Manual invoices require significant time and effort to create, increasing the risk of human error and delays in payment processing. Automated invoices streamline the billing process by instantly generating accurate and consistent invoices, improving cash flow and reducing administrative overhead. Businesses benefit from automation through enhanced efficiency, better tracking, and faster revenue recognition.
Table of Comparison
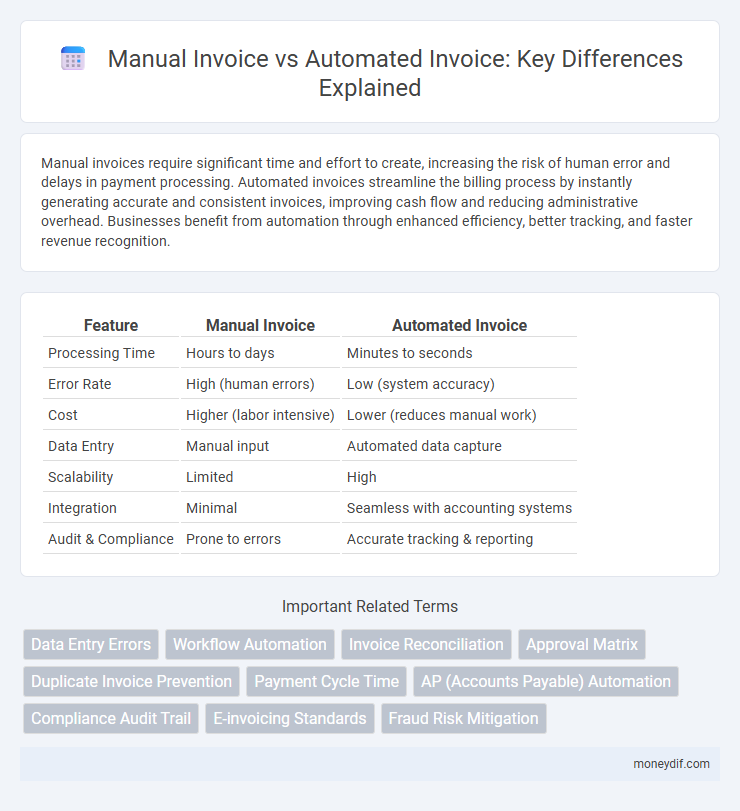
| Feature | Manual Invoice | Automated Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | Hours to days | Minutes to seconds |
| Error Rate | High (human errors) | Low (system accuracy) |
| Cost | Higher (labor intensive) | Lower (reduces manual work) |
| Data Entry | Manual input | Automated data capture |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
| Integration | Minimal | Seamless with accounting systems |
| Audit & Compliance | Prone to errors | Accurate tracking & reporting |
Introduction to Manual and Automated Invoicing
Manual invoicing involves creating and sending invoices by hand, typically using spreadsheets or word processors, which can lead to errors and time-consuming processes. Automated invoicing uses specialized software to generate, send, and track invoices electronically, improving accuracy and efficiency. Businesses adopting automated invoicing benefit from faster payment cycles, reduced operational costs, and seamless integration with accounting systems.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Invoicing
Manual invoicing involves creating and sending invoices by hand, which increases the risk of human errors and delays in payment processing. Automated invoicing leverages software to generate, send, and track invoices, improving accuracy, speed, and cash flow management. Key differences include error reduction, time efficiency, integration with accounting systems, and enhanced reporting capabilities.
Time Efficiency: Manual vs Automated Invoice Processes
Manual invoice processes consume significantly more time due to repetitive data entry, approval cycles, and the potential for human error, often leading to delays in payment processing. Automated invoice systems leverage software to streamline data capture, validation, and routing, reducing processing time from days to mere hours or minutes. Businesses implementing automation report up to 80% faster invoice turnaround times and improved cash flow management compared to manual workflows.
Error Rates in Manual vs Automated Invoicing
Manual invoicing consistently exhibits higher error rates due to human data entry mistakes, often reaching up to 10% depending on complexity and volume. Automated invoicing utilizes software algorithms and AI-driven validation, reducing errors to below 1%, enhancing accuracy and consistency. Error reduction in automated systems minimizes costly corrections and improves cash flow management.
