Choosing between the annuity option and the lump-sum option for pension payouts depends on individual financial goals and risk tolerance. The annuity option provides a steady, guaranteed income stream for life, offering financial security and protection against outliving your savings. In contrast, the lump-sum option gives immediate access to the entire pension amount, allowing flexibility for investment or large purchases but exposes the individual to market risks and the challenge of managing the funds wisely.
Table of Comparison
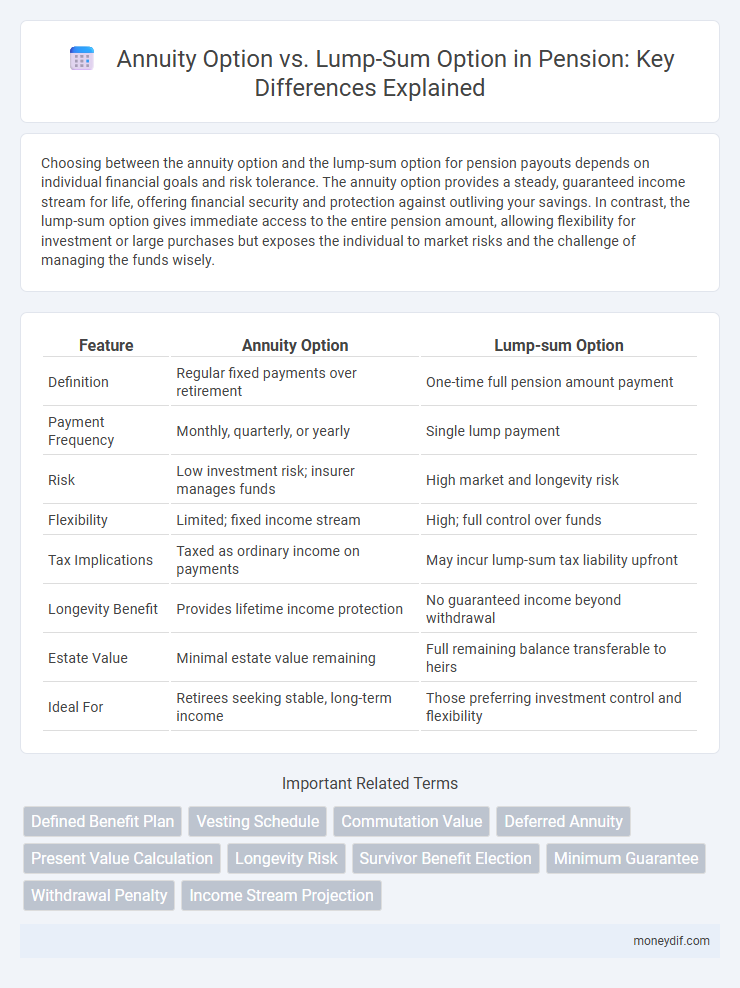
| Feature | Annuity Option | Lump-sum Option |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regular fixed payments over retirement | One-time full pension amount payment |
| Payment Frequency | Monthly, quarterly, or yearly | Single lump payment |
| Risk | Low investment risk; insurer manages funds | High market and longevity risk |
| Flexibility | Limited; fixed income stream | High; full control over funds |
| Tax Implications | Taxed as ordinary income on payments | May incur lump-sum tax liability upfront |
| Longevity Benefit | Provides lifetime income protection | No guaranteed income beyond withdrawal |
| Estate Value | Minimal estate value remaining | Full remaining balance transferable to heirs |
| Ideal For | Retirees seeking stable, long-term income | Those preferring investment control and flexibility |
Understanding the Basics: Annuity vs Lump-Sum Pension Options
Choosing between annuity and lump-sum pension options depends on individual financial goals and risk tolerance. Annuity offers a steady income stream for life, providing financial security and predictable cash flow, while lump-sum allows immediate access to the entire pension amount, offering flexibility for investment or large expenses. Understanding the tax implications and potential growth opportunities of each option is crucial for making an informed decision in retirement planning.
Key Differences Between Annuity and Lump-Sum Payouts
Annuity payouts provide steady, guaranteed income over a retiree's lifetime, reducing longevity risk and ensuring financial stability. Lump-sum payouts offer immediate access to the entire pension amount, allowing for flexible investment but exposing retirees to market volatility and the risk of outliving their savings. Choosing between annuity and lump-sum depends on individual risk tolerance, income needs, and financial planning strategies.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Pension Option
When choosing between an annuity option and a lump-sum option in pension plans, factors such as life expectancy, risk tolerance, and current financial needs play a crucial role. An annuity provides guaranteed income for life, mitigating longevity risk, while a lump sum offers flexibility and potential for investment growth but requires careful management to avoid outliving savings. Tax implications and the availability of other retirement resources also significantly influence the optimal pension distribution strategy.
