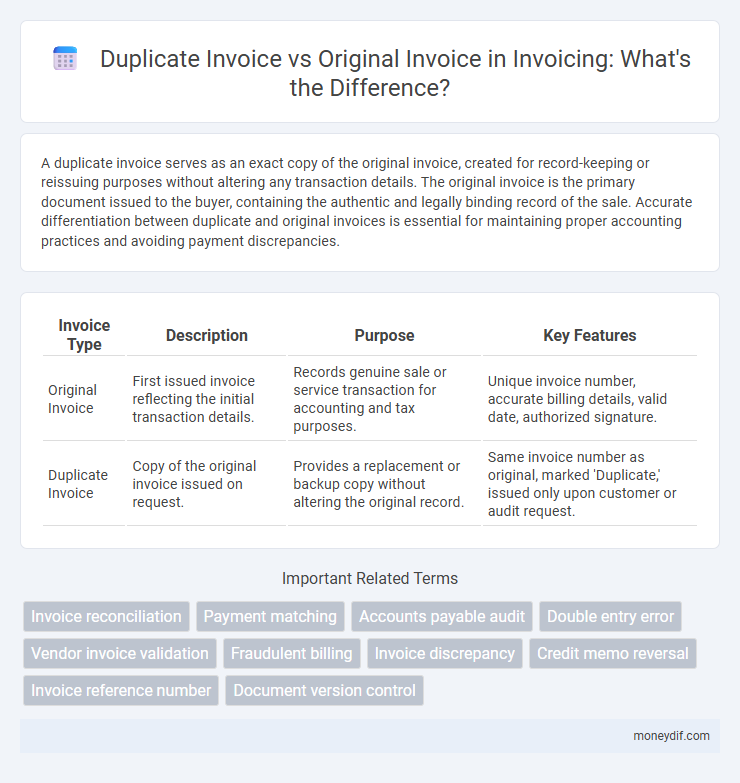
A duplicate invoice serves as an exact copy of the original invoice, created for record-keeping or reissuing purposes without altering any transaction details. The original invoice is the primary document issued to the buyer, containing the authentic and legally binding record of the sale. Accurate differentiation between duplicate and original invoices is essential for maintaining proper accounting practices and avoiding payment discrepancies.
Table of Comparison
| Invoice Type | Description | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original Invoice | First issued invoice reflecting the initial transaction details. | Records genuine sale or service transaction for accounting and tax purposes. | Unique invoice number, accurate billing details, valid date, authorized signature. |
| Duplicate Invoice | Copy of the original invoice issued on request. | Provides a replacement or backup copy without altering the original record. | Same invoice number as original, marked 'Duplicate,' issued only upon customer or audit request. |
Understanding Duplicate and Original Invoices
An original invoice serves as the primary document issued by a seller to a buyer detailing goods or services provided and the amount owed. A duplicate invoice is a copy of the original, often used for record-keeping or when the original is lost or damaged, retaining all the same information as the original. Understanding the distinction ensures accurate accounting and prevents payment errors in financial management.
Key Differences Between Duplicate and Original Invoices
Original invoices serve as the primary billing document issued by a seller to a buyer, containing authentic transaction details, unique invoice numbers, and official authorization. Duplicate invoices are exact copies of original invoices, generated for record-keeping, reference, or when the original is lost, but they often carry a "Duplicate" watermark or annotation to indicate their status. Key differences include legal validity, with original invoices holding official financial credibility for tax and audit purposes, whereas duplicate invoices primarily function as informational or backup documents without independent legal standing.
Importance of Original Invoices in Accounting
Original invoices serve as primary evidence for business transactions, ensuring accuracy in financial records and compliance with tax regulations. Maintaining original invoices helps prevent discrepancies, supports audit trails, and validates expenses or revenue recognition. Duplicate invoices can be useful for reference but lack the authoritative weight of originals in official accounting processes.
When Is a Duplicate Invoice Issued?
A duplicate invoice is issued when the original invoice is lost, misplaced, or damaged to provide the buyer with a valid proof of purchase without altering the initial transaction details. Businesses generate a duplicate invoice to maintain accurate financial records while ensuring compliance with tax regulations. Issuance of duplicate invoices helps prevent payment delays and supports audit trails for accounts payable and receivable.
