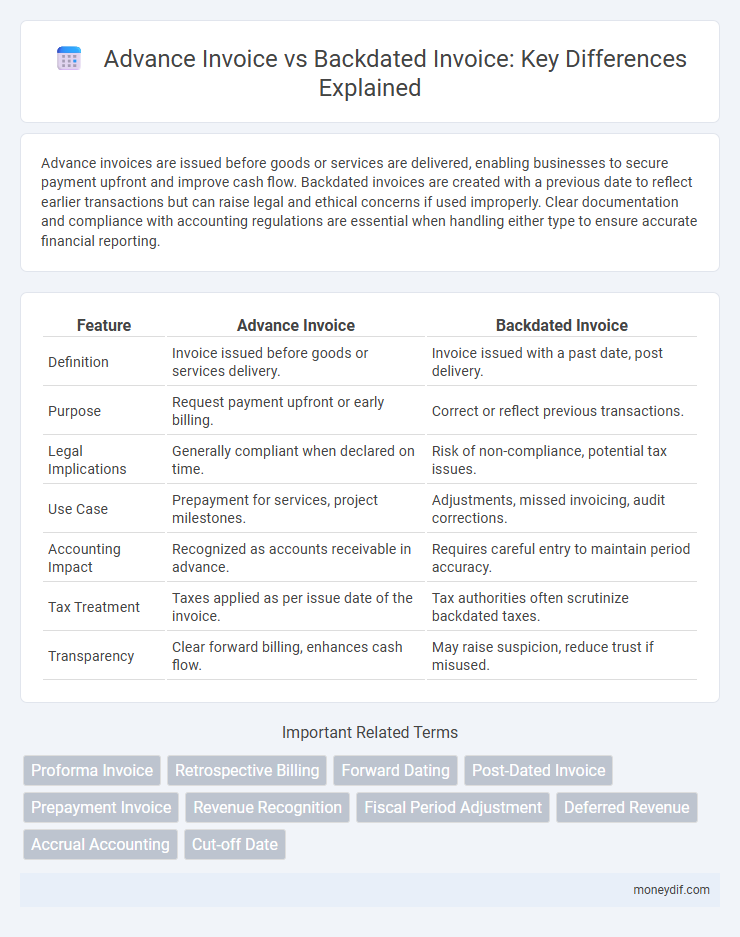
Advance invoices are issued before goods or services are delivered, enabling businesses to secure payment upfront and improve cash flow. Backdated invoices are created with a previous date to reflect earlier transactions but can raise legal and ethical concerns if used improperly. Clear documentation and compliance with accounting regulations are essential when handling either type to ensure accurate financial reporting.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Advance Invoice | Backdated Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invoice issued before goods or services delivery. | Invoice issued with a past date, post delivery. |
| Purpose | Request payment upfront or early billing. | Correct or reflect previous transactions. |
| Legal Implications | Generally compliant when declared on time. | Risk of non-compliance, potential tax issues. |
| Use Case | Prepayment for services, project milestones. | Adjustments, missed invoicing, audit corrections. |
| Accounting Impact | Recognized as accounts receivable in advance. | Requires careful entry to maintain period accuracy. |
| Tax Treatment | Taxes applied as per issue date of the invoice. | Tax authorities often scrutinize backdated taxes. |
| Transparency | Clear forward billing, enhances cash flow. | May raise suspicion, reduce trust if misused. |
Understanding Advance Invoice: Definition and Purpose
An advance invoice is a billing document issued before goods or services are delivered, securing payment ahead of fulfillment to ensure cash flow and commitment from the buyer. It outlines expected charges and payment terms, facilitating upfront financial planning for both parties. Advance invoices are commonly used in project-based industries and custom orders where initial costs must be covered prior to commencement.
What is a Backdated Invoice? Key Concepts
A backdated invoice is a billing document that reflects a date earlier than the actual date of issue, often used to account for previously provided goods or services not invoiced at the time of delivery. This practice can affect accounting accuracy and tax reporting, potentially leading to legal and compliance risks if not properly documented. Key concepts include the necessity for transparency, adherence to regulatory standards, and the impact on financial statements and audit trails.
Legal Implications: Advance vs Backdated Invoices
Advance invoices, issued before goods or services are delivered, comply with legal frameworks when clearly stating payment terms and delivery schedules, ensuring transparency and preventing disputes. Backdated invoices may violate tax regulations and accounting standards by misstating transaction dates, risking penalties, fines, or legal action for fraud or tax evasion. Businesses must adhere to jurisdiction-specific laws on invoice dating to maintain accurate financial records and uphold regulatory compliance.