Pros and Cons of Selecting an Annuity Pension
Selecting an annuity pension guarantees a steady income stream for life, providing financial security and protection against outliving savings. This option often includes inflation adjustments and spousal benefits but typically offers lower initial payouts compared to lump-sum payments. The lack of liquidity and reduced flexibility to access large sums upfront can be a drawback for individuals needing immediate capital or estate planning flexibility.
Benefits and Risks of Taking a Lump-Sum Pension
Taking a lump-sum pension offers immediate access to a large amount of capital, allowing for flexible investment choices and potential for higher returns compared to annuity payouts. However, it carries risks such as the possibility of outliving the funds, exposure to market volatility, and the challenge of managing the withdrawal strategy effectively. Unlike annuities, lump-sum payments provide no guaranteed lifetime income, increasing the importance of financial discipline and careful planning.
Tax Implications for Annuity and Lump-Sum Options
Choosing between annuity and lump-sum pension options significantly affects tax obligations. Annuity payments are typically taxed as ordinary income over time, potentially lowering annual tax liability by spreading income. Lump-sum distributions may trigger a large tax bill in the year received, with tax rates depending on the total amount and applicable tax brackets.
How Inflation Affects Your Pension Choice
Choosing between an annuity and a lump-sum option significantly depends on inflation rates and their impact on purchasing power over time. Annuities provide steady income but may lose value in real terms if inflation rises and payments are not inflation-adjusted. In contrast, lump-sum withdrawals allow flexibility to invest in assets that can potentially outpace inflation, preserving and growing retirement savings.
Case Studies: Real-Life Scenarios Comparing Both Options
Case studies reveal retirees choosing the annuity option benefit from guaranteed, steady income streams that protect against market volatility and longevity risk. Those opting for lump-sum payouts often invest portions in diversified portfolios, which can yield higher returns but carry uncertainty and require disciplined management. Comparative analyses highlight that individuals prioritizing financial stability and predictability frequently favor annuities, while those with strong investment acumen and risk tolerance lean towards lump sums for potential growth.
Tips for Deciding the Best Pension Withdrawal Strategy
Evaluate your life expectancy and financial needs carefully when choosing between an annuity option and a lump-sum withdrawal in your pension plan. Annuities provide a steady income stream that mitigates the risk of outliving savings, while lump-sum payments offer flexibility for large expenses or investment opportunities. Consider consulting a financial advisor to balance tax implications, inflation impact, and personal spending habits to optimize your retirement income strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions About Annuity and Lump-Sum Options
Choosing between annuity and lump-sum pension options depends on individual financial goals and risk tolerance. Annuities provide a steady income stream for life, reducing longevity risk, while lump-sum payments offer immediate access to a large capital amount with flexibility in investment and spending. Frequently asked questions often address tax implications, withdrawal penalties, and the impact on survivor benefits for both options.
Important Terms
Defined Benefit Plan
Choosing a Defined Benefit Plan's annuity option provides guaranteed lifetime income, while the lump-sum option offers immediate access to the total retirement benefit for flexible investment or spending.
Vesting Schedule
Choosing an annuity option over a lump-sum option impacts the vesting schedule by providing phased, guaranteed payments aligned with long-term financial security instead of immediate full access to benefits.
Commutation Value
Choosing the annuity option provides a steady income stream, while the commutation value offers a lump-sum payment calculated as a present value of future annuity payments.
Deferred Annuity
Deferred annuity offers a structured income stream starting at a future date, contrasting with a lump-sum option that provides immediate, full payment but lacks long-term guaranteed income.
Present Value Calculation
Comparing Present Value calculations reveals that selecting an annuity option provides a series of discounted cash flows over time, while a lump-sum option offers a single discounted payment today, making the choice dependent on the discount rate and payment frequency.
Longevity Risk
Longevity risk increases the financial security of annuity options by providing lifetime income, whereas lump-sum options expose retirees to the risk of outliving their savings.
Survivor Benefit Election
Choosing the Survivor Benefit Election's annuity option ensures continuous post-retirement income for beneficiaries, while the lump-sum option provides a one-time payment with no ongoing survivor benefits.
Minimum Guarantee
The Minimum Guarantee ensures a fixed return on annuity payments, providing more predictable income compared to the potentially variable lump-sum option.
Withdrawal Penalty
Choosing the annuity option over a lump-sum option typically reduces withdrawal penalties by spreading distributions over time, thereby minimizing tax liabilities and early withdrawal charges.
Income Stream Projection
Income stream projection for annuity options provides a steady, predictable cash flow based on life expectancy and payment frequency, whereas lump-sum options offer immediate access to the entire amount but require careful investment planning to sustain long-term income. Evaluating projected returns, tax implications, and risk tolerance is crucial when comparing annuity payments to lump-sum withdrawals for retirement financial security.
Annuity option vs Lump-sum option Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com