issuance of recurring invoices.
Advantages of Single Invoices
Single invoices provide clear transactional records with precise billing for one-time purchases or services, simplifying payment processing and inventory tracking. They reduce the risk of billing errors or disputes by capturing exact charges for individual transactions. This approach enhances cash flow management by ensuring immediate revenue recognition without dependency on future recurring payments.
When to Use Recurring Invoices
Recurring invoices are ideal for businesses with ongoing services or subscriptions, such as monthly software licenses or regular maintenance contracts, ensuring consistent cash flow and reducing administrative tasks. Use recurring invoices when customers require scheduled, repeated billing without manual intervention, helping to automate payment collection and improve financial forecasting. This approach minimizes errors and strengthens client relationships by providing predictable billing cycles aligned with service delivery.
When to Choose Single Invoices
Single invoices are ideal for one-time purchases or services without a need for ongoing billing, ensuring straightforward payment processing and clear transaction records. They provide flexibility when clients require customized billing schedules or variable amounts unrelated to recurring intervals. Selecting single invoices minimizes complexity in cases where payment frequency or amount cannot be standardized.
Common Use Cases for Recurring Billing
Recurring invoices streamline billing for subscription services, membership fees, and ongoing maintenance contracts, ensuring consistent cash flow and reducing administrative workload. They are ideal for businesses offering regular delivery of goods or continuous professional services, such as software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms or utility providers. Single invoices typically suit one-time transactions like project-based work or occasional purchases where ongoing payments are not required.
Impact on Cash Flow Management
Recurring invoices stabilize cash flow by generating predictable and consistent revenue streams, enabling businesses to plan expenses and investments more effectively. Single invoices create irregular cash flow patterns, making it challenging to forecast income and manage liquidity efficiently. Businesses that prioritize recurring billing structures experience improved cash flow management and reduced risk of payment delays.
Choosing the Right Invoice Type for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate invoice type depends on your business model and payment frequency. Recurring invoices automate regular billing for subscription services or ongoing projects, ensuring timely payments and improved cash flow management. Single invoices suit one-time sales or unique transactions, providing flexibility for variable billing amounts and client-specific agreements.
Important Terms
Subscription Billing
Subscription billing generates recurring invoices at regular intervals, unlike single invoices which are issued one-time for individual transactions.
One-time Payment
A one-time payment differs from a recurring invoice by being a single transaction, whereas a recurring invoice automates multiple payments over a specified period.
Automated Invoicing
Automated invoicing streamlines billing processes by efficiently managing recurring invoices for subscription-based services and single invoices for one-time transactions.
Billing Cycle
The billing cycle determines the frequency of invoice generation, with recurring invoices issued automatically at regular intervals while single invoices are generated once for one-time transactions.
Retainer Invoice
Retainer invoices establish upfront payments for ongoing services, contrasting with single invoices billed once and recurring invoices issued periodically to ensure continuous cash flow and service engagement.
Payment Schedule
Payment schedules for recurring invoices automate regular billing cycles, while single invoices require one-time manual payment arrangements.
Proforma Invoice
A proforma invoice outlines estimated costs for goods or services, while recurring invoices automate repeated billing cycles and single invoices are issued once for one-time transactions.
Standing Order
Standing Orders automate recurring payments by authorizing fixed amounts at regular intervals, while single invoices request one-time payments for specific transactions.
Invoice Frequency
Invoice frequency determines billing cycles by distinguishing recurring invoices issued regularly from single invoices sent once for one-time transactions.
Usage-Based Billing
Usage-based billing generates recurring invoices based on actual consumption, while single invoices are fixed charges issued once regardless of usage.
Recurring Invoice vs Single Invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com