The Early Retirement Factor reduces pension benefits when individuals retire before the Normal Retirement Age, reflecting the longer payout period. Normal Retirement Age is the standard age at which full pension benefits are available without penalties or reductions. Understanding how these factors interact helps optimize retirement planning and financial security.
Table of Comparison
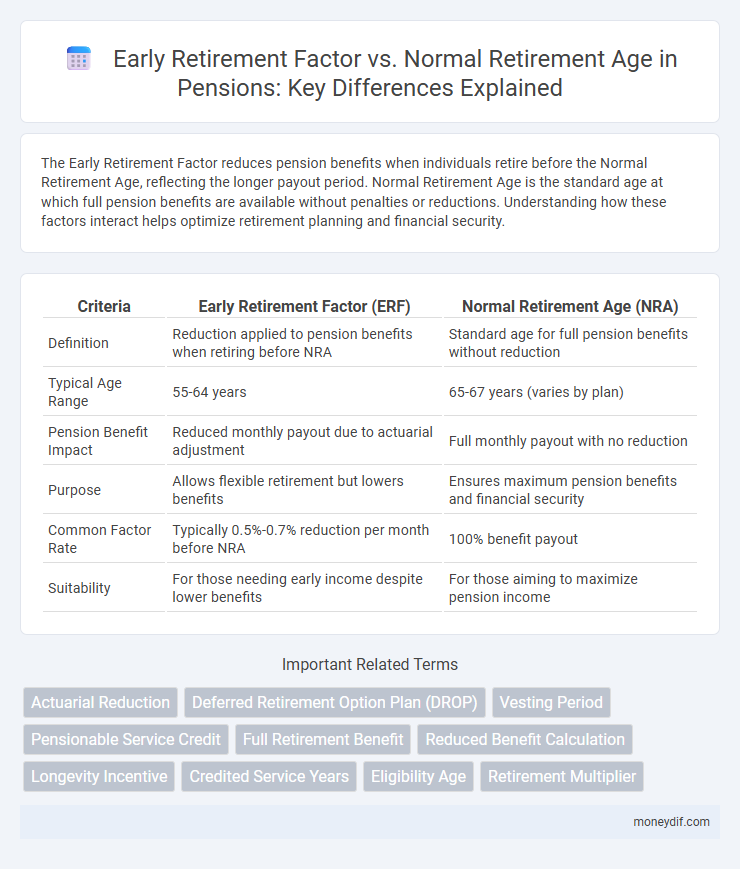
| Criteria | Early Retirement Factor (ERF) | Normal Retirement Age (NRA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction applied to pension benefits when retiring before NRA | Standard age for full pension benefits without reduction |
| Typical Age Range | 55-64 years | 65-67 years (varies by plan) |
| Pension Benefit Impact | Reduced monthly payout due to actuarial adjustment | Full monthly payout with no reduction |
| Purpose | Allows flexible retirement but lowers benefits | Ensures maximum pension benefits and financial security |
| Common Factor Rate | Typically 0.5%-0.7% reduction per month before NRA | 100% benefit payout |
| Suitability | For those needing early income despite lower benefits | For those aiming to maximize pension income |
Understanding Early Retirement Factor
The Early Retirement Factor (ERF) reduces monthly pension benefits to account for longer payout periods when retiring before the Normal Retirement Age (NRA), often set between 65 and 67 years depending on the pension plan. This factor applies a percentage reduction, commonly ranging from 3% to 6% per year, to adjust for early withdrawals and maintain the fund's actuarial balance. Understanding the ERF helps retirees make informed decisions on the financial trade-offs between retiring early and maximizing lifetime pension income.
Defining Normal Retirement Age
Normal Retirement Age (NRA) is the designated age at which individuals become eligible to receive full pension benefits without reductions for early withdrawal. This age is typically set between 65 and 67, depending on specific pension plan rules and government regulations. Understanding the NRA is crucial for calculating the Early Retirement Factor, which adjusts pension benefits downward if retirement occurs before reaching NRA.
How Pension Benefits are Calculated
Pension benefits are calculated by applying an early retirement factor that reduces monthly payments if claims occur before the normal retirement age, typically 65 or 67 depending on the pension plan. This factor adjusts benefits downward to account for the longer payout period when retiring early, often ranging from a 3% to 8% reduction per year before the normal retirement age. Conversely, waiting until the normal retirement age or beyond ensures full benefit payments based on years of service and average salary, maximizing the pension value.
Impact of Early Retirement on Pension Value
The Early Retirement Factor reduces pension benefits by a specific percentage for each year retirement precedes the Normal Retirement Age, often resulting in significantly lower monthly payouts. Actuarial adjustments account for longer payout periods, reflecting the financial impact of early retirement on pension value. Understanding these reductions is crucial for retirees optimizing their financial planning and ensuring adequate income throughout retirement.
Comparing Early vs Normal Retirement Payouts
Early retirement factors reduce monthly pension payouts compared to benefits received at normal retirement age, reflecting the longer payment period. Normal retirement age offers maximum pension benefits without actuarial reductions, increasing overall lifetime income. Comparing early versus normal retirement payouts requires evaluating the trade-off between immediate access to funds and the total value of delayed benefits.