Cost Implications of Manual and Automated Invoicing
Manual invoicing incurs higher labor costs due to time-consuming data entry and increased risk of human errors leading to costly corrections. Automated invoicing reduces operational expenses by streamlining the billing process, minimizing errors, and accelerating payment cycles. Businesses adopting automated invoicing systems often experience significant cost savings and improved cash flow management.
Impact on Cash Flow Management
Manual invoice processing often results in delayed payments and increased errors, negatively affecting cash flow visibility and predictability. Automated invoicing accelerates invoice generation and delivery, improving payment cycles and providing real-time cash flow insights. Businesses utilizing automated invoices typically experience enhanced liquidity and more efficient working capital management.
Scalability: Adapting to Business Growth
Manual invoices often hinder scalability due to time-consuming data entry and higher error rates, limiting a business's ability to handle increased transaction volumes. Automated invoicing systems streamline processes by generating and sending invoices quickly, enabling seamless adaptation to business growth. Integrating automation supports scalability through faster processing, improved accuracy, and reduced operational costs.
Data Security and Compliance Considerations
Manual invoice processing often exposes sensitive financial data to higher risks of human error and unauthorized access due to limited security controls, increasing compliance challenges with regulations such as GDPR and SOX. Automated invoicing systems enhance data security through encryption, user access controls, and audit trails, ensuring stricter compliance with industry standards and reducing the likelihood of data breaches. Organizations adopting automated invoices benefit from real-time monitoring and secure storage, which streamline regulatory reporting and protect confidential information throughout the invoicing lifecycle.
Integration with Accounting Systems
Manual invoices often require separate data entry into accounting systems, increasing the risk of errors and delays in financial reporting. Automated invoices streamline this process by directly integrating with accounting software, ensuring real-time synchronization and accurate record-keeping. Integration with platforms like QuickBooks, Xero, or SAP enhances efficiency and reduces reconciliation time significantly.
Choosing the Right Invoicing Solution for Your Business
Choosing the right invoicing solution for your business impacts accuracy, efficiency, and cash flow management. Manual invoices require time-consuming data entry and higher risk of errors, while automated invoicing systems enable faster processing, seamless integration with accounting software, and real-time tracking. Businesses with high transaction volumes benefit most from automation, which reduces administrative costs and improves overall financial reporting accuracy.
Important Terms
Data Entry Errors
Manual invoice processing increases data entry errors by up to 70% compared to automated invoicing systems that utilize optical character recognition and artificial intelligence for accuracy.
Workflow Automation
Automated invoice processing reduces errors and processing time by up to 80% compared to manual invoice handling in workflow automation systems.
Invoice Reconciliation
Automated invoice reconciliation reduces errors and processing time compared to manual invoice reconciliation, enhancing accuracy and operational efficiency.
Approval Matrix
The Approval Matrix streamlines workflow by establishing distinct authorization levels for Manual Invoices, which require individual scrutiny, versus Automated Invoices, which are processed based on predefined criteria for efficiency.
Duplicate Invoice Prevention
Automated invoice systems significantly reduce duplicate invoice prevention errors compared to manual invoice processing by leveraging algorithmic validations and cross-referencing capabilities.
Payment Cycle Time
Automated invoicing reduces payment cycle time by up to 60% compared to manual invoice processing, enhancing billing accuracy and accelerating cash flow.
AP (Accounts Payable) Automation
Automated invoice processing in AP automation reduces manual data entry errors, accelerates payment cycles, and enhances cost efficiency compared to traditional manual invoice handling.
Compliance Audit Trail
Compliance audit trails meticulously document every action taken during the invoice processing lifecycle, ensuring transparency and accountability in distinguishing manual invoices from automated invoices. Automated invoices generate precise, timestamped records that minimize human errors, whereas manual invoices require rigorous verification to maintain compliance and prevent discrepancies.
E-invoicing Standards
Automated e-invoicing standards enhance accuracy, compliance, and processing speed compared to manual invoice handling, reducing errors and operational costs.
Fraud Risk Mitigation
Automated invoice processing significantly reduces fraud risk by minimizing human errors and unauthorized manipulations compared to manual invoice handling.
Manual Invoice vs Automated Invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com