Accounting Treatment Differences
Advance invoices are recorded as a liability in accounting since payment is received before goods or services are delivered, impacting cash flow recognition and requiring revenue to be deferred until the actual delivery. Backdated invoices, often used to reflect a transaction date prior to issuance, can raise compliance issues and affect revenue recognition by misstating the period in which services or goods were provided. Properly distinguishing between advance and backdated invoices ensures accurate financial reporting and adherence to accounting standards like IFRS or GAAP.
Common Use Cases for Advance Invoices
Advance invoices are commonly used in service-based industries where clients pay before project commencement, such as consulting, construction, and event planning. They facilitate cash flow management by securing partial or full payment upfront, reducing financial risks for providers. Advance invoices also support transparent budgeting and resource allocation for upcoming tasks or deliveries.
Common Use Cases for Backdated Invoices
Backdated invoices are commonly used to record transactions that occurred in a previous accounting period, ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with tax regulations. They help businesses correct delayed billing or document missed revenue recognition without affecting current financial records. Typical scenarios include adjusting for late service delivery confirmations or aligning invoice dates with contract terms retrospectively.
Risks of Issuing Backdated Invoices
Issuing backdated invoices poses significant legal and financial risks, including penalties for tax evasion and potential audits by tax authorities. Backdated invoices can undermine financial transparency, leading to breaches in accounting standards and damaging business credibility. Companies risk regulatory fines, loss of trust with stakeholders, and complications in cash flow management due to inaccurate revenue reporting.
Compliance and Tax Considerations
Advance invoices require issuing billing documents before goods or services are delivered, ensuring compliance with tax regulations by accurately reflecting the transaction date. Backdated invoices, often used to record sales retroactively, can trigger legal risks and tax penalties due to misrepresentation of the actual transaction period. Maintaining proper documentation and adhering to local tax laws is critical to avoid audits and ensure transparent financial reporting.
Impact on Cash Flow and Financial Reporting
Advance invoices improve cash flow by securing payments before goods or services are delivered, boosting liquidity and enabling better financial planning. Backdated invoices can distort financial reporting by inaccurately reflecting revenue periods, potentially leading to compliance issues and misleading stakeholders. Accurate timing of invoices ensures transparent accounting, supporting reliable cash flow management and adherence to accounting standards.
Best Practices for Invoice Management
Advance invoices should be issued before goods or services are delivered to ensure clear payment terms and maintain accurate cash flow records. Backdated invoices risk violating accounting standards and legal regulations, potentially leading to audit complications or penalties. Best practices include timely invoicing aligned with transaction dates, transparent documentation, and compliance with financial policies to support effective invoice management.
Important Terms
Proforma Invoice
A Proforma Invoice serves as a preliminary bill of sale often used for Advance Invoices, while a Backdated Invoice involves altering the invoice date to an earlier time, which can affect legal and tax implications.
Retrospective Billing
Retrospective billing involves issuing backdated invoices to correct past charges, whereas advance invoices are generated beforehand to request payment for future services.
Forward Dating
Forward dating sets an invoice date in the future for advance invoices to align payment schedules, whereas backdated invoices record a prior date to reflect earlier transactions or services rendered.
Post-Dated Invoice
A post-dated invoice records a future payment date, contrasting with an advance invoice issued before delivery and a backdated invoice reflecting an earlier transaction date.
Prepayment Invoice
Prepayment invoices require customers to pay in advance before services are rendered, whereas advance invoices request partial or full payment upfront for future goods or services, and backdated invoices inaccurately reflect a prior date for accounting or compliance purposes.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue recognition policies must differentiate between advance invoices, which record revenue before delivery, and backdated invoices, which inaccurately alter revenue timing, impacting financial statement integrity.
Fiscal Period Adjustment
Fiscal period adjustment involves correcting revenue recognition by comparing advance invoices issued before service delivery with backdated invoices reflecting actual transaction dates to ensure accurate financial reporting.
Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue arises when advance invoices record payments before service delivery, unlike backdated invoices that retroactively date transactions without affecting revenue recognition timing.
Accrual Accounting
Accrual accounting records revenue and expenses when earned or incurred, making advance invoices recognize income before delivery while backdated invoices improperly adjust revenue to prior periods.
Cut-off Date
Cut-off date determines whether an invoice is recorded as an advance invoice issued before the service period or as a backdated invoice issued after the service period.
Advance Invoice vs Backdated Invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com