Pros and Cons of Retiring Early
Retiring before the Normal Retirement Age often triggers the application of an Early Retirement Factor, which reduces monthly pension benefits to account for the longer payout period. Pros of early retirement include increased leisure time and the ability to pursue personal interests sooner, while cons involve permanently lower income and potential gaps in healthcare coverage. Evaluating the Early Retirement Factor helps in balancing immediate lifestyle desires against long-term financial stability.
Eligibility Criteria for Early and Normal Retirement
Early retirement eligibility typically requires meeting a minimum age, often around 55 to 60 years, combined with a certain number of contribution years, such as 20 to 30, depending on the pension system. Normal retirement age usually ranges from 65 to 67 years, with full pension benefits granted upon reaching this threshold regardless of contribution length. Early retirement factors often result in reduced monthly benefits due to actuarial adjustments, whereas normal retirement guarantees full entitled benefits.
Financial Implications of Retirement Timing
The Early Retirement Factor reduces monthly pension benefits by a specific percentage for each year taken before the Normal Retirement Age, directly impacting long-term financial stability. Opting for retirement at the Normal Retirement Age ensures full pension benefits without reductions, maximizing lifetime income and Social Security advantages. Understanding the trade-off between immediate access and total benefit amount is essential for optimizing retirement income and managing post-retirement expenses effectively.
Strategies to Maximize Pension Benefits
Maximizing pension benefits involves understanding the early retirement factor, which reduces monthly payments when claiming before the normal retirement age, typically 65 or 67 depending on the plan. Strategically delaying retirement past the normal age can significantly increase pension payouts due to accrued benefit credits and reduced actuarial reductions. Evaluating personal health, financial needs, and life expectancy helps determine the optimal claiming age to balance immediate income with long-term pension maximization.
Making the Right Choice: Early vs Normal Retirement
Choosing between early retirement and normal retirement age significantly impacts pension benefits, as early retirement typically reduces monthly payouts by a specific percentage for each year taken before the standard age, often 65 or 67 depending on the country. Carefully evaluating the Early Retirement Factor, which adjusts benefits based on the reduced contribution period and longer expected payout duration, helps optimize financial security. Understanding the trade-off between immediate access to funds and maximizing pension income ensures a well-informed decision aligned with personal financial goals and longevity expectations.
Important Terms
Actuarial Reduction
Actuarial reduction calculates the decrease in retirement benefits applied when early retirement occurs before the Normal Retirement Age (NRA), adjusting payouts based on the Early Retirement Factor to account for longer payment periods.
Deferred Retirement Option Plan (DROP)
The Deferred Retirement Option Plan (DROP) allows employees to accumulate retirement benefits in a separate account while delaying actual retirement, often influencing the calculation of the Early Retirement Factor (ERF) versus benefits computed at Normal Retirement Age (NRA). Typically, the ERF applies a reduction to retirement benefits if taken before NRA, whereas DROP participants can maximize benefits by deferring receipt until reaching NRA, optimizing pension payouts.
Vesting Period
The vesting period determines the minimum time an employee must work to qualify for retirement benefits, which affects the calculation of the Early Retirement Factor by reducing benefits if retirement occurs before the Normal Retirement Age. Early Retirement Factor applies a percentage reduction to pension benefits for retirements before reaching the Normal Retirement Age, reflecting penalties for shorter vesting periods and earlier benefit claims.
Pensionable Service Credit
Pensionable Service Credit calculates the total years an employee has contributed towards retirement benefits, directly impacting the Early Retirement Factor, which reduces pension benefits based on the number of years taken before reaching the Normal Retirement Age. The Normal Retirement Age serves as the benchmark for full pension entitlement, with service credits accrued influencing the degree of benefit adjustment applied during early retirement.
Full Retirement Benefit
Full Retirement Benefit refers to the Social Security payment amount one is entitled to receive at Normal Retirement Age (usually 66 or 67), while Early Retirement Factor reduces this benefit if claimed before this age, typically decreasing benefits by about 6-7% per year taken early. Understanding the impact of Early Retirement Factor is crucial for optimizing long-term Social Security income based on individual retirement timing.
Reduced Benefit Calculation
Reduced Benefit Calculation decreases retirement benefits proportionally based on the Early Retirement Factor applied before reaching the Normal Retirement Age.
Longevity Incentive
The Longevity Incentive adjusts pension benefits by reducing the Early Retirement Factor when benefits are claimed before the Normal Retirement Age, encouraging retirees to delay their pension start for increased monthly payouts. This mechanism balances actuarial fairness by lowering payments for early retirees while rewarding extended contribution periods beyond the Normal Retirement Age.
Credited Service Years
Credited service years directly influence the early retirement factor by reducing retirement benefits proportionally before reaching the normal retirement age, which typically maximizes pension payouts.
Eligibility Age
Eligibility age for early retirement typically starts at 62 with a reduced benefit due to the Early Retirement Factor, while Normal Retirement Age is usually between 66 and 67, offering full benefits without reduction.
Retirement Multiplier
The Retirement Multiplier quantifies the reduction in annual benefits when opting for Early Retirement, reflecting how claiming Social Security benefits before the Normal Retirement Age diminishes monthly payments.
Early Retirement Factor vs Normal Retirement Age Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com