Legal Implications: Duplicate vs Original Invoices
Original invoices carry legal weight as primary proof of transaction, crucial for tax reporting and audits, whereas duplicate invoices serve as secondary documentation without the same authoritative validity. Issuing or accepting duplicate invoices in place of originals may lead to compliance issues with financial regulations and potential disputes in legal proceedings. Maintaining accurate records of original invoices ensures adherence to statutory requirements and minimizes the risk of penalties or challenges from tax authorities.
Acceptability of Duplicate Invoices for Tax Purposes
Duplicate invoices are generally acceptable for tax purposes when they contain all the original invoice details, including invoice number, date, supplier information, and payment terms, ensuring consistency and authenticity. Tax authorities often require that duplicate invoices are clearly marked as copies to prevent fraudulent claims or double deductions. Maintaining proper documentation and identical content between original and duplicate invoices supports compliance with tax regulations and audit requirements.
Common Scenarios for Duplicate Invoice Usage
Duplicate invoices commonly arise in scenarios such as lost original documents, split payments requiring multiple copies, or internal auditing processes demanding verification of transaction records. Businesses often generate duplicates to ensure seamless accounting continuity when originals are misplaced or during reconciliation between vendor and purchaser accounts. Proper identification and labeling of duplicate invoices help prevent payment errors and maintain accurate financial records.
Preventing Errors with Duplicate Invoices
Duplicate invoices can lead to significant financial discrepancies and payment errors, impacting cash flow and vendor relationships. Implementing automated invoice matching systems and thorough verification processes ensures only original invoices are processed, reducing the risk of duplicate payments. Accurate tracking through accounting software and consistent supplier communication are essential for preventing errors associated with duplicate invoices.
Best Practices for Managing Invoice Copies
Maintaining clear distinctions between original invoices and duplicate invoices is crucial for accurate financial record-keeping and audit compliance. Original invoices serve as the primary proof of transaction, while duplicates should be clearly marked to avoid confusion and prevent payment errors. Implementing digital document management systems and standardized labeling enhances traceability and ensures that all invoice copies are properly archived and accessible.
Audit Considerations: Original vs Duplicate Invoices
Audit considerations emphasize verifying original invoices over duplicate copies to ensure authenticity and prevent fraud. Original invoices typically contain unique identifiers such as original signatures, watermarks, or invoice numbers crucial for audit trails and compliance. Duplicate invoices require careful cross-referencing with originals to detect discrepancies and avoid financial misstatements during audits.
Important Terms
Invoice reconciliation
Invoice reconciliation ensures accurate financial records by identifying discrepancies between duplicate invoices and original invoices, preventing payment errors and potential fraud. Automated systems use unique identifiers, invoice numbers, and purchase order references to detect duplicates, streamline matching processes, and maintain audit compliance.
Payment matching
Payment matching ensures accurate ledger reconciliation by distinguishing duplicate invoices from original invoices through unique identifiers and transaction amounts.
Accounts payable audit
Accounts payable audits focus on identifying discrepancies such as duplicate invoices, which occur when a vendor invoice is submitted more than once, versus original invoices that represent the initial legitimate billing for goods or services received. Detecting duplicate invoices is critical for preventing overpayments and ensuring financial accuracy in accounts payable processes.
Double entry error
Double entry errors often occur when a duplicate invoice is mistakenly recorded alongside the original invoice, leading to overstated liabilities or expenses in accounting records. Ensuring rigorous invoice verification processes and implementing automated matching systems can significantly reduce the risk of such discrepancies.
Vendor invoice validation
Vendor invoice validation ensures accurate payment by detecting duplicate invoices to prevent double processing and verifying original invoices to confirm legitimacy.
Fraudulent billing
Fraudulent billing often involves submitting duplicate invoices that mimic original invoices to receive unauthorized payments.
Invoice discrepancy
Duplicate invoices cause payment delays and accounting errors when they are processed instead of the original invoice.
Credit memo reversal
Credit memo reversal resolves discrepancies by accurately linking duplicate invoices to their corresponding original invoices, ensuring precise financial records.
Invoice reference number
Invoice reference numbers serve as unique identifiers distinguishing original invoices from duplicate invoices, ensuring accurate tracking and preventing payment errors. Proper use of these reference numbers facilitates efficient invoice reconciliation, audit trails, and fraud prevention in financial processes.
Document version control
Document version control ensures accurate tracking and management of invoice versions by distinguishing duplicate invoices from original invoices, reducing errors and preventing payment discrepancies. Proper version control systems enable organizations to maintain a clear audit trail, verify invoice authenticity, and streamline financial reconciliation processes.
Duplicate invoice vs Original invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com